CAN/ASC - EN 301 549:2024 Accessibility requirements for ICT products and services (EN 301 549:2021, IDT)
Information
Table of contents
Technical committee members
- Abishek Gupta, ML Engineer, RAI Researcher, Founder, Principal Researcher, Montreal AI Ethics Institute, Boston Consulting Group (BCG), BCG Henderson Institute
- John Wills, Senior Program Advisor, OPS Accessibility Office, Centre of Excellence for Human Rights.
- Lisa Snider, Senior Digital Accessibility Consultant and Trainer, Access Changes Everything Inc.
- Gary Birch, Executive Director, Neil Squire Society
- Nancy McLaughlin, Senior Policy Advisor on Accessibility, Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission
- Alison Paprica, Professor (adjunct) and Senior Fellow, Institute for Health Policy, Management and Evaluation, University of Toronto
- Clayton Lewis, Professor, University of Colorado
- Lisa Liskovoi, Senior Inclusive Designer and Digital Accessibility Specialist, Inclusive Design Research Center, OCAD University
- Julia Stoyanovich, Associate Professor, Director, Tandon School of Engineering NYU
- Jutta Treviranus (Chairperson), Director, Professor, Inclusive Design Research Center, OCAD University
- Anne Jackson, Professor, Seneca College
- Saeid Molladavoudi, Senior Data Science Advisor, Statistics Canada
- Kave Noori, Artificial Intelligence Policy Officer, European Disability Forum
- Mia Ahlgren, Human Rights and Disability Officer, Swedish Disability Rights Federation
- John Weigelt, CTO Microsoft Canada, Microsoft Canada
- Julianna Rowsell, Senior Product Manager, Product Equity, Adobe
- Kate Kalcevich, Head of Accessibility Innovation, Fable
- Merve Hickok, Founder, President and Research Director, Aiethicist.org Center for AI and Digital Policy, University of Michigan
- Sambhavi Chandrashekar, Global Accessibility Lead, D2L Corporation
Section 0
This Publication reproduces EN 301 549:2021, which was developed by CEN and ETSI, with permission of ETSI, 650, Route des Lucioles, 06921 Sophia-Antipolis Cedex, France. This Publication constitutes an identical adoption.
TM


About Accessibility Standards Canada
Accessibility Standards Canada, under whose auspices this standard has been produced, is a Government of Canada departmental corporation mandated through the Accessible Canada Act. Accessibility Standards Canada’s Standards contribute to the purpose of the Accessible Canada Act, which is to benefit all persons, especially persons with disabilities, through the realization of a Canada without barriers through the identification, removal, and prevention of accessibility barriers.
Disability, as defined by the Accessible Canada Act, means any impairment, including a physical, mental, intellectual, cognitive, learning, communication or sensory impairment — or a functional limitation — whether permanent, temporary, or episodic in nature, or evident or not, that, in interaction with a barrier, hinders a person’s full and equal participation in society.
All of Accessibility Standards Canada’s standards development work, including the work of our technical committees, is carried out in recognition of, and in accordance with, the following principles in the Accessible Canada Act:
- all persons must be treated with dignity regardless of their disabilities;
- all persons must have the same opportunity to make for themselves the lives that they are able and wish to have regardless of their disabilities;
- all persons must have barrier-free access to full and equal participation in society, regardless of their disabilities;
- all persons must have meaningful options and be free to make their own choices, with support if they desire, regardless of their disabilities;
- laws, policies, programs, services, and structures must take into account the disabilities of persons, the different ways that persons interact with their environments and the multiple and intersecting forms of marginalization and discrimination faced by persons;
- persons with disabilities must be involved in the development and design of laws, policies, programs, services, and structures; and
- the development and revision of accessibility standards and the making of regulations must be done with the objective of achieving the highest level of accessibility for persons with disabilities.
These principles align with the principles of the United Nations’ Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities, ratified by the Government of Canada in 2010 to recognize the importance of promoting, protecting, and upholding the human rights of persons with disabilities to participate fully in their communities.
Accessibility Standards Canada seeks to create standards that are aligned with its vision. This includes commitments to break down barriers to accessibility and abide by the principle of “nothing without us” in our standards development process, where everyone, including persons with disabilities, can expect a Canada without barriers.
The standards development process used by Accessibility Standards Canada is the most accessible in Canada, if not the world. Accessibility Standards Canada provides accommodations to meet the needs of Technical Committee members with disabilities. Accessibility Standards Canada provides compensation for people with disabilities to encourage their active participation. Accessibility Standards Canada ensures an accessible public review process, including accessible permission forms and multiple formats of the standard, to encourage Canadians with disabilities to comment.
Standards developed by Accessibility Standards Canada are designed to achieve the highest levels of accessibility. This means that Accessibility Standards Canada standards create equity-based technical requirements while taking into consideration national and international best practices, as opposed to focusing on minimum technical requirements.
Accessibility Standards Canada applies an intersectional framework to capture the experiences of people with disabilities who also identify as LGBTQ2+, Indigenous Peoples, women, and visible minorities. Its standards development process requires that technical committees apply a cross-disability perspective to ensure that no new barriers to accessibility are unintentionally created. In addition, standards developed by Accessibility Standards Canada align with 14 of the 17 United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, which were adopted by Canada in 2015 to promote partnership, peace and prosperity for all people and the planet by 2030.
Accessibility Standards Canada is engaged in the production of voluntary accessibility standards, which are developed by technical committees using a consensus-based approach. Each technical committee is composed of a balanced group of experts who develop the technical content of a standard. At least 30% of these technical experts are people with disabilities and lived experience and 30% are from equity seeking groups including LGBTQ2+, indigenous peoples, women and visible minorities. These technical experts also include consumers and other users, government and authorities, labour and unions, other standards development organizations, businesses and industry, academic and research bodies, and non-governmental organizations.
All Accessibility Standards Canada standards also incorporate related findings from research reports conducted through Accessibility Standards Canada’s Advancing Accessibility Grants and Contributions program. This program involves persons with disabilities, experts, and organizations to advance accessibility standards research and supports research projects that help with the identification, removal, and prevention of new barriers to accessibility.
Accessibility Standards Canada standards are subject to review and revision to ensure that they reflect current trends and best practices. Accessibility Standards Canada will follow the international maintenance review cycle for this standard. Suggestions for improvement, which are always welcome, should be brought to the notice of the respective technical committee. Changes to standards are issued either as separate amendments or in new editions of standards.
As a Standards Council of Canada Accredited Standards Development Organization, all Accessibility Standards Canada standards are developed through an accredited standards development process and follow Standard Council of Canda’s Requirements and Guidance for Standards Development Organizations. These voluntary standards apply to federally regulated entities and can be recommended to the Minister responsible for the Accessible Canada Act (i.e., the Minister of Employment, Workforce Development and Disability Inclusion).
In addition to its focus on developing accessibility standards, Accessibility Standards Canada has been a leader amongst Canadian federal organizations for promoting and adopting accessibility internal to government. Accessibility Standards Canada is the first organization in the federal government to have a Board of Directors majority-led by persons with disabilities. Accessibility Standards Canada has a state-of-the-art accessible office space for its employees, Board of Directors, and Technical Committee Members. The carefully designed accessible workspace aligns with the organization’s belief in the importance of universal accessibility.
To obtain additional information on Accessibility Standards Canada, its standards or publications, please contact:
Web site: https://accessible.canada.ca/
E-mail: Info.Accessibility.Standards-Normes.Accessibilite.Info@canada.gc.ca
Mail: Accessibility Standards Canada
320, St-Joseph Boulevard
Suite 246
Gatineau, QC K1A 0H3
Standards Council of Canada statement
A National Standard of Canada is a standard developed by a Standards Council of Canada (SCC) accredited Standards Development Organization, in compliance with requirements and guidance set out by SCC. More information on National Standards of Canada can be found at www.scc.ca.
SCC is a Crown corporation within the portfolio of Innovation, Science and Economic Development (ISED) Canada. With the goal of enhancing Canada's economic competitiveness and social well-being, SCC leads and facilitates the development and use of national and international standards. SCC also coordinates Canadian participation in standards development, and identifies strategies to advance Canadian standardization efforts.
Accreditation services are provided by SCC to various customers, including product certifiers, testing laboratories, and standards development organizations. A list of SCC programs and accredited bodies is publicly available at www.scc.ca.
ASC Legal Notice – Final Publication
Please read this Legal Notice before using the standard document.
Legal Notice for Standards
The Canadian Accessibility Standards Development Organization (operating as “Accessibility Standards Canada”) standards are developed through a consensus-based standards development process approved by the Standards Council of Canada. This process brings together volunteers representing varied viewpoints and interests to achieve consensus and develop standards.
Understanding this Edition of the Standard
Amendments and errata may have been or may eventually be developed in relation to this edition of the standard, and published separately. It is the responsibility of the users of this document to verify if any amendments or errata exist.
Disclaimer and exclusion of liability
This document was developed as a reference document for voluntary use. It is the responsibility of the users to verify if laws or regulations make the application of this standard mandatory or if trade regulations or market conditions stipulate its use, for example, in technical regulations, inspection plans originating from regulatory authorities, and certification programs.
Although the primary application of this standard is stated in its scope, it remains the responsibility of the users of this standard to judge its suitability for their particular purpose. It is also the responsibility of the users to consider limitations and restrictions specified in the purpose and/or scope of this standard.
This document is provided without any representations, warranties, or conditions of any kind, expressed or implied, including without limitation, implied representations, warranties or conditions concerning this document’s fitness for a particular purpose or use, its merchantability, or its non-infringement of any third party’s intellectual property rights. Accessibility Standards Canada makes no representations or warranties in respect of the accuracy, completeness, or currency of any of the information published in this document. Accessibility Standards Canada makes no representations or warranties regarding this document’s compliance with any applicable statute, rule, regulation or combination thereof.
IN NO EVENT SHALL ACCESSIBILITY STANDARDS CANADA, ITS CONTRACTORS, AGENTS, EMPLOYEES, DIRECTORS, OR OFFICERS, OR HIS MAJESTY THE KING IN RIGHT OF CANADA, HIS EMPLOYEES, CONTRACTORS, AGENTS, DIRECTORS, OR OFFICERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INJURY, LOSS, COSTS, OR EXPENSES, HOWEVER CAUSED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO SPECIAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, LOST REVENUE, BUSINESS INTERRUPTION, LOST OR DAMAGED DATA, OR ANY OTHER COMMERCIAL OR ECONOMIC LOSS, WHETHER BASED IN CONTRACT, TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE), OR ANY OTHER THEORY OF LIABILITY, ARISING OUT OF OR RESULTING FROM ACCESS TO OR POSESSSION OR USE OF THIS DOCUMENT, EVEN IF ACCESSIBILITY STANDARDS CANADA OR ANY OF THEM HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES, INJURY, LOSS, COSTS, OR EXPENSES.
In publishing and making this document available, Accessibility Standards Canada is not undertaking to render professional or other services for or on behalf of any person or entity or to perform any duty owed by any person or entity to another person or entity. The information in this document is directed to those who have the appropriate degree of knowledge and experience to use and apply its contents, and Accessibility Standards Canada accepts no responsibility whatsoever arising in any way from any and all use of or reliance on the information contained in this document.
Accessibility Standards Canada publishes voluntary standards and related documents. Accessibility Standards Canada has no power, nor does it undertake, to enforce conformance with the contents of the standards or other documents published by Accessibility Standards Canada.
Intellectual property and ownership
As between Accessibility Standards Canada and users of this document (whether it be printed, electronic or alternate form), Accessibility Standards Canada is the owner, or the authorized licensee, of all copyright and moral rights contained herein. Additionally, Accessibility Standards Canada is the owner of its official mark. Without limitation, the unauthorized use, modification, copying, or disclosure of this document may violate laws that protect Accessibility Standards Canada and / or others’ intellectual property and may give rise to a right in Accessibility Standards Canada and / or others to seek legal redress for such use, modification, copying, or disclosure. To the extent permitted by licence or by law, Accessibility Standards Canada reserves all intellectual property and other rights in this document.
Patent rights
Some elements of this standard may be the subject of patent rights or pending patent applications. Accessibility Standards Canada shall not be held responsible for identifying any or all such patent rights. Users of this standard are expressly informed that determination of the existence and / or validity of any such patent rights is entirely their own responsibility.
Assignment of copyright
In this legal notice, a “comment” refers to all written or orally provided information, including all suggestions, that a user provides to Accessibility Standards Canada in relation to a standard and / or a draft standard. By providing a comment to Accessibility Standards Canada in relation to a standard and / or draft standard, the commenter grants to Accessibility Standards Canada and the Government of Canada a non-exclusive, royalty-free, perpetual, worldwide, and irrevocable licence to use, translate, reproduce, disclose, distribute, publish, modify, authorize to reproduce, communicate to the public by telecommunication, record, perform, or sublicense the comment, in whole or in part and in any form or medium, for revising the standard and/or draft standard, and/or for non-commercial purposes. By providing the comment, the commenter being the sole owner of the copyright or having the authority to license the copyright on behalf of their employer, confirms their ability to confer the licence and the commenter waives all associated moral rights, including, without limitation, all rights of attribution in respect of the comment. Where the provider of the comment is not the comment’s author, the provider confirms that a waiver of moral rights by the author has been made in favour of the provider or the comment’s copyright owner. At the time of providing a comment, the commenter must declare and provide a citation for any and all intellectual property within the comment that is owned by a third party.
Authorized Uses of this document
This document, in all formats including alternate formats, is being provided by Accessibility Standards Canada for informational, educational, and non-commercial use only. The users of this document are authorized to do only the following:
- Load this document onto a computer for the sole purpose of reviewing it;
- Search and browse this document;
- Print this document if it is in electronic format; and
- Disseminate this document for informational, educational, and non-commercial purposes.
Users shall not and shall not permit others to:
- Alter this document in any way or remove this Legal Notice from the attached standard;
- Sell this document without authorization from Accessibility Standards Canada;
- Use this document to mislead any users of a product, process or service addressed by this standard; or
- Reproduce all of, or specific portions of the standard within other publicly available standards documents or works, unless Accessibility Standards Canada grants, in writing, permission to do so and the following attribution is included by the user: “This material comes from [insert title of standards] and cannot be further reproduced without Accessibility Standards Canada’s authorization”.
If you do not agree with any of the terms and conditions contained in this Legal Notice, you must not load or use this document or make any copies of the contents hereof. Use of this document constitutes your acceptance of the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice.
National Standard of Canada
CAN/ASC - EN 301 549:2024
Accessibility requirements for ICT products and services (EN 301 549:2021, IDT)


Published in May 2024 by Accessibility Standards Canada
A departmental corporation of the federal government
320, St-Joseph Boulevard, Suite 246, Gatineau, QC, K1A 0H3
To access standards and related publications, visit accessible.canada.ca or call 1-833-854-7628.
CETTE NORME NATIONALE DU CANADA EST DISPONIBLE EN VERSIONS FRANÇAISE ET ANGLAISE.
ICS code(s): 03.100.10, 13.180, 33.020, 35.020, and 53.080.
ISBN 978-0-660-72099-9
Catalogue number AS4-33/2024E-PDF
© HIS MAJESTY THE KING IN RIGHT OF CANADA,
as represented by the Minister responsible for the Accessible Canada Act (i.e. the Minister of Diversity, Inclusion, and Persons with Disabilities), 2024.
No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form without the prior permission of the publisher.
Technical committee members
Consumer and public interest
Abishek Gupta, ML Engineer, RAI Researcher, Founder, Principal Researcher, Montreal AI Ethics Institute, Boston Consulting Group (BCG), BCG Henderson Institute
John Wills, Senior Program Advisor, OPS Accessibility Office, Centre of Excellence for Human Rights.
Lisa Snider, Access Changes Everything
Luna Bengio, Accessibility Consultant and Strategic Advisor
Gary Birch, Executive Director, Neil Squire Society
Nancy McLaughlin, Senior Policy Advisor on Accessibility, Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission
Academic and research bodies
Alison Paprica, Professor (adjunct) and Senior Fellow, Institute for Health Policy, Management and Evaluation, University of Toronto
Clayton Lewis, Professor, University of Colorado
Lisa Liskovoi, Senior Inclusive Designer and Digital Accessibility Specialist, Inclusive Design Research Center, OCAD University
Julia Stoyanovich, Associate Professor, Director, Tandon School of Engineering NYU
Jutta Treviranus (Chairperson), Director, Professor, Inclusive Design Research Center, OCAD University
Labour and Unions
Anne Jackson, Professor, Seneca College
Federally regulated Industries and Workplaces
Saeid Molladavoudi, Senior Data Science Advisor, Statistics Canada
Government Bodies and Authorities with Jurisdiction
Kave Noori, Artificial Intelligence Policy Officer, European Disability Forum
Mia Ahlgren, Human Rights and Disability Officer, Swedish Disability Rights Federation
Business and Industry
John Weigelt, CTO Microsoft Canada, Microsoft Canada
Julianna Rowsell, Senior Product Manager, Product Equity, Adobe
Kate Kalcevich, Head of Accessibility Innovation, Fable
Merve Hickok, Founder, President and Research Director, Aiethicist.org Center for AI and Digital Policy, University of Michigan
Sambhavi Chandrashekar, Global Accessibility Lead, D2L Corporation
English version
ICS 53.080
Supersedes EN 301549:2019
Accessibility requirements for ICT products and services
Exigences d'accessibilité pour les produits et services TIC
Barrierefreiheitsanforderungen für IKT-Produkte und -Dienstleistungen
This European Standard was approved by CEN on 23 April 2021.
CEN and CENELEC members are bound to comply with the CEN/CENELEC Internal Regulations which stipulate the conditions for giving this European Standard the status of a national standard without any alteration. Up-to-date lists and bibliographical references concerning such national standards may be obtained on application to the CEN-CENELEC Management Centre or to any CEN and CENELEC member.
This European Standard exists in three official versions (English, French, German). A version in any other language made by translation under the responsibility of a CEN and CENELEC member into its own language and notified to the CEN-CENELEC Management Centre has the same status as the official versions.
CEN and CENELEC members are the national standards bodies and national electrotechnical committees of Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Republic of North Macedonia, Romania, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Turkey and United Kingdom.


CEN-CENELEC Management Centre:
Rue de la Science 23,
B-1040 Brussels
Belgium
ETSI Secretariat
650, Route des Lucioles
06921 Sophia-Antipolis Cedex
France
All rights of exploitation in any form and by any means reserved worldwide for CEN national Members and for CENELEC Members.
Reference
REN/HF-00301549v321
Keywords
accessibility, HF, ICT, procurement
CEN
Rue de la science, 23
B-1040 Brussels
- BELGIUM
Tel: + 32 2 550 08 11
Fax: + 32 2 550 08 19
CENELEC
Rue de la science, 23
B-1040 Brussels
- BELGIUM
Tel.: +32 2 519 68 71
Fax: +32 2 519 69 19
ETSI
650 Route des Lucioles
F-06921 Sophia Antipolis Cedex - FRANCE
Tel.: +33 4 92 94 42 00
Fax: +33 4 93 65 47 16
Siret N° 348 623 562 00017 - NAF 742 C
Association à but non lucratif enregistrée à la
Sous-Préfecture de Grasse (06) N° 7803/88
Important notice
Individual copies of the present document can be downloaded from:
ETSI Search & Browse Standards
The present document may be made available in electronic versions and/or in print. The content of any electronic and/or print versions of the present document shall not be modified without the prior written authorization of ETSI. In case of any existing or perceived difference in contents between such versions and/or in print, the prevailing version of an ETSI deliverable is the one made publicly available in PDF format at ETSI Deliverables.
Users of the present document should be aware that the document may be subject to revision or change of status. Information on the current status of this and other ETSI documents is available at
ETSI deliverable status
If you find errors in the present document, please send your comment to one of the following services:
ETSI Committee Support Staff
Copyright Notification
No part may be reproduced or utilized in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying and microfilm except as authorized by written permission of ETSI.
The content of the PDF version shall not be modified without the written authorization of ETSI.
The copyright and the foregoing restriction extend to reproduction in all media.
© European Telecommunications Standards Institute 2021.
© Comité Européen de Normalisation 2021.
© Comité Européen de Normalisation Electrotechnique 2021.
All rights reserved.
DECT™, PLUGTESTS™, UMTS™ and the ETSI logo are trademarks of ETSI registered for the benefit of its Members.
3GPP™ and LTE™ are trademarks of ETSI registered for the benefit of its Members and
of the 3GPP Organizational Partners.
oneM2M™ logo is a trademark of ETSI registered for the benefit of its Members and
of the oneM2M Partners.
GSM® and the GSM logo are trademarks registered and owned by the GSM Association.
Intellectual Property Rights
Essential patents
IPRs essential or potentially essential to normative deliverables may have been declared to ETSI. The information pertaining to these essential IPRs, if any, is publicly available for ETSI members and non-members, and can be found in ETSI SR 000 314: "Intellectual Property Rights (IPRs); Essential, or potentially Essential, IPRs notified to ETSI in respect of ETSI standards", which is available from the ETSI Secretariat. Latest updates are available on the ETSI Web server (https://ipr.etsi.org/).
Pursuant to the ETSI IPR Policy, no investigation, including IPR searches, has been carried out by ETSI. No guarantee can be given as to the existence of other IPRs not referenced in ETSI SR 000 314 (or the updates on the ETSI Web server) which are, or may be, or may become, essential to the present document.
Trademarks
The present document may include trademarks and/or tradenames which are asserted and/or registered by their owners. ETSI claims no ownership of these except for any which are indicated as being the property of ETSI, and conveys no right to use or reproduce any trademark and/or tradename. Mention of those trademarks in the present document does not constitute an endorsement by ETSI of products, services or organizations associated with those trademarks.
Foreword
This Harmonised European Standard (EN) has been produced by ETSI Technical Committee Human Factors (HF), and the eAccessibility Joint Working Group (JWG) of CEN/CENELEC/ETSI and is now submitted for the combined Public Enquiry and Vote phase of the standards EN Approval Procedure.
EN 301 549 was originally produced under Mandate M 376 [i.3] and specified functional accessibility requirements applicable to ICT products and services, together with a description of the test procedures and evaluation methodology for each accessibility requirement in a form that is suitable for use in procurement. The other deliverables prepared in response to the original Mandate M 376 were: ETSI TR 102 612 [i.9] "Human Factors (HF); European accessibility requirements for public procurement of products and services in the ICT domain (European Commission Mandate M 376, Phase 1)", TR 101 550 [i.7] "Documents relevant to EN 301 549 "Accessibility requirements suitable for public procurement of ICT products and services in Europe"", TR 101 551 [i.8] "Guidelines on the use of accessibility award criteria suitable for public procurement of ICT products and services in Europe", and TR 101 552 [i.30] "Guidance for the application of conformity assessment to accessibility requirements for public procurement of ICT products and services in Europe". These have not been updated to reflect any changes to the content or scope of the present document, made as a part of the M 554 revision effort.
This revision to EN 301 549 has been prepared under the Commission's standardisation request C(2017)2585 final [i.27] to provide, in additions to its other uses, one voluntary means of conforming to the essential requirements of Directive 2016/2102 on the accessibility of the websites and mobile applications of public sector bodies [i.28]. The minimum requirements of the European Web Accessibility Directive (Directive 2016/2102) are explicitly detailed in Annex A.
Once the present document is cited in the Official Journal of the European Union under Directive 2016/2102 [i.28], conformance with the normative clauses of the present document given in Tables A.1 and A.2 confers, within the limits of the scope of the present document, a presumption of conformity with the corresponding essential requirements of that Directive and associated EFTA regulations.
The present document has been developed from EN 301 549 [i.29] (V2.1.2) (08-2018).
The significant changes since EN 301 549 [i.29] (V2.1.2) are:
- the requirements related to Real-Time Text (RTT) in clause 6.2 have been revised and extended;
- the WCAG 2.1 AAA Success Criteria that were previously in an Annex D are now included in clause 9.5;
- a new Annex D, "Further resources for cognitive accessibility", has been added;
- a new Annex E "Guidance for users of the present document" has been added.
- a new Annex F "change history" has been added.
Date of adoption of this EN: | 10 March 2021 |
Date of latest announcement of this EN (doa): | 30 June 2021 |
Date of latest publication of new National Standard or endorsement of this EN (dop/e): | 31 December 2021 |
Date of withdrawal of any conflicting National Standard (dow): | 31 December 2022 |
Modal verbs terminology
In the present document "shall", "shall not", "should", "should not", "may", "may not", "need", "need not", "will", "will not", "can" and "cannot" are to be interpreted as described in clause 3.2 of the ETSI Drafting Rules (Verbal forms for the expression of provisions).
"must" and "must not" are NOT allowed in ETSI deliverables except when used in direct citation.
Introduction
The present document is developed in response to standardisation request M 554 [i.27] from the European Commission to CEN, CENELEC and ETSI. It is a revision of the European Standard (EN) that was initially prepared in response to Phase 2 of Mandate M 376 [i.3].
The present document covers a wide range of requirements for a variety of ICT solutions. It is relevant for all organizations who buy, develop or manufacture ICT products or services. It consists of fourteen clauses and six annexes:
- Clauses 0 to 3 include background information, the scope of the standard, and links to other standards, definitions and explanations of abbreviations.
- Clause 4 contains functional performance statements that explain the functionality that is needed to enable users with different abilities to locate, identify and operate functions in technology. The user needs underlying the functional performance statements are the basis for the requirements in subsequent clauses.
- Clauses 5 to 13 provide specific testable criteria for accessible ICT, related to technical requirements for different kinds of ICT, starting with generic requirements in clause 5.
- Clause 14 is about conformance. All clauses except those in clause 12, related to documentation and support services, are self-scoping. This means they are introduced with the phrase 'Where ICT <pre-condition>'. Conformance is achieved when the pre-condition is true and the corresponding test (in Annex C) is passed. When the pre-condition is false the requirement is not applicable.
- Annex A has two tables with requirements related to Directive 2016/2102 on the accessibility of the websites and mobile applications of public sector bodies [i.28]. The first table applies to web pages and documents and the second applies to mobile applications. The minimum requirements are collected from clauses 9, 10 and 11 and some requirements from clauses 5, 6, 7 and 12 that are relevant to fulfill the Directive.
- Annex B contains a table showing which of the requirements set out in clauses 5 to 13 related to different types of ICT support the user needs as expressed in the functional performance statements of clause 4.
- Annex C is a normative annex that sets out the means necessary to determine conformance with the individual requirements. It does not provide a testing methodology.
- Annex D points to additional resources related to improving accessibility for users with limited cognitive, language and learning abilities.
- Annex E provides an overview and simple explanation of the structure of the present document, including an explanation of how it can be used.
- Annex F provides a change history table.
When the present document is used for most purposes, including when used in ICT procurement, all of the requirements in clauses 5 to 13, as well as the functional performance statements in clause 4 should be considered. The potential applicability of any requirement can be determined from the self-scoping phrase at the beginning of each requirement.
When the present document is used as the basis to determine conformity with the essential requirements of Directive 2016/2102 on the accessibility of the websites and mobile applications of public sector bodies [i.28], Tables A.1 and A.2 in Annex A identify all the applicable requirements.
NOTE 1: The present document reflects the content of the W3C WCAG 2.1 Recommendation [5].
NOTE 2: Annex E provides an overview and simple explanation of the structure of the present document, including an explanation of how it can be used. Readers who are unfamiliar with the present document are recommended to read Annex E first to give them a better understanding of the present document and how to use it.
The WCAG 2.1 [5] content referenced in clauses 9, 10 and 11 is subject to the following specific copyright provisions: Copyright © 2017-2018 W3C® (MIT, ERCIM, Keio, Beihang). The W3C document license applies.
See the document use license and copyright FAQ for more information:
1. Scope
The present document specifies the functional accessibility requirements applicable to ICT products and services, together with a description of the test procedures and evaluation methodology for each accessibility requirement in a form that is suitable for use in public procurement within Europe. The present document is intended to be used with web based technologies, non-web technologies and hybrids that use both. It covers both software and hardware as well as services. It is intended for use by both providers and procurers, but it is expected that it will also be of use to many others as well.
The relationship between the present document and the essential requirements of Directive 2016/2102 on the accessibility of the websites and mobile applications of public sector bodies [i.28] is given in Annex A.
The present document contains the necessary functional requirements and provides a reference document such that if procedures are followed by different actors, the results of testing are similar and the interpretation of those results is clear. The test descriptions and evaluation methodology included in the present document are elaborated to a level of detail compliant with ISO/IEC 17007:2009 [i.14], so that conformance testing can give conclusive results.
2. References
2.1 Normative references
References are either specific (identified by date of publication and/or edition number or version number) or non-specific. For specific references, only the cited version applies. For non-specific references, the latest version of the referenced document (including any amendments) applies.
Referenced documents which are not found to be publicly available in the expected location might be found at ETSI References in docbox.
NOTE: While any hyperlinks included in this clause were valid at the time of publication, ETSI cannot guarantee their long term validity.
The following referenced documents are necessary for the application of the present document.
[1]
ETSI ETS 300 381 (Edition 1) (December 1994): "Telephony for hearing impaired people; Inductive coupling of telephone earphones to hearing aids".
[2]
ETSI ES 200 381-1 (V1.2.1) (October 2012): "Telephony for hearing impaired people; Inductive coupling of telephone earphones to hearing aids; Part 1: Fixed-line speech terminals".
[3]
ETSI ES 200 381-2 (V1.1.1) (October 2012): "Telephony for hearing impaired people; Inductive coupling of telephone earphones to hearing aids; Part 2: Cellular speech terminals".
[4]
W3C Recommendation (December 2008)/ISO/IEC 40500:2012: "Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.0".
NOTE: Available at WCAG 2.0.
[5]
W3C Recommendation (June 2018): "Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.1".
NOTE: Available at WCAG 2.1.
2.2 Informative references
References are either specific (identified by date of publication and/or edition number or version number) or non-specific. For specific references, only the cited version applies. For non-specific references, the latest version of the referenced document (including any amendments) applies.
NOTE: While any hyperlinks included in this clause were valid at the time of publication, ETSI cannot guarantee their long term validity.
The following referenced documents are not necessary for the application of the present document but they assist the user with regard to a particular subject area.
[i.1]
ANSI/IEEE C63.19 (2011): "American National Standard Method of Measurement of Compatibility between Wireless Communication Devices and Hearing Aids".
[i.2]
ANSI/TIA-4965: "Receive volume control requirements for digital and analogue wireline terminals".
[i.3]
European Commission M 376-EN: "Standardization Mandate to CEN, CENELEC and ETSI in support of European accessibility requirements for public procurement of products and services in the ICT domain".
[i.4]
ETSI EG 201 013: "Human Factors (HF); Definitions, abbreviations and symbols".
[i.5]
ETSI ES 202 975: "Human Factors (HF); Requirements for relay services".
[i.6]
ETSI ETS 300 767: "Human Factors (HF); Telephone Prepayment Cards; Tactile Identifier".
[i.7]
ETSI/CEN/CENELEC TR 101 550: "Documents relevant to EN 301 549 "Accessibility requirements suitable for public procurement of ICT products and services in Europe"".
[i.8]
ETSI/CEN/CENELEC TR 101 551: "Guidelines on the use of accessibility award criteria suitable for public procurement of ICT products and services in Europe".
[i.9]
ETSI TR 102 612: "Human Factors (HF); European accessibility requirements for public procurement of products and services in the ICT domain (European Commission Mandate M 376, Phase 1)".
[i.10]
ETSI TS 126 114: "Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS); Multimedia telephony; Media handling and interaction (3GPP TS 26.114)".
[i.11]
ETSI TS 122 173: "Digital cellular telecommunications system (Phase 2+) (GSM); Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; IP Multimedia Core Network Subsystem (IMS) Multimedia Telephony Service and supplementary services; Stage 1 (3GPP TS 22.173)".
[i.12]
ETSI TS 134 229: "Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS); LTE; Internet Protocol (IP) multimedia call control protocol based on Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) and Session Description Protocol (SDP); User Equipment (UE) conformance specification (3GPP TS 34.229)".
[i.13]
IETF RFC 4103 (2005): "RTP Payload for Text Conversation".
[i.14]
ISO/IEC 17007:2009: "Conformity assessment - Guidance for drafting normative documents suitable for use for conformity assessment".
[i.15]
ISO 9241-11:2018: "Ergonomics of human-system interaction - Part 11: Usability: Definitions and concepts".
[i.16]
ISO 9241-110:2006: "Ergonomics of human-system interaction - Part 110: Dialogue principles".
[i.17]
ISO 9241-171:2008: "Ergonomics of human-system interaction - Part 171: Guidance on software accessibility".
[i.18]
Void.
[i.19]
ISO/IEC 13066-1:2011: "Information technology - Interoperability with assistive technology (AT) - Part 1: Requirements and recommendations for interoperability".
[i.20]
Recommendation ITU-T E.161 (2001): "Arrangement of digits, letters and symbols on telephones and other devices that can be used for gaining access to a telephone network".
[i.21]
Recommendation ITU-T G.722 (1988): "7 kHz audio-coding within 64 kbit/s".
[i.22]
Recommendation ITU-T G.722.2 (2003): "Wideband coding of speech at around 16 kbit/s using Adaptive Multi-Rate Wideband (AMR-WB)".
[i.23]
Recommendation ITU-T V.18 (2000): "Operational and interworking requirements for DCEs operating in the text telephone mode".
[i.24]
TIA-1083-A (2010): "Telecommunications; Telephone Terminal equipment; Handset magnetic measurement procedures and performance requirements".
[i.25]
Section 508 of the United States Rehabilitation Act of 1973, revised 2017.
NOTE: Available at https://www.section508.gov/manage/laws-and-policies.
[i.26]
W3C Working Group Note 5 September 2013: "Guidance on Applying WCAG 2.0 to Non-Web Information and Communications Technologies (WCAG2ICT)".
NOTE: Available at http://www.w3.org/TR/wcag2ict/.
[i.27]
M 554 Commission Implementing Decision C(2017)2585 of 27.4.2017 on a standardisation request to the European standardisation organisations in support of Directive (EU) 2016/2102 of the European Parliament and of the Council on the accessibility of the websites and mobile applications of public sector bodies.
[i.28]
Directive (EU) 2016/2102 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 26 October 2016 on the accessibility of the websites and mobile applications of public sector bodies.
[i.29]
ETSI/CEN/CENELEC EN 301 549 (V2.1.2) (August 2018): "Accessibility requirements for ICT products and services".
[i.30]
ETSI/CEN/CENELEC TR 101 552: "Guidance for the application of conformity assessment to accessibility requirements for public procurement of ICT products and services in Europe".
[i.31]
ISO/IEC TS 20071-25:2017: "Information technology - User interface component accessibility - Part 25: Guidance on the audio presentation of text in videos, including captions, subtitles and other on-screen text".
[i.32]
W3C Recommendation (September 2015): "Authoring Tool Accessibility Guidelines (ATAG) 2.0".
NOTE: Available at http://www.w3.org/TR/ATAG20/.
[i.33]
W3C Recommendation (September 2015): "User Agent Accessibility Guidelines (UAAG) 2.0".
NOTE: vailable at http://www.w3.org/TR/UAAG20/.
[i.34]
ISO 21542:2011: "Building construction - Accessibility and usability of the built environment".
[i.35]
ISO/IEC Guide 71:2014: "Guide for addressing accessibility in standards".
[i.36]
Recommendation ITU-T T.140 (1988): "Protocol for multimedia application text conversation".
[i.37]
Recommendation ITU-T F.703 (2000): "Multimedia conversational services".
[i.38]
W3C WebSchemas/Accessibility 2.0.
NOTE: Available at https://www.w3.org/wiki/WebSchemas/Accessibility.
[i.39]
Void.
[i.40]
Directive 2014/24/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 26 February 2014 on public procurement and repealing Directive 2004/18/EC.
3. Definition of terms, symbols and abbreviations
3.1 Terms
For the purposes of the present document, the terms given in ETSI EG 201 013 [i.4] and the following apply:
accessibility: extent to which products, systems, services, environments and facilities can be used by people from a population with the widest range of user needs, characteristics and capabilities, to achieve identified goals in identified contexts of use (from ISO 9241-11:2018 [i.15])
NOTE 1: Context of use includes direct use or use supported by assistive technologies.
NOTE 2: The context in which the ICT is used may affect its overall accessibility. This context could include other products and services with which the ICT may interact.
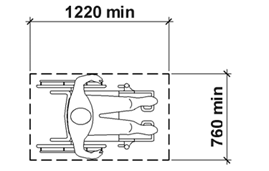
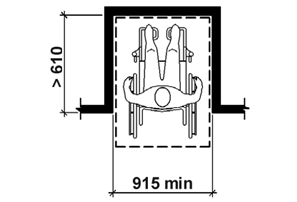
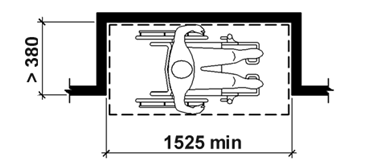
access space: space intended to be occupied by the person, including their Assistive Technology, while they are using the product
Assistive Listening Devices (ALDs): devices that help separate the sounds, particularly speech, that a person wants to hear from background noise by bringing sound directly into the ear
NOTE: These are often found in meetings and public venues such as plays, concerts and places of worship. They can also be used at home with televisions and other products with auditory output.
Assistive Technology (AT): equipment, product system, hardware, software or service that is used to increase, maintain or improve capabilities of individuals (from ISO/IEC Guide 71:2014 [i.35])
NOTE 1: Assistive technology is an umbrella term that is broader than assistive products.
NOTE 2: Assistive technology can include assistive services, and professional services needed for assessment, recommendation and provision.
NOTE 3: Where ICT does not support directly connected assistive technology, but which can be operated by a system connected over a network or other remote connection, such a separate system (with any included assistive technology) can also be considered assistive technology. This is an additional note, not included in ISO/IEC Guide 71:2014 [i.35].
audio description: additional audible narrative, interleaved with the dialogue, which describes the significant aspects of the visual content of audio-visual media that cannot be understood from the main soundtrack alone
NOTE: This is also variously described using terms such as "video description" or variants such as "descriptive narration".
authoring tool: software that can be used to create or modify content
NOTE 1: An authoring tool may be used by a single user or multiple users working collaboratively.
NOTE 2: An authoring tool may be a single stand-alone application or be comprised of collections of applications.
NOTE 3: An authoring tool may produce content that is intended for further modification or for use by end-users.
caption: synchronized visual and/or text alternative for both speech and non-speech audio information needed to understand the media content (after WCAG 2.1 [5])
NOTE: This is also variously described using terms such as "subtitles" or variants such as "subtitles for the deaf and hard-of-hearing".
closed functionality: functionality that is limited by characteristics that prevent a user from attaching, installing or using assistive technology
content: information and sensory experience to be communicated to the user by means of software, including code or mark-up that defines the content's structure, presentation, and interactions (after WCAG2ICT [i.26])
NOTE: Content occurs in three places: web pages, documents and software. When content occurs in a web page or a document, a user agent is needed in order to communicate the content's information and sensory experience to the user. When content occurs in software, a separate user agent is not needed in order to communicate the content's information and sensory experience to the user - the software itself performs that function.
context of use: combination of users, goals and tasks, resources, and environment. (from ISO 9241-11:2018 [i.15])
NOTE: The "environment" in a context of use includes the technical, physical, social, cultural and organizational environments.
document: logically distinct assembly of content (such as a file, set of files, or streamed media) that functions as a single entity rather than a collection, that is not part of software and that does not include its own user agent (after WCAG2ICT [i.26])
NOTE 1: A document always requires a user agent to present its content to the user.
NOTE 2: Letters, e-mail messages, spreadsheets, books, pictures, presentations, and movies are examples of documents.
NOTE 3: Software configuration and storage files such as databases and virus definitions, as well as computer instruction files such as source code, batch/script files, and firmware, are examples of files that function as part of software and thus are not examples of documents. If and where software retrieves "information and sensory experience to be communicated to the user" from such files, it is just another part of the content that occurs in software and is covered by WCAG2ICT like any other parts of the software. Where such files contain one or more embedded documents, the embedded documents remain documents under this definition.
NOTE 4: A collection of files zipped together into an archive, stored within a single virtual hard drive file, or stored in a single encrypted file system file, do not constitute a single document when so collected together. The software that archives/encrypts those files or manages the contents of the virtual hard drive does not function as a user agent for the individually collected files in that collection because that software is not providing a fully functioning presentation of that content.
NOTE 5: Anything that can present its own content without involving a user agent, such as a self-playing book, is not a document but is software.
NOTE 6: A single document may be composed of multiple files such as the video content and closed caption text. This fact is not usually apparent to the end-user consuming the document/content.
NOTE 7: An assembly of files that represented the video, audio, captions and timing files for a movie is an example of a document.
NOTE 8: A binder file used to bind together the various exhibits for a legal case would not be a document.
NOTE 9: Documents may contain sub-documents.
embedded: directly included in the content that is downloaded to the user agent and its extension, and is intended to be used in rendering the web page
NOTE: Something that is downloaded using a mechanism on the web page but is not used in rendering the page is not "embedded" in the page.
ICT network: technology and resources supporting the connection and operation of interconnected ICT
Information and Communication Technology (ICT): technology, equipment, or interconnected system or subsystem of equipment for which the principal function is the creation, conversion, duplication, automatic acquisition, storage, analysis, evaluation, manipulation, management, movement, control, display, switching, interchange, transmission, reception, or broadcast of data or information
NOTE: Examples of ICT are web pages, electronic content, telecommunications products, computers and ancillary equipment, software including mobile applications, information kiosks and transaction machines, videos, IT services, and multifunction office machines which copy, scan, and fax documents.
mechanically operable part: operable part that has a mechanical interface to activate, deactivate, or adjust the ICT
NOTE: Examples of mechanically operable parts include scanner covers, notebook docking stations and lids as well as physical switches and latches.
mechanism for private listening: auditory output designed so that only the current user can receive the sound
NOTE: Personal headsets, directional speakers and audio hoods are examples of mechanisms for private listening.
non-text content: content that is not a sequence of characters that can be programmatically determined or where the sequence is not expressing something in human language (after WCAG 2.1 [5])
non-web document: document that is not a web page, not embedded in web pages nor used in the rendering or functioning of the page
non-web software: software that is not a web page, not embedded in web pages nor used in the rendering or functioning of the page
open functionality: functionality that supports access by assistive technology
NOTE: This is the opposite of closed functionality.
operable part: component of ICT used to activate, deactivate, or adjust the ICT
NOTE 1: Operable parts can be provided in either hardware (see mechanically operable parts, above) or software. An on-screen button is an example of an operable part provided by software.
NOTE 2: Operable parts do not include parts involved only in maintenance or repair or other actions that are not expected of a typical user if the product is not malfunctioning. These actions include: clearing paper jams internal to the machine, replacing items or parts internal to the machine that may expose the end user to sharp or hot surfaces, replacing or repairing items designated by manufacturers as service or maintenance items in user documentation.
platform software (platform): collection of software components that runs on an underlying software or hardware layer, and that provides a set of software services to other software components that allows those applications to be isolated from the underlying software or hardware layer (after ISO/IEC 13066-1 [i.19])
NOTE: A particular software component might play the role of a platform in some situations and a client in others.
programmatically determinable: able to be read by software from developer-supplied data in a way that other software, including assistive technologies, can extract and present this information to users in different modalities
NOTE: WCAG 2.1 uses "determined" where this definition uses "able to be read" (to avoid ambiguity with the word "determined").
Real-Time Text (RTT): form of a text conversation in point to point situations or in multipoint conferencing where the text being entered is sent in such a way that the communication is perceived by the user as being continuous
NOTE 1: Users will perceive communication as continuous if the delay between text being created by the sender and received by the recipient is less than 500 ms. However, the actual delay will be dependent on the communication network.
NOTE 2: The creation of text will differ between systems where text is entered on a word-by-word basis (e.g. speech‑to‑text and predictive-text based systems) and systems where each character is separately generated (e.g. typing on a physical keyboard).
satisfies a success criterion: success criterion does not evaluate to "false" when applied to the ICT (after WCAG 2.1 [5])
single user connection: connection that consists of sound, RTT or video (or a combination of two or three of those media) that is established by a single user action
NOTE: Even though the different media may travel over different channels, and more than one piece of hardware may be involved, it appears to the user like a single connection, and is treated by any intermediate technologies (e.g. network, auto-reception) as a single connection for purposes such as transfer.
spoken captions/subtitles audio captions/subtitles: captions/subtitles that are voiced over the audiovisual content (from ISO/IEC TS 20071-25 [i.31])
stationary ICT: ICT that stands on the floor, or is mounted on a wall or other immovable structure, and is not intended to be moved by its user
NOTE 1: Typically, stationary ICT rests on the ground (such as an information kiosk) or is installed in a wall (such as a machine that dispenses cash or performs other banking services).
NOTE 2: A manufacturer cannot control the height of ICT that is put on a table by someone else, but they are able to control the reach dimensions of self-contained ICT that rests on the ground and can specify the heights for installation in walls.
terminal: combination of hardware and/or software with which the end user directly interacts and that provides the user interface
NOTE 1: The hardware may consist of more than one device working together e.g. a mobile device and a computer.
NOTE 2: For some systems, the software that provides the user interface may reside on more than one device such as a telephone and a server.
turn-taking: type of organization in conversation and discourse where participants speak one at a time in alternating turns
user agent: software that retrieves and presents content for users (after WCAG 2.1 [5])
NOTE 1: Software that only displays the content contained within it is treated as software and not considered to be a user agent.
NOTE 2: An example of software that is not a user agent is a calculator application that does not retrieve the calculations from outside the software to present it to a user. In this case, the calculator software is not a user agent, it is simply software with a user interface.
NOTE 3: Software that only shows a preview of content such as a thumbnail or other non-fully functioning presentation is not providing user agent functionality.
user interface: all components of an interactive system (software or hardware) that provide information and/or controls for the user to accomplish specific tasks with the interactive system (from ISO 9241-110 [i.16])
user interface element: entity of the user interface that is presented to the user by the software (after ISO 9241-171 [i.17])
NOTE 1: This term is also known as "user interface component".
NOTE 2: User-interface elements can be interactive or not.
web content: content that belongs to a web page, and that is used in the rendering or that is intended to be used in the rendering of the web page
web page: non-embedded resource obtained from a single URI using HTTP plus any other resources that are used in the rendering or intended to be rendered together with it by a user agent (after WCAG 2.1 [5])
3.2 Symbols
Void.
3.3 Abbreviations
For the purposes of the present document, the following abbreviations apply:
4. Functional performance
4.1 Meeting functional performance statements
The statements set out in clause 4.2 are intended to describe the functional performance of ICT enabling people to locate, identify, and operate ICT functions, and to access the information provided, regardless of physical, cognitive or sensory abilities. Any differences in ability may be permanent, temporary or situational. The requirements in clauses 5 to 13 provide specific testable criteria for accessible ICT, corresponding to the user needs reflected in clause 4.2.
NOTE 1: The relationship between the requirements from clauses 5 to 13 and the functional performance statements is set out in Annex B.
NOTE 2: The intent of clause 4.2 is to describe the ICT performance in enabling users to access the full functionality and documentation of the product or the service with or without the use of assistive technologies.
NOTE 3: The methods of meeting the accessibility needs of users with multiple access needs will depend on the specific combination of needs. Meeting these user accessibility needs may be addressed by considering multiple clauses in clause 4.2.
NOTE 4: Several users' accessibility needs rely on ICT providing specific modes of operation. If a user is to activate, engage or switch to the mode that complies with his or her user accessibility needs, the method for activating, engaging or switching to that mode would need to comply with the same user accessibility needs.
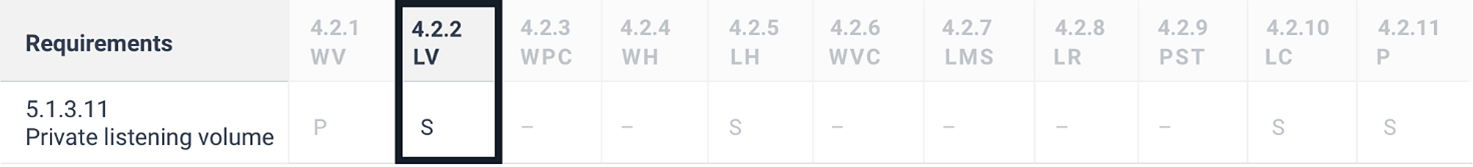
4.2 Functional performance statements
4.2.1 Usage without vision
Where ICT provides visual modes of operation, the ICT provides at least one mode of operation that does not require vision. This is essential for users without vision and benefits many more users in different situations.
NOTE 1: A web page or application with a well formed semantic structure can allow users without vision to identify, navigate and interact with a visual user interface.
NOTE 2: Audio and tactile user interfaces may contribute towards meeting this clause.
4.2.2 Usage with limited vision
Where ICT provides visual modes of operation, the ICT provides features that enable users to make better use of their limited vision. This is essential for users with limited vision and benefits many more users in different situations.
NOTE 1: Magnification, reduction of required field of vision and control of contrast, brightness and intensity can contribute towards meeting this clause.
NOTE 2: Where significant features of the user interface are dependent on depth perception, the provision of additional methods of distinguishing between the features may contribute towards meeting this clause.
NOTE 3: Users with limited vision may also benefit from non-visual access (see clause 4.2.1).
4.2.3 Usage without perception of colour
Where ICT provides visual modes of operation, the ICT provides a visual mode of operation that does not require user perception of colour. This is essential for users with limited colour perception and benefits many more users in different situations.
NOTE: Where significant features of the user interface are colour-coded, the provision of additional methods of distinguishing between the features may contribute towards meeting this clause.
4.2.4 Usage without hearing
Where ICT provides auditory modes of operation, the ICT provides at least one mode of operation that does not require hearing. This is essential for users without hearing and benefits many more users in different situations.
NOTE: Visual and tactile user interfaces, including those based on sign language, may contribute towards meeting this clause.
4.2.5 Usage with limited hearing
Where ICT provides auditory modes of operation, the ICT provides enhanced audio features. This is essential for users with limited hearing and benefits many more users in different situations.
NOTE 1: Enhancement of the audio clarity, reduction of background noise, providing a joint monaural option, adjustment of balance of both audio channels, increased range of volume and greater volume in the higher frequency range can contribute towards meeting this clause.
NOTE 2: Allowing the use of Assistive Listening Devices, such as headsets with noise cancellation (connected by cable, Bluetooth or WLAN) can contribute towards meeting this clause.
NOTE 3: Users with limited hearing may also benefit from non-hearing access (see clause 4.2.4).
4.2.6 Usage with no or limited vocal capability
Where ICT requires vocal input from users, the ICT provides at least one mode of operation that does not require them to generate vocal output. This is essential users with no or limited vocal capability and benefits many more users in different situations.
NOTE 1: Vocal output includes speech and other orally generated sounds, such as whistles and clicks.
NOTE 2: Keyboard, pen or touch user interfaces may contribute towards meeting this clause.
4.2.7 Usage with limited manipulation or strength
Where ICT requires manual actions, the ICT provides features that enable users to make use of the ICT through alternative actions not requiring manipulation, simultaneous action or hand strength. This is essential for users with limited manipulation or strength and benefits many more users in different situations.
NOTE 1: Examples of operations that users may not be able to perform include those that require fine motor control, path dependant gestures, pinching, twisting of the wrist, tight grasping, or simultaneous manual actions.
NOTE 2: One-handed operation, sequential key entry and speech user interfaces may contribute towards meeting this clause.
NOTE 3: Some users have limited hand strength and may not be able to achieve the level of strength to perform an operation. Alternative user interface solutions that do not require hand strength may contribute towards meeting this clause.
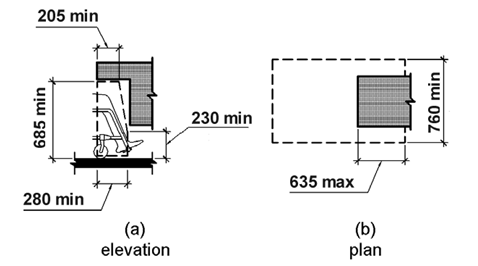
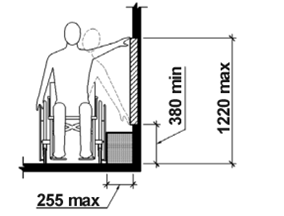
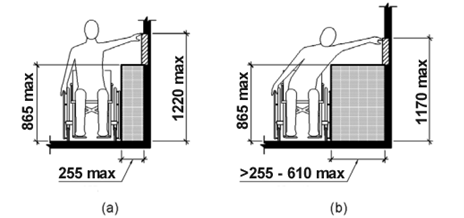
4.2.8 Usage with limited reach
Where ICT products are free-standing or installed, all the elements required for operation will need to be within reach of all users. This is essential for users with limited reach and benefits many more users in different situations.
NOTE: Considering the needs of wheelchair users and the range of user statures in the placing of operational elements of the user interface may contribute towards meeting this clause.
4.2.9 Minimize photosensitive seizure triggers
Where ICT provides visual modes of operation, the ICT provides at least one mode of operation that minimizes the potential for triggering photosensitive seizures. This is essential for users with photosensitive seizure triggers.
NOTE: Limiting the area and number of flashes per second may contribute towards meeting this clause.
4.2.10 Usage with limited cognition, language or learning
The ICT provides features and/or presentation that makes it simpler and easier to understand, operate and use. This is essential for users with limited cognition, language or learning, and benefits many more users in different situations.
NOTE 1: Adjustable timings, error indication and suggestion, and a logical focus order are examples of design features that may contribute towards meeting this clause.
NOTE 2: Providing an audio output of the text is an example of providing support for people with limited reading abilities.
NOTE 3: Providing spelling aid and word prediction of the text is an example of providing support for people with limited writing abilities.
NOTE 4: Interaction with content can be made easier, and less prone to errors, by presenting tasks in steps that are easy to follow.
4.2.11 Privacy
Where ICT provides features for accessibility, the ICT maintains the privacy of users of these features at the same level as other users.
NOTE: Enabling the connection of personal headsets for private listening, not providing a spoken version of characters being masked and enabling user control of legal, financial and personal data are examples of design features that may contribute towards meeting this clause.
5. Generic requirements
5.1 Closed functionality
5.1.1 Introduction (informative)
ICT has closed functionality for many reasons, including design or policy. Some of the functionality of products can be closed because the product is self-contained and users are precluded from adding peripherals or software in order to access that functionality.
ICT may have closed functionality in practice even though the ICT was not designed, developed or supplied to be closed.
Computers that do not allow end-users to adjust settings or install software are functionally closed.
5.1.2 General
5.1.2.1 Closed functionality
Where ICT has closed functionality, it shall meet the requirements set out in clauses 5.2 to 13, as applicable.
NOTE 1: ICT may close some, but not all, of its functionalities. Only the closed functionalities have to conform to the requirements of clause 5.1.
NOTE 2: The requirements within this clause replace those in clauses 5.2 to 13 that specifically state that they do not apply to closed functionality. This may be because they relate to compatibility with assistive technology or to the ability for the user to adjust system accessibility settings in products with closed functionality (e.g. products that prevent access to the system settings control panel).
5.1.2.2 Assistive technology
Where ICT has closed functionality, that closed functionality shall be operable without requiring the user to attach, connect or install assistive technology and shall conform to the generic requirements of clauses 5.1.3 to 5.1.6 as applicable. Personal headsets and personal induction loops shall not be classed as assistive technology for the purpose of this clause.
5.1.3 Non-visual access
5.1.3.1 Audio output of visual information
Where visual information is needed to enable the use of those functions of ICT that are closed to assistive technologies for screen reading, ICT shall provide at least one mode of operation using non-visual access to enable the use of those functions.
NOTE 1: Non-visual access may be in an audio form, including speech, or a tactile form such as braille for deaf-blind users.
NOTE 2: The visual information needed to enable use of some functions may include operating instructions and orientation, transaction prompts, user input verification, error messages and non-text content.
5.1.3.2 Auditory output delivery including speech
Where auditory output is provided as non-visual access to closed functionality, the auditory output shall be delivered:
- either directly by a mechanism included in or provided with the ICT; or
- by a personal headset that can be connected through a 3,5 mm audio jack, or an industry standard connection, without requiring the use of vision.
NOTE 1: Mechanisms included in or provided with ICT may be, but are not limited to, a loudspeaker, a built-in handset/headset, or other industry standard coupled peripheral.
NOTE 2: An industry standard connection could be a wireless connection.
NOTE 3: Some users may benefit from the provision of an inductive loop.
5.1.3.3 Auditory output correlation
Where auditory output is provided as non-visual access to closed functionality, and where information is displayed on the screen, the ICT should provide auditory information that allows the user to correlate the audio with the information displayed on the screen.
NOTE 1: Many people who are legally blind still have visual ability, and use aspects of the visual display even if it cannot be fully comprehended. An audio alternative that is both complete and complementary includes all visual information such as focus or highlighting, so that the audio can be correlated with information that is visible on the screen at any point in time.
NOTE 2: Examples of auditory information that allows the user to correlate the audio with the information displayed on the screen include structure and relationships conveyed through presentation.
5.1.3.4 Speech output user control
Where speech output is provided as non-visual access to closed functionality, the speech output shall be capable of being interrupted and repeated when requested by the user, where permitted by security requirements.
NOTE 1: It is best practice to allow the user to pause speech output rather than just allowing them to interrupt it.
NOTE 2: It is best practice to allow the user to repeat only the most recent portion rather than requiring play to start from the beginning.
5.1.3.5 Speech output automatic interruption
Where speech output is provided as non-visual access to closed functionality, the ICT shall interrupt current speech output when a user action occurs and when new speech output begins.
NOTE: Where it is essential that the user hears the entire message, e.g. a safety instruction or warning, the ICT may need to block all user action so that speech is not interrupted.
5.1.3.6 Speech output for non-text content
Where ICT presents non-text content, the alternative for non-text content shall be presented to users via speech output unless the non-text content is pure decoration or is used only for visual formatting. The speech output for non-text content shall follow the guidance for "text alternative" described in WCAG 2.1 [5] Success Criterion 1.1.1.
5.1.3.7 Speech output for video information
Where pre-recorded video content is needed to enable the use of closed functions of ICT and where speech output is provided as non-visual access to closed functionality, the speech output shall present equivalent information for the pre-recorded video content.
NOTE: This speech output can take the form of an audio description or an auditory transcript of the video content.
5.1.3.8 Masked entry
Where auditory output is provided as non-visual access to closed functionality, and the characters displayed are masking characters, the auditory output shall not be a spoken version of the characters entered unless the auditory output is known to be delivered only to a mechanism for private listening, or the user explicitly chooses to allow non-private auditory output.
NOTE 1: Masking characters are usually displayed for security purposes and include, but are not limited to asterisks representing personal identification numbers.
NOTE 2: Unmasked character output might be preferred when closed functionality is used, for example, in the privacy of the user's home. A warning highlighting privacy concerns might be appropriate to ensure that the user has made an informed choice.
5.1.3.9 Private access to personal data
Where auditory output is provided as non-visual access to closed functionality, and the output contains data that is considered to be private according to the applicable privacy policy, the corresponding auditory output shall only be delivered through a mechanism for private listening that can be connected without requiring the use of vision, or through any other mechanism explicitly chosen by the user.
NOTE 1: This requirement does not apply in cases where data is not defined as being private according to the applicable privacy policy or where there is no applicable privacy policy.
NOTE 2: Non-private output might be preferred when closed functionality is used, for example, in the privacy of the user's home. A warning highlighting privacy concerns might be appropriate to ensure that the user has made an informed choice.
5.1.3.10 Non-interfering audio output
Where auditory output is provided as non-visual access to closed functionality, the ICT shall not automatically play, at the same time, any interfering audible output that lasts longer than three seconds.
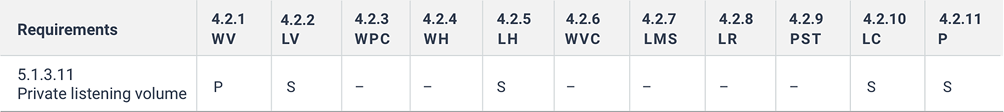
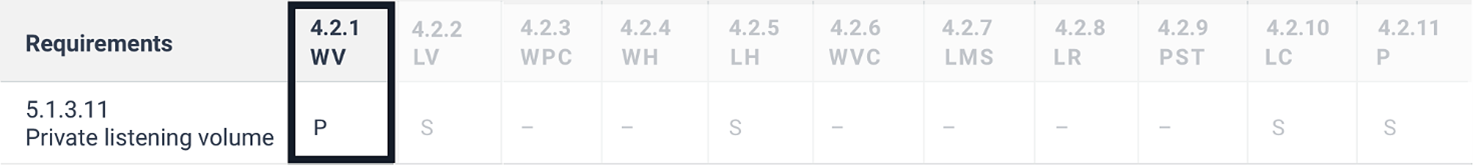
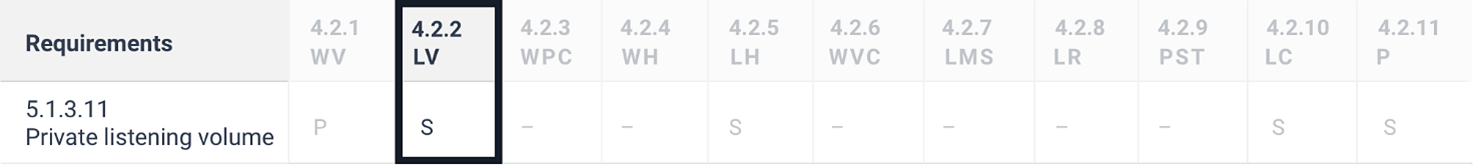
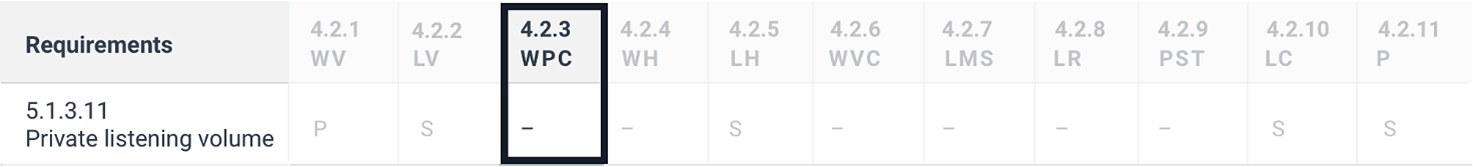
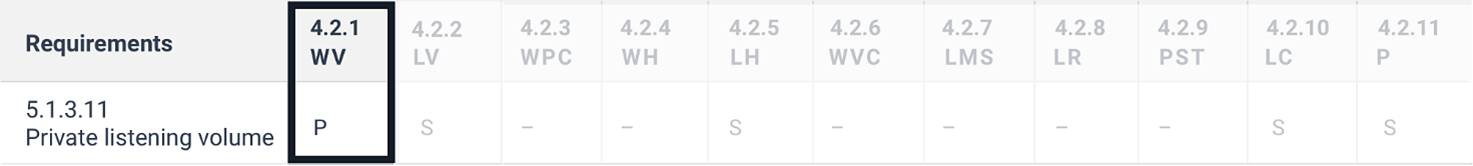
5.1.3.11 Private listening volume
Where auditory output is provided as non-visual access to closed functionality and is delivered through a mechanism for private listening, ICT shall provide at least one non-visual mode of operation for controlling the volume.
5.1.3.12 Speaker volume
Where auditory output is provided as non-visual access to closed functionality and is delivered through speakers on ICT, a non-visual incremental volume control shall be provided with output amplification up to a level of at least 65 dBA (-29 dBPaA).
NOTE: For noisy environments, 65 dBA may not be sufficient.
5.1.3.13 Volume reset
Where auditory output is provided as non-visual access to closed functionality, a function that resets the volume to be at a level of 65 dBA or less after every use, shall be provided, unless the ICT is dedicated to a single user.
NOTE: A feature to disable the volume reset function may be provided in order to enable the single-user exception to be met.
5.1.3.14 Spoken languages
Where speech output is provided as non-visual access to closed functionality, speech output shall be in the same human language as the displayed content provided, except:
- for proper names, technical terms, words of indeterminate language, and words or phrases that have become part of the vernacular of the immediately surrounding text;
- where the content is generated externally and not under the control of the ICT vendor, the present clause shall not be required to apply for languages not supported by the ICT's speech synthesizer;
- for displayed languages that cannot be selected using non-visual access;
- where the user explicitly selects a speech language that is different from the language of the displayed content.
5.1.3.15 Non-visual error identification
Where speech output is provided as non-visual access to closed functionality and an input error is automatically detected, speech output shall identify and describe the item that is in error.
5.1.3.16 Receipts, tickets, and transactional outputs
Where ICT is closed to visual access and provides receipts, tickets or other outputs as a result of a self-service transaction, speech output shall be provided which shall include all information necessary to complete or verify the transaction. In the case of ticketing machines, printed copies of itineraries and maps shall not be required to be audible.
NOTE: The speech output may be provided by any element of the total ICT system.
5.1.4 Functionality closed to text enlargement
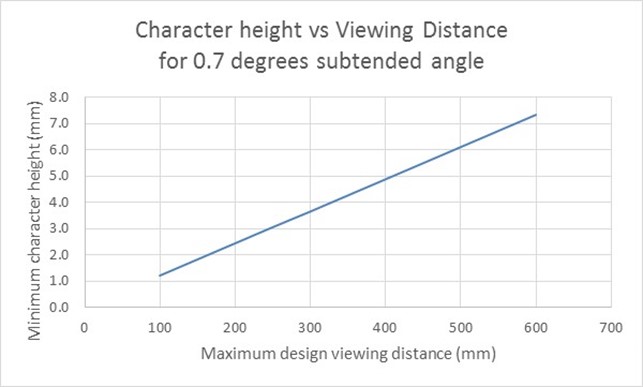
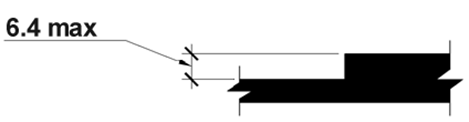
Where any functionality of ICT is closed to the text enlargement features of platform or assistive technology, the ICT shall provide a mode of operation where the text and images of text necessary for all functionality is displayed in such a way that a non-accented capital "H" subtends an angle of at least 0,7 degrees at a viewing distance specified by the supplier.
The subtended angle, in degrees, may be calculated from:
Ψ = (180 x H) / (π x D)
Where:
- ψ is the subtended angle in degrees
- H is the height of the text
- D is the viewing distance
- D and H are expressed in the same units
NOTE 1: The intent is to provide a mode of operation where text is large enough to be used by most users with low vision.
NOTE 2: Table 5.1 and Figure 1 illustrate the relationship between the maximum viewing distance and minimum character height at the specified minimum subtended angle.
Minimum subtended angle | Maximum design viewing distance | Minimum character height |
|---|---|---|
0,7 degrees | 100 mm | 1,2 mm |
200 mm | 2,4 mm | |
250 mm | 3,1 mm | |
300 mm | 3,7 mm | |
350 mm | 4,3 mm | |
400 mm | 4,9 mm | |
450 mm | 5,5 mm | |
500 mm | 6,1 mm | |
550 mm | 6,7 mm | |
600 mm | 7,3 mm |
5.1.5 Visual output for auditory information
Where auditory information is needed to enable the use of closed functions of ICT, the ICT shall provide visual information that is equivalent to the auditory output.
NOTE: This visual information can take the form of captions or text transcripts.
5.1.6 Operation without keyboard interface
5.1.6.1 Closed functionality
Where ICT functionality is closed to keyboards or keyboard interfaces, all functionality shall be operable without vision as required by clause 5.1.3.
5.1.6.2 Input focus
Where ICT functionality is closed to keyboards or keyboard interfaces and where input focus can be moved to a user interface element, it shall be possible to move the input focus away from that element using the same mechanism, in order to avoid trapping the input focus.
5.1.7 Access without speech
Where speech is needed to operate closed functions of ICT, the ICT shall provide at least one mode of operation using an alternative input mechanism that does not require speech.
5.2 Activation of accessibility features
Where ICT has documented accessibility features, it shall be possible to activate those documented accessibility features that are required to meet a specific need without relying on a method that does not support that need.
5.3 Biometrics
Where ICT uses biological characteristics, it shall not rely on the use of a particular biological characteristic as the only means of user identification or for control of ICT.
NOTE 1: Alternative means of user identification or for control of ICT could be non-biometric or biometric.
NOTE 2: Biometric methods based on dissimilar biological characteristics increase the likelihood that individuals with disabilities possess at least one of the specified biological characteristics. Examples of dissimilar biological characteristics are fingerprints, eye retinal patterns, voice, and face.
5.4 Preservation of accessibility information during conversion
Where ICT converts information or communication it shall preserve all documented non-proprietary information that is provided for accessibility, to the extent that such information can be contained in or supported by the destination format.
5.5 Operable parts
5.5.1 Means of operation
Where ICT has operable parts that require grasping, pinching, or twisting of the wrist to operate, an accessible alternative means of operation that does not require these actions shall be provided.
5.5.2 Operable parts discernibility
Where ICT has operable parts, it shall provide a means to discern each operable part, without requiring vision and without performing the action associated with the operable part.
NOTE: One way of meeting this requirement is by making the operable parts tactilely discernible.
5.6 Locking or toggle controls
5.6.1 Tactile or auditory status
Where ICT has a locking or toggle control and the status of that control is visually presented to the user, the ICT shall provide at least one mode of operation where the status of the control can be determined either through touch or sound without operating the control.
NOTE 1: Locking or toggle controls are those controls that can only have two or three states and that keep their state while being used.
NOTE 2: An example of a locking or toggle control is the "Caps Lock" key found on most keyboards. Another example is the volume button on a pay telephone, which can be set at normal, loud, or extra loud volume.
5.6.2 Visual status
Where ICT has a locking or toggle control and the status of the control is non-visually presented to the user, the ICT shall provide at least one mode of operation where the status of the control can be visually determined when the control is presented.
NOTE 1: Locking or toggle controls are those controls that can only have two or three states and that keep their state while being used.
NOTE 2: An example of a locking or toggle control is the "Caps Lock" key found on most keyboards. An example of making the status of a control determinable is a visual status indicator on a keyboard.
5.7 Key repeat
Where ICT has a key repeat function that cannot be turned off:
- the delay before the key repeat shall be adjustable to at least 2 seconds; and
- the key repeat rate shall be adjustable down to one character per 2 seconds.
5.8 Double-strike key acceptance
Where ICT has a keyboard or keypad, the delay after any keystroke, during which an additional key-press will not be accepted if it is identical to the previous keystroke, shall be adjustable up to at least 0,5 seconds.
5.9 Simultaneous user actions
Where ICT has a mode of operation requiring simultaneous user actions for its operation, such ICT shall provide at least one mode of operation that does not require simultaneous user actions to operate the ICT.
NOTE: Having to use both hands to open the lid of a laptop, having to press two or more keys at the same time or having to touch a surface with more than one finger are examples of simultaneous user actions.
6. ICT with two-way voice communication
6.1 Audio bandwidth for speech
Where ICT provides two-way voice communication, in order to provide good audio quality, that ICT shall be able to encode and decode two-way voice communication with a frequency range with an upper limit of at least 7 000 Hz.
NOTE 1: For the purposes of interoperability, support of Recommendation ITU-T G.722 [i.21] is widely used.
NOTE 2: Where codec negotiation is implemented, other standardized codecs such as Recommendation ITU-T G.722.2 [i.22] are sometimes used so as to avoid transcoding.
6.2 Real-Time Text (RTT) functionality
6.2.1 RTT provision
6.2.1.1 RTT communication
Where ICT is in a mode that provides a means for two-way voice communication, the ICT shall provide a means for two-way RTT communication, except where this would require design changes to add input or output hardware to the ICT.
NOTE 1: This requirement includes those products which do not have physical display or text entry capabilities but have the capability to connect to devices that do have such capabilities. It also includes intermediate ICT between the endpoints of the communication.
NOTE 2: There is no requirement to add: a hardware display, a hardware keyboard, or hardware to support the ability to connect to a display or keyboard, wired or wirelessly, if this hardware would not normally be provided.
NOTE 3: For the purposes of interoperability, support of Recommendation ITU-T T.140 [i.36] is widely used.
6.2.1.2 Concurrent voice and text
Where ICT provides a means for two-way voice communication and for users to communicate by RTT, it shall allow concurrent voice and text through a single user connection.
NOTE 1: With many-party communication, as in a conference system, it is allowed (but not required or necessarily recommended) that RTT be handled in a single display field and that "turn-taking" be necessary to avoid confusion (in the same way that turn-taking is required for those presenting/talking with voice).
NOTE 2: With many-party communication, best practice is for hand-raising for voice users and RTT users to be handled in the same way, so that voice and RTT users are in the same queue.
NOTE 3: With a many-party conference system that has chat as one of its features - the RTT (like the voice) would typically be separate from the chat so that RTT use does not interfere with chat (i.e. people can be messaging in the chat field while the person is presenting/talking with RTT - in the same manner that people message using the chat feature while people are talking with voice). RTT users would then use RTT for presenting and use the Chat feature to message while others are presenting (via Voice or RTT).
NOTE 4: The availability of voice and RTT running concurrently (and separately from chat) can also allow the RTT field to support text captioning when someone is speaking (and it is therefore not being used for RTT since it is not the RTT user's turn to speak).
NOTE 5: Where both server-side software and local hardware and software are required to provide voice communication, where neither part can support voice communication without the other and are sold as a unit for the voice communication function, the local and server-side components are considered a single product.
6.2.2 Display of RTT
6.2.2.1 Visually distinguishable display
Where ICT has RTT send and receive capabilities, displayed sent text shall be visually differentiated from, and separated from, received text.
NOTE: The ability of the user to choose between having the send and receive text be displayed in-line or separately, and with options to select, allows users to display RTT in a form that works best for them. This would allow Braille users to use a single field and take turns and have text appear in the sequential way that they may need or prefer.
6.2.2.2 Programmatically determinable send and receive direction
Where ICT has RTT send and receive capabilities, the send/receive direction of transmitted/received text shall be programmatically determinable, unless the RTT is implemented as closed functionality.
NOTE: This enables screen readers to distinguish between incoming text and outgoing text when used with RTT functionality.
6.2.2.3 Speaker identification
Where ICT has RTT capabilities, and provides speaker identification for voice, the ICT shall provide speaker identification for RTT.
NOTE: This is necessary to enable both voice and RTT participants to know who is currently communicating, whether it be in RTT or voice.
6.2.2.4 Visual indicator of Audio with RTT
Where ICT provides two-way voice communication, and has RTT capabilities, the ICT shall provide a real-time visual indicator of audio activity on the display.
NOTE 1: The visual indicator may be a simple character position on the display that flickers on and off to reflect audio activity, or presentation of the information in another way that can be both visible to sighted users and passed on to deaf-blind users who are using a braille display.
NOTE 2: Without this indication a person who lacks the ability to hear does not know when someone is talking.
6.2.3 Interoperability
Where ICT with RTT functionality interoperates with other ICT with RTT functionality (as required by clause 6.2.1.1) they shall support the applicable RTT interoperability mechanisms described below:
- ICT interoperating with other ICT directly connected to the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN), using Recommendation ITU-T V.18 [i.23] or any of its annexes for text telephony signals at the PSTN interface;
- ICT interoperating with other ICT using VOIP with Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) and using RTT that conforms to IETF RFC 4103 [i.13]. For ICT interoperating with other ICT using the IP Multimedia Sub-System (IMS) to implement VOIP, the set of protocols specified in ETSI TS 126 114 [i.10], ETSI TS 122 173 [i.11] and ETSI TS 134 229 [i.12] describe how IETF RFC 4103 [i.13] would apply;
- ICT interoperating with other ICT using technologies other than a or b, above, using a relevant and applicable common specification for RTT exchange that is published and available for the environments in which they will be operating. This common specification shall include a method for indicating loss or corruption of characters;
- ICT interoperating with other ICT using a standard for RTT that has been introduced for use in any of the above environments, and is supported by all of the other active ICT that support voice and RTT in that environment.
NOTE 1: In practice, new standards are introduced as an alternative codec/protocol that is supported alongside the existing common standard and used when all end-to-end components support it while technology development, combined with other reasons including societal development and cost efficiency, may make others become obsolete.
NOTE 2: Where multiple technologies are used to provide voice communication, multiple interoperability mechanisms may be needed to ensure that all users are able to use RTT.
EXAMPLE: A conferencing system that supports voice communication through an internet connection might provide RTT over an internet connection using a proprietary RTT method (option c). However, regardless of whether the RTT method is proprietary or non-proprietary, if the conferencing system also offers telephony communication it will also need to support options a or b to ensure that RTT is supported over the telephony connection.
6.2.4 RTT responsiveness
Where ICT utilises RTT input, that RTT input shall be transmitted to the ICT network or platform on which the ICT runs within 500 ms of the time that the smallest reliably composed unit of text entry is available to the ICT for transmission. Delays due to platform or network performance shall not be included in the 500 ms limit.
NOTE 1: For character by character input, the "smallest reliably composed unit of text entry" would be a character. For word prediction it would be a word. For some voice recognition systems - the text may not exit the recognition software until an entire word (or phrase) has been spoken. In this case, the smallest reliably composed unit of text entry available to the ICT would be the word (or phrase).
NOTE 2: The 500 ms limit allows buffering of characters for this period before transmission so character by character transmission is not required unless the characters are generated more slowly than 1 per 500 ms.
NOTE 3: A delay of 300 ms, or less, produces a better impression of flow to the user.
6.3 Caller ID
Where ICT provides caller identification or similar telecommunications functions, the caller identification and similar telecommunications functions shall be available in text form as well as being programmatically determinable, unless the functionality is closed.
6.4 Alternatives to voice-based services
Where ICT provides real-time voice-based communication and also provides voice mail, auto-attendant, or interactive voice response facilities, the ICT shall offer users a means to access the information and carry out the tasks provided by the ICT without the use of hearing or speech.
NOTE 1: Tasks that involve both operating the interface and perceiving the information would require that both the interface and information be accessible without use of speech or hearing.
NOTE 2: Solutions capable of handling audio, RTT and video media could satisfy the above requirement.
6.5 Video communication
6.5.1 General (informative)
Clause 6.5 (Video communications) provides performance requirements that support users who communicate using sign language and lip-reading. For these users, good usability is achieved with a resolution of at least Quarter Video Graphics Array (QVGA, 320 x 240), a frame rate of 20 frames per second and over, with a time difference between speech audio and video that does not exceed 100 ms.
Increasing the resolution and frame rate further improves both sign language (especially finger spelling) and lipreading, with frame rate being more important than resolution.
Time differences between audio and video (asynchronicity) can have a great impact onlip-reading - with video that lags behind audio having greater negative effect.
End-to-end latency can be a problem in video (sign) communication. Overall delay values below 400 ms are preferred, with an increase in preference down to 100 ms. Overall delay depends on multiple factors, including e.g. network delay and video processing. For this reason a testable requirement on minimum values for overall delay cannot be produced.
NOTE: Recommendation ITU-T F.703 [i.37] defines and gives requirements for Total Conversation that relate to the integration of audio, RTT and video in a single user connection.
6.5.2 Resolution
Where ICT that provides two-way voice communication includes real-time video functionality, the ICT:
- shall support at least QVGA resolution;
- should preferably support at least VGA resolution.
6.5.3 Frame rate
Where ICT that provides two-way voice communication includes real-time video functionality, the ICT:
- shall support a frame rate of at least 20 Frames Per Second (FPS);
- should preferably support a frame rate of at least 30 Frames Per Second (FPS) with or without sign language in the video stream.
6.5.4 Synchronization between audio and video
Where ICT that provides two-way voice communication includes real-time video functionality, the ICT shall ensure a maximum time difference of 100 ms between the speech and video presented to the user.
NOTE: Recent research shows that, if audio leads the video, the intelligibility suffers much more than the reverse.
6.5.5 Visual indicator of audio with video
Where ICT provides two-way voice communication, and includes real-time video functionality, the ICT shall provide a real-time visual indicator of audio activity.
NOTE 1: The visual indicator may be a simple visual dot or LED, or other type of on/off indicator, that flickers to reflect audio activity.
NOTE 2: Without this indication a person who lacks the ability to hear does not know when someone is talking.
6.5.6 Speaker identification with video (sign language) communication
Where ICT provides speaker identification for voice users, it shall provide a means for speaker identification for real-time signing and sign language users once the start of signing has been indicated.
NOTE 1: The speaker ID can be in the same location as for voice users for multiparty calls.
NOTE 2: This mechanism might be triggered manually by a user, or automatically where this is technically achievable.
6.6 Alternatives to video-based services
Where ICT provides real-time video-based communication and also provides answering machine, auto attendant or interactive response facilities, the ICT should offer users a means to access the information and carry out the tasks related to these facilities:
- for audible information, without the use of hearing;
- for spoken commands, without the use of speech;
- for visual information, without the use of vision.
NOTE: Solutions capable of generating real-time captions or handling RTT could satisfy the above requirement.
7. ICT with video capabilities
7.1 Caption processing technology
7.1.1 Captioning playback
Where ICT displays video with synchronized audio, it shall have a mode of operation to display the available captions. Where closed captions are provided as part of the content, the ICT shall allow the user to choose to display the captions.
NOTE 1: Captions may contain information about timing, colour and positioning. This caption data is necessary for caption users. Timing is used for caption synchronization. Colour can be used for speaker identification. Position can be used to avoid obscuring important information.
NOTE 2: If a Braille device is connected, the ICT should provide an option to display captions on the Braille device.
NOTE 3: Clause 7.1.1 refers to the ability of the player to display captions. Clauses 9.1.2.2, 10.1.2.2 and 11.1.2.2 refer to the provision of captions for the content (the video).
7.1.2 Captioning synchronization
Where ICT displays captions, the mechanism to display captions shall preserve synchronization between the audio and the corresponding captions as follows:
- Captions in recorded material: within 100 ms of the time stamp of the caption.
- Live captions: within 100 ms of the availability of the caption to the player.
7.1.3 Preservation of captioning
Where ICT transmits, converts or records video with synchronized audio, it shall preserve caption data such that it can be displayed in a manner consistent with clauses 7.1.1 and 7.1.2.
Additional presentational aspects of the text such as screen position, text colours, text style and text fonts may convey meaning, based on regional conventions. Altering these presentational aspects could change the meaning and should be avoided wherever possible.
7.1.4 Captions characteristics
Where ICT displays captions, it shall provide a way for the user to adapt the displayed characteristics of captions to their individual requirements, except where the captions are displayed as unmodifiable characters.
NOTE 1: Defining the background and foreground colour of subtitles, font type, size opacity of the background box of subtitles, and the contour or border of the fonts can contribute to meeting this requirement.
NOTE 2: Subtitles that are bitmap images are examples of unmodifiable characters.
7.1.5 Spoken subtitles
Where ICT displays video with synchronized audio, it shall have a mode of operation to provide a spoken output of the available captions, except where the content of the displayed captions is not programmatically determinable.
NOTE 1: Being able to manage speech output range for spoken subtitles independently from general ICT speech is preferable for most users. That is possible when the audio file with spoken subtitle is delivered in a separate audio track and mixed in the end users device.
NOTE 2: Presenting the separate audio track with spoken subtitles in synchronization with the displayed subtitles/captions improves understandability of the subtitles.
NOTE 3: Providing subtitles/captions as separate text-streams, facilitates converting the respective texts into audio.
NOTE 4: Subtitles that are bitmap images are examples where the content of the displayed captions will not be programmatically determinable.
7.2 Audio description technology
7.2.1 Audio description playback
Where ICT displays video with synchronized audio, it shall provide a mechanism to select and play available audio description to the default audio channel.
Where video technologies do not have explicit and separate mechanisms for audio description, an ICT is deemed to satisfy this requirement if the ICT enables the user to select and play several audio tracks.
NOTE 1: In such cases, the video content can include the audio description as one of the available audio tracks.
NOTE 2: Audio descriptions in digital media sometimes include information to allow descriptions that are longer than the gaps between dialogue. Support in digital media players for this "extended audio description" feature is useful, especially for digital media that is viewed personally.
7.2.2 Audio description synchronization
Where ICT has a mechanism to play audio description, it shall preserve the synchronization between the audio/visual content and the corresponding audio description.
7.2.3 Preservation of audio description
Where ICT transmits, converts, or records video with synchronized audio, it shall preserve audio description data such that it can be played in a manner consistent with clauses 7.2.1 and 7.2.2.
7.3 User controls for captions and audio description
Where ICT primarily displays materials containing video with associated audio content, user controls to activate subtitling and audio description shall be provided to the user at the same level of interaction (i.e. the number of steps to complete the task) as the primary media controls.
NOTE 1: Primary media controls are the set of controls that the user most commonly uses to control media.
NOTE 2: Products that have a general hardware volume control, such as a telephone, or a laptop which can be configured to display video through software but which is not its primary purpose, would not need dedicated hardware controls for captions and descriptions; however software controls, or hardware controls mapped through software, would need to be at the same level of interaction.
NOTE 3: It is best practice for ICT to include additional controls enabling the user to select whether captions and audio description are turned on or off by default.
8. Hardware
8.1 General
8.1.1 Generic requirements
The "generic requirements" of clause 5 also apply to ICT that is hardware.
8.1.2 Standard connections
Where an ICT provides user input or output device connection points, the ICT shall provide at least one input and/or output connection that conforms to an industry standard non-proprietary format, directly or through the use of commercially available adapters.
NOTE 1: The intent of this requirement is to ensure compatibility with assistive technologies by requiring the use of standard connections on ICT.
NOTE 2: The word connection applies to both physical and wireless connections.
NOTE 3: Current examples of industry standard non-proprietary formats are USB and Bluetooth.
8.1.3 Colour
Where the ICT has hardware aspects that use colour, colour shall not be used as the only visual means of conveying information, indicating an action, prompting a response, or distinguishing a visual element.
8.2 Hardware products with speech output
8.2.1 Speech volume gain
8.2.1.1 Speech volume range
Where ICT hardware has speech output, it shall provide a means to adjust the speech output volume level over a range of at least 18 dB.
NOTE: Fixed-line handsets and headsets fulfilling the requirements of ANSI/TIA-4965 [i.2] are deemed to comply with this requirement.
8.2.1.2 Incremental volume control
Where ICT hardware has speech output and its volume control is incremental, it shall provide at least one intermediate step of 12 dB gain above the lowest volume setting.
8.2.2 Magnetic coupling
8.2.2.1 Fixed-line devices
Where ICT hardware is a fixed-line communication device with speech output and which is normally held to the ear, it shall provide a means of magnetic coupling which meets the requirements of ETSI ES 200 381-1 [2] and shall carry the "T" symbol specified in ETSI ETS 300 381 [1].
NOTE 1: ICT fulfilling the requirements of TIA-1083-A [i.24] is deemed to comply with the requirements of this clause.
NOTE 2: Magnetic coupling is also known as inductive coupling for T-coil.
8.2.2.2 Wireless communication devices
Where ICT hardware is a wireless communication device with speech output which is normally held to the ear, it shall provide a means of magnetic coupling to hearing technologies which meets the requirements of ETSI ES 200 381-2 [3].
NOTE: ICT fulfilling the requirements of ANSI/IEEE C63.19 [i.1] is deemed to comply with the requirements of this clause.
8.3 Stationary ICT
8.3.0 General
The present document defines the dimensions for accessing stationary ICT that can be placed in a built environment, but does not define the dimensions of the built environment in general.
The scope includes stationary ICT, of which floors and circulation spaces are "an integral part" (typically kiosks and cabins), and where there are external reach ranges relevant for operating the stationary ICT.
Clauses 8.3.2 to 8.3.4 specify mandatory limits for the maximum and minimum height of operable parts and displays. Based on dimensions shown in Figure 53 of ISO 21542:2011 [i.34], it is recommended that the possible height range is reduced to:
- minimum and maximum heights of operable parts: 800 mm and 1 100 mm respectively, and
- minimum and maximum heights of displays: 1 200 mm and 1 400 mm respectively.
8.3.1 Forward or side reach
Stationary ICT shall conform to either clause 8.3.2 or clause 8.3.3.
NOTE 1: This does not preclude conforming to both clauses.
NOTE 2: The dimensions set out in clauses 407.8.3 and 407.8.2 of Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act, as published in January 2017 [i.25], are identical to those given in clauses 8.3.2 and 8.3.3 of the present document.
NOTE 3: Physical access to stationary ICT is dependent on the dimensions of both the ICT and the environment in which it is installed and operated. Clause 8.3 does not apply to the accessibility of the physical environment external to the ICT.
8.3.2 Forward reach
8.3.2.1 Unobstructed high forward reach
Where no part of the stationary ICT obstructs the forward reach, at least one of each type of operable part shall be located no higher than 1 220 mm (48 inches) above the floor of the access space. This is shown in Figure 2.
8.3.2.2 Unobstructed low forward reach
Where no part of the stationary ICT obstructs the forward reach, at least one of each type of operable part shall be located no lower than 380 mm (15 inches) above the floor of the access space. This is shown in Figure 2.
8.3.2.3 Obstructed forward reach
8.3.2.3.1 Clear space
Where an obstruction is an integral part of the stationary ICT and hinders the access to any type of operable part, the ICT shall provide a clear space which extends beneath the obstructing element for a distance not less than the required reach depth over the obstruction.
NOTE: Ensuring that there will be unhindered "access to any type of operable part" guarantees that a user will be able access at least one of each type of operable part.
8.3.2.3.2 Obstructed (< 510 mm) forward reach
Where the stationary ICT has an obstruction which is an integral part of the ICT and which is less than 510 mm (20 inches), the forward reach to at least one of each type of operable part shall be no higher than 1 220 mm (48 inches) above the floor contact of the ICT. This is shown in Figure 3 (a).
8.3.2.3.3 Obstructed (< 635 mm) forward reach
Where the stationary ICT has an obstruction which is an integral part of the ICT and which is not less than 510 mm (20 inches) but is less than 635 mm (25 inches) maximum, the forward reach to at least one of each type of operable part shall be no higher than 1 120 mm (44 inches) above the floor contact of the ICT. This is shown in Figure 3 (b).
8.3.2.4 Knee and toe clearance width
Where the space under an obstacle that is an integral part of the stationary ICT is part of access space, the clearance shall be at least 760 mm (30 inches) wide.
8.3.2.5 Toe clearance
Where an obstacle is an integral part of the stationary ICT, a space under the obstacle that is less than 230 mm (9 inches) above the floor is considered toe clearance and shall:
- extend 635 mm (25 inches) maximum under the whole obstacle;
- provide a space at least 430 mm (17 inches) deep and 230 mm (9 inches) above the floor under the obstacle;
- extend no more than 150 mm (6 inches) beyond any obstruction at 230 mm (9 inches) above the floor.
This is shown in Figure 4.
8.3.2.6 Knee clearance
Where an obstacle is an integral part of the stationary ICT, the space under the obstacle that is between 230 mm (9 inches) and 685 mm (25 inches) above the floor is considered knee clearance and shall:
- extend no more than 635 mm (25 inches) under the obstacle at a height of 230 mm (9 inches) above the floor;
- extend at least 280 mm (11 inches) under the obstacle at a height of 230 mm (9 inches) above the floor;
- extend at least 205 mm (8 inches) under the obstacle at a height of 685 mm (27 inches) above the floor;
- be permitted to be reduced in depth at a rate of 25 mm (1 inch) for each 150 mm (6 inches) in height.
This is shown in Figure 5.
8.3.3 Side reach
8.3.3.1 Unobstructed high side reach
Where the side reach is unobstructed or obstructed by an element that is an integral part of the stationary ICT and which is less than 255 mm (10 inches), at least one of each type of operable part shall be within a high side reach which is less than or equal to 1 220 mm (48 inches) above the floor of the access space. This is shown in Figure 6.
8.3.3.2 Unobstructed low side reach
Where the side reach is unobstructed or obstructed by an element that is an integral part of the stationary ICT and which is less than 255 mm (10 inches), at least one of each type of operable part shall be within a low side reach which is greater than or equal to 380 mm (15 inches) above the floor of the access space. This is shown in Figure 6.
8.3.3.3 Obstructed side reach
8.3.3.3.1 Obstructed (≤ 255 mm) side reach
Where stationary ICT has an obstruction which is an integral part of the ICT, the height of the obstruction shall be less than 865 mm (34 inches). Where the depth of the obstruction is less than or equal to 255 mm (10 inches), the high side reach to at least one of each type of operable part shall be no higher than 1 220 mm (48 inches) above the floor of the access space. This is shown in Figure 7 (a).
8.3.3.3.2 Obstructed (≤ 610 mm) side reach
Where stationary ICT has an obstruction which is an integral part of the ICT, the height of the obstruction shall be less than 865 mm (34 inches). Where the depth of the obstruction is greater than 255 mm (10 inches) with a maximum depth of 610 mm (24 inches), the high side reach to at least one of each type of operable part shall be no higher than 1 170 mm (46 inches) above the floor of the access space. This is shown in Figure 7 (b).
8.3.4 Clear floor or ground space
8.3.4.1 Change in level
Where stationary ICT has a floor within it, then any change of floor level within it or entering it shall be ramped with a slope no steeper than 1:48.
Exceptions:
- If the change in floor level is less than or equal to 6,4 mm (¼ inch) the change may be vertical as shown in Figure 8.
- If the change in floor level is less than or equal to 13 mm (½ inch) the change may have a slope not steeper than 1:2 as shown in Figure 9.
8.3.4.2 Clear floor or ground space
Where stationary ICT has an operating area within it, it shall provide a clear floor area that has the minimum dimensions of 760 mm (30 inches) by 1 220 mm (48 inches) from which to operate the ICT. This is shown in Figure 10.
8.3.4.3 Approach
8.3.4.3.1 General
Where stationary ICT has an access space inside it, at least one full side of the space shall be unobstructed.
8.3.4.3.2 Forward approach
Where the operating area is inside an alcove within the stationary ICT, the alcove is deeper than 610 mm (24 inches), and where a forward approach is necessary, the dimension of the access space shall be a minimum of 915 mm (36 inches) wide. This is shown in Figure 11.
8.3.4.3.3 Parallel approach
Where the operating area is inside an alcove within the stationary ICT, the alcove is deeper than 380 mm (15 inches), and where a parallel approach is possible, the dimension of the access space shall be a minimum of 1 525 mm (60 inches) wide. This is shown in Figure 12.
8.3.5 Visibility
Where stationary ICT provides one or more display screens, at least one of each type of display screen shall be positioned such that the information on the screen is legible from a point located 1 015 mm (40 inches) above the centre of the floor of the operating area).
NOTE: The intent of this requirement is that the information on the screen can be read by users with normal vision and appropriate language skills, when seated in a wheelchair.
8.3.6 Installation instructions
Installation instructions shall be made available for all stationary ICT. These instructions shall give guidance on how to install the ICT in a manner that takes into account applicable requirements for accessibility of the built environment as they apply to the installation of the ICT. Where there are no such requirements the instructions should require that the dimensions of the installed ICT conform to clauses 8.3.2 to 8.3.5 of the present document.
8.4 Mechanically operable parts
8.4.1 Numeric keys
Where provided, physical numeric keys arranged in a rectangular keypad layout shall have the number five key tactilely distinct from the other keys of the keypad.
NOTE: Recommendation ITU-T E.161 [i.20] describes the 12-key telephone keypad layout and provides further details of the form of tactile markers.
8.4.2 Operation of mechanical parts
8.4.2.1 Means of operation of mechanical parts
Where a control requires grasping, pinching, or twisting of the wrist to operate it, an accessible alternative means of operation that does not require these actions shall be provided.
8.4.2.2 Force of operation of mechanical parts
Where a control requires a force greater than 22,2 N to operate it, an accessible alternative means of operation that requires a force less than 22,2 N shall be provided.
NOTE: ISO 21542:2011 [i.34]: Building Construction - Accessibility and Usability of the Built Environment recommends a value between 2,5 and 5 Newtons.
8.4.3 Keys, tickets and fare cards
Where ICT provides keys, tickets or fare cards, and their orientation is important for further use, they shall have an orientation that is tactilely discernible.
NOTE: ETSI ETS 300 767 [i.6] defines suitable tactile indications for plastic cards.
8.5 Tactile indication of speech mode
Where ICT is designed for shared use and speech output is available, a tactile indication of the means to initiate the speech mode of operation shall be provided.
NOTE: The tactile indication could include Braille instructions.
9. Web
9.0 General (informative)
Requirements in clause 9 apply to web pages (as defined in clause 3.1) including:
- Conformance with W3C Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG 2.0) Level AA is equivalent to conforming with clauses 9.1.1, 9.1.2, 9.1.3.1 to 9.1.3.3, 9.1.4.1 to 9.1.4.5, 9.2.1.1, 9.2.1.2, 9.2.2, 9.2.3, 9.2.4, 9.3, 9.4.1.1, 9.4.1.2 and the conformance requirements of clause 9.6 of the present document.
- Conformance with W3C Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG 2.1) [5] Level AA is equivalent to conforming with all of clauses 9.1 to 9.4 and the conformance requirements of clause 9.6 of the present document.
- Requirements for non-web documents and non-web software are given in clauses 10 and 11 respectively.
NOTE 1: When evaluating web sites they are evaluated as individual web pages. Web applications, including mobile web applications, are covered under the definition of web page which is quite broad and covers all web content types.
NOTE 2: WCAG 2.0 is identical to ISO/IEC 40500:2012: "Information technology - W3C Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.0" [4].
The requirements in clauses 9.1 to 9.4 are written using the concept of satisfying success criteria (defined in clause 3.1). A web page satisfies a WCAG success criterion when the success criterion does not evaluate to false when applied to the web page. This implies that if the success criterion puts conditions on a specific feature and that specific feature does not occur in the web page, then the web page satisfies the success criterion.
NOTE 3: For example, a web page that does not contain pre-recorded audio content in synchronized media will automatically satisfy WCAG success criterion 1.2.2 (captions - pre-recorded) and, in consequence, will also conform to clause 9.1.2.2.
In addition to Level AA success criteria, the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines also include success criteria for Level AAA. These are listed in clause 9.5 of the present document. Web authors and procurement accessibility specialists are encouraged to consider whether any of the WCAG Level AAA success criteria offer suggestions that may be applicable and relevant to their project, as well as potentially beneficial to some users.
NOTE 4: The W3C states that "It is not recommended that Level AAA conformance be required as a general policy for entire sites because it is not possible to satisfy all Level AAA Success Criteria for some content".
NOTE 5: "Void" clauses have been inserted in order to maintain alignment with the numbering of WCAG 2.1 Level A and Level AA Success Criteria.
9.1 Perceivable
9.1.1 Text alternatives
9.1.1.1 Non-text content
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.1.1 Non-text content.
9.1.2 Time-based media
9.1.2.1 Audio-only and video-only (pre-recorded)
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.2.1 Audio-only and Video-only (Prerecorded).
9.1.2.2 Captions (pre-recorded)
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.2.2 Captions (Prerecorded).
9.1.2.3 Audio description or media alternative (pre-recorded)
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.2.3 Audio Description or Media Alternative (Prerecorded).
9.1.2.4 Captions (live)
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.2.4 Captions (Live).
9.1.2.5 Audio description (pre-recorded)
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.2.5 Audio Description (Prerecorded).
9.1.3 Adaptable
9.1.3.1 Info and relationships
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.3.1 Info and Relationships.
9.1.3.2 Meaningful sequence
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.3.2 Meaningful Sequence.
9.1.3.3 Sensory characteristics
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.3.3 Sensory Characteristics.
9.1.3.4 Orientation
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.3.4 Orientation.
9.1.3.5 Identify input purpose
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.3.5 Identify Input Purpose.
9.1.4 Distinguishable
9.1.4.1 Use of colour
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.1 Use of Color.
9.1.4.2 Audio control
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.2 Audio Control.
9.1.4.3 Contrast (minimum)
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.3 Contrast (Minimum).
9.1.4.4 Resize text
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.4 Resize text.
9.1.4.5 Images of text
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.5 Images of Text.
9.1.4.6 Void
9.1.4.7 Void
9.1.4.8 Void
9.1.4.9 Void
9.1.4.10 Reflow
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.10 Reflow.
9.1.4.11 Non-text contrast
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.11 Non-text Contrast.
9.1.4.12 Text spacing
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.12 Text spacing.
9.1.4.13 Content on hover or focus
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.13 Content on Hover or Focus.
9.2 Operable
9.2.1 Keyboard accessible
9.2.1.1 Keyboard
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.1.1 Keyboard.
9.2.1.2 No keyboard trap
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.1.2 No Keyboard Trap.
9.2.1.3 Void
9.2.1.4 Character key shortcuts
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.1.4 Character Key Shortcuts.
9.2.2 Enough time
9.2.2.1 Timing adjustable
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.2.1 Timing Adjustable.
9.2.2.2 Pause, stop, hide
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.2.2 Pause, Stop, Hide.
9.2.3 Seizures and physical reactions
9.2.3.1 Three flashes or below threshold
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.3.1 Three Flashes or Below Threshold.
9.2.4 Navigable
9.2.4.1 Bypass blocks
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.4.1 Bypass Blocks.
9.2.4.2 Page titled
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.4.2 Page Titled.
9.2.4.3 Focus Order
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.4.3 Focus Order.
9.2.4.4 Link purpose (in context)
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.4.4 Link Purpose (In Context).
9.2.4.5 Multiple ways
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.4.5 Multiple Ways.
9.2.4.6 Headings and labels
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.4.6 Headings and Labels.
9.2.4.7 Focus visible
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.4.7 Focus Visible.
9.2.5 Input modalities
9.2.5.1 Pointer gestures
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.5.1 Pointer Gestures.
9.2.5.2 Pointer cancellation
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.5.2 Pointer Cancellation.
9.2.5.3 Label in name
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.5.3 Label in Name.
9.2.5.4 Motion actuation
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.5.4 Motion Actuation.
9.3 Understandable
9.3.1 Readable
9.3.1.1 Language of page
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.1.1 Language of Page.
9.3.1.2 Language of parts
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.1.2 Language of Parts.
9.3.2 Predictable
9.3.2.1 On focus
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.2.1 On Focus.
9.3.2.2 On input
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.2.2 On Input.
9.3.2.3 Consistent navigation
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.2.3 Consistent Navigation.
9.3.2.4 Consistent identification
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.2.4 Consistent Identification.
9.3.3 Input assistance
9.3.3.1 Error identification
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.3.1 Error Identification.
9.3.3.2 Labels or instructions
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.3.2 Labels or Instructions.
9.3.3.3 Error suggestion
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.3.3 Error Suggestion.
9.3.3.4 Error prevention (legal, financial, data)
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.3.4 Error Prevention (Legal, Financial, Data).
9.4 Robust
9.4.1 Compatible
9.4.1.1 Parsing
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 4.1.1 Parsing.
9.4.1.2 Name, role, value
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 4.1.2 Name, Role, Value.
9.4.1.3 Status messages
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 4.1.3 Status Messages.
9.5 WCAG 2.1 AAA Success Criteria
In addition to the Level AA success criteria, included in clauses 9.1 to 9.4, the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines include success criteria for Level AAA. These are listed in Table 9.1. Web authors and procurement accessibility specialists are encouraged to consider the WCAG 2.1 Level AAA success criteria that, when it is possible to apply them, may provide access beyond that required in the present document.
NOTE: The W3C states that "It is not recommended that Level AAA conformance be required as a general policy for entire sites because it is not possible to satisfy all Level AAA Success Criteria for some content".
No. | Guideline | Success Criterion Number | Success Criteria Name |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | Time-based media | ||
2 | Time-based media | ||
3 | Time-based media | ||
4 | Time-based media | ||
5 | Adaptable | ||
6 | Distinguishable | ||
7 | Distinguishable | ||
8 | Distinguishable | ||
9 | Distinguishable | ||
10 | Keyboard Accessible | ||
11 | Enough time | ||
12 | Enough time | ||
13 | Enough time | ||
14 | Enough time | ||
15 | Seizures and physical reactions | ||
16 | Seizures and physical reactions | ||
17 | Navigable | ||
18 | Navigable | ||
19 | Navigable | ||
20 | Input modalities | ||
21 | Input modalities | ||
22 | Readable | ||
23 | Readable | ||
24 | Readable | ||
25 | Readable | ||
26 | Predictable | ||
27 | Input assistance | ||
28 | Input assistance |
9.6 WCAG conformance requirements
Where ICT is a web page, it shall satisfy all the following five WCAG 2.1 conformance requirements at Level AA [5]:
- Conformance level
- Full pages
- Complete processes
- Only Accessibility-Supported Ways of Using Technologies
- Non-interference
NOTE 1: A Web page that meets all of requirements 9.1 to 9.4, or where a Level AA conforming alternate version (as defined in WCAG 2.1 [5]) is provided, will meet conformance requirement 1.
NOTE 2: According to W3C: "WCAG 2.1 extends Web Content Accessibility Guidelines 2.0 [4], which was published as a W3C Recommendation December 2008. Content that conforms to WCAG 2.1 also conforms to WCAG 2.0, and therefore to policies that reference WCAG 2.0" [4].
NOTE 3: Conformance requirement 5 states that all content on the page, including content that is not otherwise relied upon to meet conformance, meets clauses 9.1.4.2, 9.2.1.2, 9.2.2.2 and 9.2.3.1.
10. Non-web documents
10.0 General (informative)
Requirements in clause 10 apply to:
- documents that are not web pages;
- documents that are not embedded in web pages; and
- documents that are provided with web pages but are neither embedded nor rendered together with the web page from which they are provided (i.e. the present clause applies to downloadable documents).
Clause 9 provides requirements for documents that are in web pages or that are embedded in web pages and that are used in the rendering or that are intended to be rendered together with the web page in which they are embedded.
NOTE 1: Some examples of documents are letters, spreadsheets, emails, books, pictures, presentations, and movies that have an associated user agent such as a document reader, editor or media player.
NOTE 2: A single document may be composed of multiple files such as the video content and closed caption text. This fact is not usually apparent to the end-user consuming the document/content.
NOTE 3: Documents require a user agent in order for the content to be presented to users. The requirements for user agents can be found in clause 11.
NOTE 4: The requirements for content that is part of software, can be found in clause 11.
NOTE 5: The success criteria set out in clause 10 are intended to harmonize with the Working Group Note [i.26] produced by the W3C's WCAG2ICT Task Force.
NOTE 6: "Void" clauses have been inserted in order to maintain alignment of the numbering in clauses 9, 10 and 11.
NOTE 7: Requirements in clause 10 also apply to documents that are protected using mechanisms such as digital signatures, encryption, password protection, and watermarks when they are presented to the user.
NOTE 8: It is best practice to provide meta data on the accessibility of the document within or separate to the document using WebSchemas/Accessibility 2.0 [i.38].
10.1 Perceivable
10.1.1 Text alternatives
10.1.1.1 Non-text content
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.1.1 Non-text Content.
NOTE: CAPTCHAs do not currently appear outside of the Web. However, if they do appear, this guidance is accurate.
10.1.2 Time-based media
10.1.2.1 Audio-only and video-only (pre-recorded)
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.2.1 Audio-only and Video-only (Prerecorded).
NOTE: The alternative can be provided directly in the document - or provided in an alternate version that meets the success criterion.
10.1.2.2 Captions (pre-recorded)
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.2.2 Captions (Prerecorded).
NOTE: The WCAG 2.1 definition of "captions" notes that "in some countries, captions are called subtitles". They are also sometimes referred to as "subtitles for the hearing impaired". Per the definition in WCAG 2.1, to meet this success criterion, whether called captions or subtitles, they would have to provide "synchronized visual and / or text alternative for both speech and non-speech audio information needed to understand the media content" where non-speech information includes "sound effects, music, laughter, speaker identification and location".
10.1.2.3 Audio description or media alternative (pre-recorded)
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.2.3 Audio Description or Media Alternative (Prerecorded).
NOTE 1: The WCAG 2.1 definition of "audio description" says that "audio description" is "Also called 'video description' and 'descriptive narration'".
NOTE 2: Secondary or alternate audio tracks are commonly used for this purpose.
10.1.2.4 Captions (live)
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.2.4 Captions (Live).
NOTE: The WCAG 2.1 definition of "captions" notes that "in some countries, captions are called subtitles". They are also sometimes referred to as "subtitles for the hearing impaired". Per the definition in WCAG 2.1, to meet this success criterion, whether called captions or subtitles, they would have to provide "synchronized visual and / or text alternative for both speech and non-speech audio information needed to understand the media content" where non-speech information includes "sound effects, music, laughter, speaker identification and location".
10.1.2.5 Audio description (pre-recorded)
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.2.5 Audio Description (Prerecorded).
NOTE 1: The WCAG 2.1 definition of "audio description" says that audio description is "Also called 'video description' and 'descriptive narration'".
NOTE 2: Secondary or alternate audio tracks are commonly used for this purpose.
10.1.3 Adaptable
10.1.3.1 Info and relationships
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.3.1 Info and Relationships.
NOTE: Where documents contain non-standard structure types (roles), it is best practice to map them to a standard structure type as a fall-back solution for the reader.
10.1.3.2 Meaningful sequence
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.3.2 Meaningful Sequence.
10.1.3.3 Sensory characteristics
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.3.3 Sensory Characteristics.
10.1.3.4 Orientation
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.3.4 Orientation.
10.1.3.5 Identify input purpose
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.3.5 Identify Input Purpose.
10.1.4 Distinguishable
10.1.4.1 Use of colour
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.1 Use of Color.
10.1.4.2 Audio control
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the success criterion in Table 10.1.
If any audio in a document plays automatically for more than 3 seconds, either a mechanism is available to pause or stop the audio, or a mechanism is available to control audio volume independently from the overall system volume level. |
NOTE 1: Since any part of a document that does not meet this success criterion can interfere with a user's ability to use the whole document, all content in the document (whether or not it is used to meet other success criteria) shall meet this success criterion. |
NOTE 2: This success criterion is identical to the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.2 Audio Control, replacing "on a Web page" with "in a document", "any content" with "any part of a document", "whole page" with "whole document", "on the Web page" with "in the document", removing "See Conformance Requirement 5: Non-Interference" and adding note 1. |
10.1.4.3 Contrast (minimum)
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.3 Contrast (Minimum).
10.1.4.4 Resize text
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.4 Resize Text.
NOTE 1: Content for which there are software players, viewers or editors with a 200 percent zoom feature would automatically meet this success criterion when used with such players, unless the content will not work with zoom.
NOTE 2: This success criterion is about the ability to allow users to enlarge the text on screen at least up to 200 % without needing to use assistive technologies. This means that the application provides some means for enlarging the text 200 % (zoom or otherwise) without loss of content or functionality or that the application works with the platform features that meet this requirement.
NOTE 3: It is best practice to use only fonts that allow for scaling without loss of quality (e.g. pixelized presentation). This applies in particular to embedded fonts.
10.1.4.5 Images of text
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.5 Images of Text.
10.1.4.6 Void
10.1.4.7 Void
10.1.4.8 Void
10.1.4.9 Void
10.1.4.10 Reflow
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the success criterion in Table 10.2.
Content can be presented without loss of information or functionality, and without requiring scrolling in two dimensions for:
Except for parts of the content which require two-dimensional layout for usage or meaning. |
NOTE 1: 320 CSS pixels is equivalent to a starting viewport width of 1 280 CSS pixels wide at 400 % zoom. For documents which are designed to scroll horizontally (e.g. with vertical text), the 256 CSS pixels is equivalent to a starting viewport height of 1 024 pixels at 400 % zoom. |
NOTE 2: Examples of content which require two-dimensional layout are images, maps, diagrams, video, games, presentations, data tables, and interfaces where it is necessary to keep toolbars in view while manipulating content. |
NOTE 3: This success criterion is identical to the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.10 Reflow replacing the original WCAG 2.1 notes with notes 1 and 2, above. |
10.1.4.11 Non-text contrast
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.11 Non-text Contrast.
10.1.4.12 Text spacing
Where ICT is a non-web document that does not have a fixed size content layout area that is essential to the information being conveyed, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.12 Text spacing.
10.1.4.13 Content on hover or focus
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.13 Content on Hover or Focus.
10.2 Operable
10.2.1 Keyboard accessible
10.2.1.1 Keyboard
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.1.1 Keyboard.
10.2.1.2 No keyboard trap
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the success criterion in Table 10.3.
If keyboard focus can be moved to a component of the document using a keyboard interface, then focus can be moved away from that component using only a keyboard interface, and, if it requires more than unmodified arrow or tab keys or other standard exit methods, the user is advised of the method for moving focus away. |
NOTE 1: Since any part of a document that does not meet this success criterion can interfere with a user's ability to use the whole document, it is necessary for all content in the document (whether or not it is used to meet other success criteria) to meet this success criterion. |
NOTE 2: Standard exit methods may vary by platform. For example, on many desktop platforms, the Escape key is a standard method for exiting. |
NOTE 3: This success criterion is identical to the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.1.2 No Keyboard Trap replacing "page" and "Web page" with "document", removing "See Conformance Requirement 5: Non-Interference" and with the addition of note 2 above and with note 1 above re-drafted to avoid the use of the word "must". |
10.2.1.3 Void
10.2.1.4 Character key shortcuts
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.1.4 Character Key Shortcuts.
10.2.2 Enough time
10.2.2.1 Timing adjustable
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the success criterion in Table 10.4.
For each time limit that is set by the document, at least one of the following is true:
|
NOTE 1: This success criterion helps ensure that users can complete tasks without unexpected changes in content or context that are a result of a time limit. This success criterion should be considered in conjunction with WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.2.1, which puts limits on changes of content or context as a result of user action. |
NOTE 2: This success criterion is identical to the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.2.1 Timing Adjustable replacing "the content" with "documents" and with the words "WCAG 2.1" added before the word "Success Criterion" in note 1 above. |
10.2.2.2 Pause, stop, hide
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the success criterion in Table 10.5.
For moving, blinking, scrolling, or auto-updating information, all of the following are true:
|
NOTE 1: For requirements related to flickering or flashing content, refer to WCAG 2.1 Guideline 2.3. |
NOTE 2: Since any part of a document that does not meet this success criterion can interfere with a user's ability to use the whole document, it is necessary for all content in the document (whether it is used to meet other success criteria or not) to meet this success criterion. |
NOTE 3: Content that is updated periodically by software or that is streamed to the user agent is not required to preserve or present information that is generated or received between the initiation of the pause and resuming presentation, as this may not be technically possible, and in many situations could be misleading to do so. |
NOTE 4: An animation that occurs as part of a preload phase or similar situation can be considered essential if interaction cannot occur during that phase for all users and if not indicating progress could confuse users or cause them to think that content was frozen or broken. |
NOTE 5: This success criterion is identical to the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.2.2 Pause, Stop, Hide replacing "page" and "Web page" with "document", removing "See Conformance Requirement 5: Non-Interference" in note 2 of the success criterion, with the words "WCAG 2.1" added before the word "Guideline" in note 1 above and with note 2 above re-drafted to avoid the use of the word "must". |
10.2.3 Seizures and physical reactions
10.2.3.1 Three flashes or below threshold
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the success criterion in Table 10.6.
Documents do not contain anything that flashes more than three times in any one second period, or the flash is below the general flash and red flash thresholds. |
NOTE 1: Since any part of a document that does not meet this success criterion can interfere with a user's ability to use the whole document, it is necessary for all content in the document (whether it is used to meet other success criteria or not) to meet this success criterion. |
NOTE 2: This success criterion is identical to the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.3.1 Three Flashes or Below Threshold replacing "Web pages" with "documents", "the whole page" with "the whole document", "the Web page" with "the document" and removing "See Conformance Requirement 5: Non-Interference" and with note 1 above re-drafted to avoid the use of the word "must". |
10.2.4 Navigable
10.2.4.1 Void
NOTE 1: The related web page requirement "Bypass blocks" does not apply to single documents, but to a specific definition of "sets of documents" that are rare.
NOTE 2: Although not a requirement, the ability to bypass blocks of content that are repeated within documents is generally considered best practice and addresses user needs.
10.2.4.2 Document titled
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the success criterion in Table 10.7.
Documents have titles that describe topic or purpose. |
NOTE 1: The name of a document (e.g. document, media file) is a sufficient title if it describes the topic or purpose. |
NOTE 2: This success criterion is identical to the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.4.2 Page Titled replacing "Web pages" with "documents" and with the addition of note 1 above. |
10.2.4.3 Focus Order
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the success criterion in Table 10.8.
If a document can be navigated sequentially and the navigation sequences affect meaning or operation, focusable components receive focus in an order that preserves meaning and operability. |
NOTE: This success criterion is identical to the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.4.3 Focus Order replacing "Web page" with "document". |
10.2.4.4 Link purpose (in context)
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.4.4 Link Purpose (In Context).
10.2.4.5 Void
NOTE: The related web page requirement "Multiple ways" does not apply to single documents, but to a specific definition of "sets of documents" that are rare.
10.2.4.6 Headings and labels
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.4.6 Headings and Labels.
10.2.4.7 Focus visible
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.4.7 Focus Visible.
10.2.5 Input modalities
10.2.5.1 Pointer gestures
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the success criterion in Table 10.9.
All functionality that uses multipoint or path-based gestures for operation can be operated with a single pointer without a path-based gesture, unless a multipoint or path-based gesture is essential. |
NOTE 1: This requirement applies to documents that interpret pointer actions (i.e. this does not apply to actions that are required to operate the user agent or assistive technology). |
NOTE 2: This success criterion is identical to the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.5.1 Pointer Gestures replacing the original WCAG 2.1 note with note 1 above. |
10.2.5.2 Pointer cancellation
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the success criterion in Table 10.10.
For functionality that can be operated using a single pointer, at least one of the following is true:
|
NOTE 1: Functions that emulate a keyboard or numeric keypad key press are considered essential. |
NOTE 2: This requirement applies to a document that interprets pointer actions (i.e. this does not apply to actions that are required to operate the user agent or assistive technology). |
NOTE 3: This success criterion is identical to the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.5.2 Pointer Cancellation replacing the original WCAG 2.1 note with notes 1 and 2 above. |
10.2.5.3 Label in name
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.5.3 Label in Name.
10.2.5.4 Motion actuation
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.5.4 Motion Actuation.
10.3 Understandable
10.3.1 Readable
10.3.1.1 Language of document
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the success criterion in Table 10.11.
The default human language of each document can be programmatically determined. |
NOTE: This success criterion is identical to the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.1.1 Language of Page replacing "web page" with "document". |
10.3.1.2 Language of parts
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the success criterion in Table 10.12.
The human language of each passage or phrase in the document can be programmatically determined except for proper names, technical terms, words of indeterminate language, and words or phrases that have become part of the vernacular of the immediately surrounding text. |
NOTE 1: There are some document technologies where there is no assistive technology supported method for marking the language for the different passages or phrases in the document, and it would not be possible to meet this success criterion with those technologies. |
NOTE 2: Inheritance is one common method. For example a document provides the language that it is using and it can be assumed that all of the text or user interface elements within that document will be using the same language unless it is indicated. |
NOTE 3: This success criterion is identical to the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.1.2 Language of Parts replacing "content" with "document" and with the addition of notes 1 and 2 above. |
10.3.2 Predictable
10.3.2.1 On focus
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.2.1 On Focus.
NOTE: Some compound documents and their user agents are designed to provide significantly different viewing and editing functionality depending upon what portion of the compound document is being interacted with (e.g. a presentation that contains an embedded spreadsheet, where the menus and toolbars of the user agent change depending upon whether the user is interacting with the presentation content, or the embedded spreadsheet content). If the user uses a mechanism other than putting focus on that portion of the compound document with which they mean to interact (e.g. by a menu choice or special keyboard gesture), any resulting change of context would not be subject to this success criterion because it was not caused by a change of focus.
10.3.2.2 On input
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.2.2 On Input.
10.3.2.3 Void
NOTE: The related web page requirement "Consistent navigation" does not apply to single documents, but to a specific definition of "sets of documents" that are rare.
10.3.2.4 Void
NOTE: The related web page requirement "Consistent identification" does not apply to single documents, but to a specific definition of "sets of documents" that are rare.
10.3.3 Input assistance
10.3.3.1 Error identification
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.3.1 Error Identification.
10.3.3.2 Labels or instructions
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.3.2 Labels or Instructions.
10.3.3.3 Error suggestion
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.3.3 Error Suggestion.
10.3.3.4 Error prevention (legal, financial, data)
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the success criterion in Table 10.13.
For documents that cause legal commitments or financial transactions for the user to occur, that modify or delete user-controllable data in data storage systems, or that submit user test responses, at least one of the following is true:
|
NOTE: This success criterion is identical to the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.3.4 Error Prevention (Legal, Financial, Data) replacing "web pages" with "documents". |
10.4 Robust
10.4.1 Compatible
10.4.1.1 Parsing
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the success criterion in Table 10.14.
For documents that use markup languages, in such a way that the markup is separately exposed and available to assistive technologies and accessibility features of software or to a user-selectable user agent, elements have complete start and end tags, elements are nested according to their specifications, elements do not contain duplicate attributes, and any IDs are unique, except where the specifications allow these features. |
NOTE 1: Start and end tags that are missing a critical character in their formation, such as a closing angle bracket or a mismatched attribute value quotation mark are not complete. |
NOTE 2: Markup is not always available to assistive technology or to user selectable user agents such as browsers. In such cases, conformance to this [requirement] would have no impact on accessibility as it can for web content where it is exposed. |
NOTE 3: Examples of markup that is separately exposed and available to assistive technologies and to user agents include but are not limited to: documents encoded in HTML, ODF, and OOXML. In these examples, the markup can be parsed entirely in two ways: (a) by assistive technologies which may directly open the document, (b) by assistive technologies using DOM APIs of user agents for these document formats. |
NOTE 4: This success criterion is identical to the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 4.1.1 Parsing replacing "In content implemented using markup languages" with "For documents that use markup languages, in such a way that the markup is separately exposed and available to assistive technologies and accessibility features of software or to a user-selectable user agent" with the addition of notes 2 and 3 above. |
10.4.1.2 Name, role, value
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy the success criterion in Table 10.15.
For all user interface components (including but not limited to: form elements, links and components generated by scripts), the name and role can be programmatically determined; states, properties, and values that can be set by the user can be programmatically set; and notification of changes to these items is available to user agents, including assistive technologies. |
NOTE 1: This success criterion is primarily for software developers who develop or use custom user interface components. Standard user interface components on most accessibility-supported platforms already meet this success criterion when used according to specification. |
NOTE 2: For document formats that support interoperability with assistive technology, standard user interface components often meet this success criterion when used according to the general design and accessibility guidance for the document format. |
NOTE 3: This success criterion is identical to the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 4.1.2 Name, Role, Value replacing the original WCAG 2.1 note with: "This success criterion is primarily for software developers who develop or use custom user interface components. For example, standard user interface components on most accessibility-supported platforms already meet this success criterion when used according to specification." and with the addition of note 2 above. |
10.4.1.3 Status messages
Where ICT is a non-web document, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 4.1.3 Status Messages.
10.5 Caption positioning
Where ICT is a non-web document that contains synchronized media with captions, the captions should not obscure relevant information in the synchronized media.
10.6 Audio description timing
Where ICT is a non-web document that contains synchronized media with audio description, the audio description should not interfere with relevant audio information in the synchronized media.
11. Software
11.0 General (informative)
This clause provides requirements for:
- platform software;
- software that provides a user interface including content that is in the software;
- authoring tools;
- software that operates as assistive technology;
- mobile applications.
NOTE 1: User agents are examples of software that provide a user interface. They retrieve, render and facilitate end user interaction with authored content. User agents play a necessary role in the accessibility of authored content rendered in the user interface. UAAG 2.0 [i.33] provides additional advice for those who are creating user agents and want to increase functionality when rendering authored content in an accessible way.
NOTE 2: The requirements for Web content, including software that is Web content, can be found in clause 9.
NOTE 3: The requirements for documents, that may be presented by user agents, can be found in clause 10.
NOTE 4: Although the accessibility of command line interfaces is not dealt with in the present document, accessibility may be achieved by context specific requirements, some of which may be found in clauses 5 or 11.
Requirements in clauses 11.1 to 11.5 apply to software:
- that is not a web page;
- not embedded in web pages nor used in the rendering or functioning of the page.
Clause 9 provides requirements for software that is in web pages or that is embedded in web pages and that is used in the rendering or that is intended to be rendered together with the web page in which it is embedded.
Some requirements in clauses 11.1 to 11.5 have different versions for open or closed functionality. In those cases, the corresponding clause will be divided into two subclauses.
The success criteria set out in clauses 11.1 to 11.5 are intended to harmonize with the W3C Working Group Note [i.26] produced by the W3C's WCAG2ICT Task Force.
NOTE 5: Software that provides a user interface includes its own content. Some examples of content in software include: the controls and text displayed in a menu bar of a graphical user interface application, images that appear in a toolbar, prompts spoken in an auditory user interface, other user interaction controls, and other text, graphics or material that is not loaded from outside the software.
NOTE 6: "Void" clauses have been inserted in order to maintain alignment of the numbering in clauses 9, 10 and 11.
11.1 Perceivable
11.1.1 Text alternatives
11.1.1.1 Non-text content
11.1.1.1.1 Non-text content (open functionality)
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface and that supports access to assistive technologies for screen reading, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.1.1 Non-text Content.
NOTE: CAPTCHAs do not currently appear outside of the Web. However, if they do appear, this guidance is accurate.
11.1.1.1.2 Non-text content (closed functionality)
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface which is closed to assistive technologies for screen reading, it shall meet requirement 5.1.3.6 (Speech output for non-text content).
11.1.2 Time-based media
11.1.2.1 Audio-only and video-only (pre-recorded)
11.1.2.1.1 Audio-only and video-only (pre-recorded - open functionality)
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface and that supports access to assistive technologies for screen reading and where pre-recorded auditory information is not needed to enable the use of closed functions of ICT, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.2.1 Audio-only and Video-only (Prerecorded).
NOTE: The alternative can be provided directly in the software - or provided in an alternate version that meets the success criterion.
11.1.2.1.2 Audio-only and video-only (pre-recorded - closed functionality)
11.1.2.1.2.1 Pre-recorded audio-only (closed functionality)
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface which is closed to assistive technologies for screen reading and where pre-recorded auditory information is needed to enable the use of closed functions of ICT, the functionality of software that provides a user interface shall meet requirement 5.1.5 (Visual output for auditory information).
11.1.2.1.2.2 Pre-recorded video-only (closed functionality)
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface which is closed to assistive technologies for screen reading, it shall meet requirement 5.1.3.7 (Speech output for video information).
11.1.2.2 Captions (pre-recorded)
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.2.2 Captions (Prerecorded).
NOTE: The WCAG 2.1 definition of "captions" notes that "in some countries, captions are called subtitles". They are also sometimes referred to as "subtitles for the hearing impaired". Per the definition in WCAG 2.1, to meet this success criterion, whether called captions or subtitles, they would have to provide "synchronized visual and / or text alternative for both speech and non-speech audio information needed to understand the media content" where non-speech information includes "sound effects, music, laughter, speaker identification and location".
11.1.2.3 Audio description or media alternative (pre-recorded)
11.1.2.3.1 Audio description or media alternative (pre-recorded - open functionality)
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface and that supports access to assistive technologies for screen reading, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.2.3 Audio Description or Media Alternative (Prerecorded).
NOTE 1: The WCAG 2.1 definition of "audio description" says that "audio description" is "also called 'video description' and 'descriptive narration'".
NOTE 2: Secondary or alternate audio tracks are commonly used for this purpose.
11.1.2.3.2 Audio description or media alternative (pre-recorded - closed functionality)
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface which is closed to assistive technologies for screen reading, it shall meet requirement 5.1.3.7 (Speech output for video information).
11.1.2.4 Captions (live)
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.2.4 Captions (Live).
NOTE: The WCAG 2.1 definition of "captions" notes that "in some countries, captions are called subtitles". They are also sometimes referred to as "subtitles for the hearing impaired". Per the definition in WCAG 2.1, to meet this success criterion, whether called captions or subtitles, they would have to provide "synchronized visual and / or text alternative for both speech and non-speech audio information needed to understand the media content" where non-speech information includes "sound effects, music, laughter, speaker identification and location".
11.1.2.5 Audio description (pre-recorded)
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.2.5 Audio Description (Prerecorded).
NOTE 1: The WCAG 2.1 definition of "audio description" says that audio description is "Also called 'video description' and 'descriptive narration'".
NOTE 2: Secondary or alternate audio tracks are commonly used for this purpose.
11.1.3 Adaptable
11.1.3.1 Info and relationships
11.1.3.1.1 Info and relationships (open functionality)
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface and that supports access to assistive technologies for screen reading, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.3.1 Info and Relationships.
NOTE: In software, programmatic determinability is best achieved through the use of accessibility services provided by platform software to enable interoperability between software and assistive technologies and accessibility features of software. (see clause 11.5 Interoperability with assistive technology).
11.1.3.1.2 Info and relationships (closed functionality)
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface which is closed to assistive technologies for screen reading and where information is displayed on the screen, the ICT should provide auditory information that allows the user to correlate the audio with the information displayed on the screen.
NOTE 1: Many people who are legally blind still have visual ability, and use aspects of the visual display even if it cannot be fully comprehended. An audio alternative that is both complete and complementary includes all visual information such as focus or highlighting, so that the audio can be correlated with information that is visible on the screen at any point in time.
NOTE 2: Examples of auditory information that allows the user to correlate the audio with the information displayed on the screen include structure and relationships conveyed through presentation.
11.1.3.2 Meaningful sequence
11.1.3.2.1 Meaningful sequence (open functionality)
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface and that supports access to assistive technologies for screen reading, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.3.2 Meaningful Sequence.
11.1.3.2.2 Meaningful sequence (closed functionality)
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface which is closed to assistive technologies for screen reading and where information is displayed on the screen, the ICT should provide auditory information that allows the user to correlate the audio with the information displayed on the screen.
NOTE 1: Many people who are legally blind still have visual ability, and use aspects of the visual display even if it cannot be fully comprehended. An audio alternative that is both complete and complementary includes all visual information such as focus or highlighting, so that the audio can be correlated with information that is visible on the screen at any point in time.
NOTE 2: Examples of auditory information that allows the user to correlate the audio with the information displayed on the screen include structure and relationships conveyed through presentation.
11.1.3.3 Sensory characteristics
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.3.3 Sensory Characteristics.
11.1.3.4 Orientation
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.3.4 Orientation.
11.1.3.5 Identify input purpose
11.1.3.5.1 Identify input purpose (open functionality)
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface and supports access to assistive technologies for screen reading, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.3.5 Identify Input Purpose.
11.1.3.5.2 Identify input purpose (closed functionality)
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface and is closed to assistive technologies, in at least one mode of operation the ICT shall present to the user, in an audio form, the purpose of each input field collecting information about the user when the input field serves a purpose identified in the WCAG 2.1 Input Purposes for User Interface Components section.
11.1.4 Distinguishable
11.1.4.1 Use of colour
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.1 Use of Color.
11.1.4.2 Audio control
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface, it shall satisfy the success criterion in Table 11.1.
If any audio in a software plays automatically for more than 3 seconds, either a mechanism is available to pause or stop the audio, or a mechanism is available to control audio volume independently from the overall system volume level. |
NOTE 1: Since any part of a software that does not meet this success criterion can interfere with a user's ability to use the whole software, all content in the software (whether or not it is used to meet other success criteria) shall meet this success criterion. |
NOTE 2: This success criterion is identical to the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.2 Audio Control replacing "on a Web page" with "in a software", "any content" with "any part of a software", "whole page" with "whole software", "on the Web page" with "in the software", removing "See Conformance Requirement 5: Non-Interference" and adding note 1. |
11.1.4.3 Contrast (minimum)
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.3 Contrast (Minimum).
11.1.4.4 Resize text
11.1.4.4.1 Resize text (open functionality)
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface and that supports access to enlargement features of platform or assistive technology, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.4 Resize Text.
NOTE 1: Content for which there are software players, viewers or editors with a 200 percent zoom feature would automatically meet this success criterion when used with such players, unless the content will not work with zoom.
NOTE 2: This success criterion is about the ability to allow users to enlarge the text on screen at least up to 200 % without needing to use assistive technologies. This means that the application provides some means for enlarging the text 200 % (zoom or otherwise) without loss of content or functionality or that the application works with the platform features that meet this requirement.
11.1.4.4.2 Resize text (closed functionality)
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface which is not able to access the enlargement features of platform or assistive technology, it shall meet requirement 5.1.4 (Functionality closed to text enlargement).
NOTE: Because the text rendering support in a closed environment may be more limited than the support found in user agents for the Web, meeting the present clause in a closed environment may place a much heavier burden on the content author.
11.1.4.5 Images of text
11.1.4.5.1 Images of text (open functionality)
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface and that supports access to assistive technologies for screen reading, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.5 Images of Text.
11.1.4.5.2 Images oz text (closed functionality)
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface which is closed to assistive technologies for screen reading, it shall meet requirement 5.1.3.6 (Speech output for non-text content).
11.1.4.6 Void
11.1.4.7 Void
11.1.4.8 Void
11.1.4.9 Void
11.1.4.10 Reflow
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface it shall satisfy the success criterion in Table 11.2.
Content can be presented without loss of information or functionality, and without requiring scrolling in two dimensions for:
Except for parts of the content which require two-dimensional layout for usage or meaning. |
NOTE 1: 320 CSS pixels is equivalent to a starting viewport width of 1 280 CSS pixels wide at 400 % zoom. For non-web software which are designed to scroll horizontally (e.g. with vertical text), the 256 CSS pixels is equivalent to a starting viewport height of 1 024 px at 400 % zoom. |
NOTE 2: Examples of content which require two-dimensional layout are images, maps, diagrams, video, games, presentations, data tables, and interfaces where it is necessary to keep toolbars in view while manipulating content. |
NOTE 3: This success criterion is identical to the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.10 Reflow replacing the original WCAG 2.1 notes with notes 1 and 2, above. |
11.1.4.11 Non-text contrast
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.11 Non-text Contrast.
11.1.4.12 Text spacing
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface and that does not have a fixed size content layout area that is essential to the information being conveyed, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.12 Text spacing.
11.1.4.13 Content on hover or focus
Where ICT is a non-web software that provides a user interface, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.13 Content on hover or focus.
11.2 Operable
11.2.1 Keyboard accessible
11.2.1.1 Keyboard
11.2.1.1.1 Keyboard (open functionality)
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface and that supports access to keyboards or a keyboard interface, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.1.1 Keyboard.
NOTE: This does not imply that software is required to directly support a keyboard or "keyboard interface". Nor does it imply that software is required to provide a soft keyboard. Underlying platform software may provide device independent input services to applications that enable operation via a keyboard. Software that supports operation via such platform device independent services would be operable by a keyboard and would comply.
11.2.1.1.2 Keyboard (closed functionality)
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface which is closed to keyboards or keyboard interface, it shall meet requirement 5.1.6.1 (Operation without keyboard interface: Closed functionality).
11.2.1.2 No keyboard trap
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface, it shall satisfy the success criterion in Table 11.3.
If keyboard focus can be moved to a component of the software using a keyboard interface, then focus can be moved away from that component using only a keyboard interface, and, if it requires more than unmodified arrow or tab keys or other standard exit methods, the user is advised of the method for moving focus away. |
NOTE 1: Since any part of a software that does not meet this success criterion can interfere with a user's ability to use the whole software, it is necessary for all content in the software (whether or not it is used to meet other success criteria) to meet this success criterion. |
NOTE 2: Standard exit methods may vary by platform. For example, on many desktop platforms, the Escape key is a standard method for exiting. |
NOTE 3: This success criterion is identical to the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.1.2 No Keyboard Trap replacing "content", "page" and "Web page" with "software", removing "See Conformance Requirement 5: Non-Interference" and with the addition of note 2 above and with note 1 above re-drafted to avoid the use of the word "shall". |
11.2.1.3 Void
11.2.1.4 Character key shortcuts
11.2.1.4.1 Character key shortcuts (open functionality)
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.1.4 Character Key Shortcuts.
11.2.1.4.2 Character key shortcuts (closed functionality)
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface which is closed to keyboards or keyboard interface, it shall meet requirement 5.1.6.1 (Operation without keyboard interface: Closed functionality).
11.2.2 Enough time
11.2.2.1 Timing adjustable
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface, it shall satisfy the success criterion in Table 11.4.
For each time limit that is set by the software, at least one of the following is true:
|
NOTE 1: This success criterion helps ensure that users can complete tasks without unexpected changes in content or context that are a result of a time limit. This success criterion should be considered in conjunction with WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.2.1, which puts limits on changes of content or context as a result of user action. |
NOTE 2: This success criterion is identical to the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.2.1 Timing Adjustable replacing "the content" with "software" and with the words "WCAG 2.1" added before the word "Success Criterion" in note 1 above. |
11.2.2.2 Pause, stop, hide
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface, it shall satisfy the success criterion in Table 11.5.
For moving, blinking, scrolling, or auto-updating information, all of the following are true:
|
NOTE 1: For requirements related to flickering or flashing content, refer to WCAG 2.1 Guideline 2.3. |
NOTE 2: This success criteria is applicable to all content in the software (whether or not there is an alternate accessible mode of operation of the software) since any part of a software that does not meet this success criterion can interfere with a user's ability to use the whole software (including a user interface element that enables the user to activate the alternate accessible mode of operation). |
NOTE 3: Content that is updated periodically by software or that is streamed to the user agent is not required to preserve or present information that is generated or received between the initiation of the pause and resuming presentation, as this may not be technically possible, and in many situations could be misleading to do so. |
NOTE 4: An animation that occurs as part of a preload phase or similar situation can be considered essential if interaction cannot occur during that phase for all users and if not indicating progress could confuse users or cause them to think that content was frozen or broken. |
NOTE 5: This is to be applied to all content. Any content, whether informative or decorative, that is updated automatically, blinks, or moves may create an accessibility barrier. |
NOTE 6: This success criterion is identical to the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.2.2 Pause, Stop, Hide replacing "page" and "Web page" with "software", removing "See Conformance Requirement 5: Non-Interference" in note 2 of the success criterion, with the words "WCAG 2.1" added before the word "Guideline" in note 1 above, with note 2 above re-drafted to avoid the use of the word "must" and with the addition of note 5 above. |
11.2.3 Seizures and physical reactions
11.2.3.1 Three flashes or below threshold
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface, it shall satisfy the success criterion in Table 11.6.
Software does not contain anything that flashes more than three times in any one second period, or the flash is below the general flash and red flash thresholds. |
NOTE 1: This success criteria is applicable to all content in the software (whether or not there is an alternate accessible mode of operation of the software) since any part of a software that does not meet this success criterion can interfere with a user's ability to use the whole software (including a user interface element that enables the user to activate the alternate accessible mode of operation). |
NOTE 2: This success criterion is identical to the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.3.1 Three Flashes or Below Threshold replacing "Web pages" with "software", "the whole page" with "the whole software", "the Web page" with "the software" and removing "See Conformance Requirement 5: Non-Interference" and with note 1 above re-drafted to avoid the use of the word "must". |
11.2.4 Navigable
11.2.4.1 Void
NOTE 1: The related web page requirement "Bypass blocks" does not apply to single software programs, but to a specific definition of "sets of software programs" that are extremely rare.
NOTE 2: Although not a requirement, it is generally considered best practice, and to address user needs, to be able to bypass blocks of content that are repeated within software.
11.2.4.2 Void
NOTE 1: The related web page requirement "Page titled" does not apply to single software programs, but to a specific definition of "sets of software programs" that are extremely rare.
NOTE 2: Although the name of a software product could be a sufficient title if it describes the topic or purpose, software names are trademarked and trademark names cannot by law be descriptive names. It is not practical to make software names both unique and descriptive.
11.2.4.3 Focus order
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface, it shall satisfy the success criterion in Table 11.7.
If software can be navigated sequentially and the navigation sequences affect meaning or operation, focusable components receive focus in an order that preserves meaning and operability. |
NOTE: This success criterion is identical to the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.4.3 Focus order replacing "Web page" with "software". |
11.2.4.4 Link purpose (in context)
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.4.4 Link Purpose (In Context).
11.2.4.5 Void
NOTE: The related web page requirement for "Multiple ways" applies to "Sets" of web pages. In software, the equivalent to "sets of web pages" would be "sets of software", but these are extremely rare and an equivalent is not included in this clause on software requirements.
11.2.4.6 Headings and labels
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.4.6 Headings and Labels.
NOTE: In software, headings and labels are used to describe sections of content and controls respectively. In some cases it may be unclear whether a piece of static text is a heading or a label. But whether treated as a label or a heading, the requirement is the same: that if they are present they describe the topic or purpose of the item(s) they are associated with.
11.2.4.7 Focus visible
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.4.7 Focus Visible.
11.2.5 Input modalities
11.2.5.1 Pointer gestures
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface, it shall satisfy the success criterion in Table 11.8.
All functionality that uses multipoint or path-based gestures for operation can be operated with a single pointer without a path-based gesture, unless a multipoint or path-based gesture is essential. |
NOTE 1: This requirement applies to non-web software that interprets pointer actions (i.e. this does not apply to actions that are required to operate the user agent or assistive technology). |
NOTE 2: This success criterion is identical to the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.5.1 Pointer Gestures replacing the original WCAG 2.1 note with note 1 above. |
11.2.5.2 Pointer cancellation
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface, it shall satisfy the success criterion in Table 11.9.
For functionality that can be operated using a single pointer, at least one of the following is true:
|
NOTE 1: Functions that emulate a keyboard or numeric keypad key press are considered essential. |
NOTE 2: This requirement applies to non-web software that interprets pointer actions (i.e. this does not apply to actions that are required to operate the user agent or assistive technology). |
NOTE 3: This success criterion is identical to the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.5.2 Pointer Cancellation replacing the original WCAG 2.1 note with notes 1 and 2 above. |
11.2.5.3 Label in name
11.2.5.3.1 Label in name (open functionality)
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.5.3 Label in Name.
11.2.5.3.2 Label in name (closed functionality)
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface which is closed to assistive technologies for screen reading, it should meet requirement 5.1.3.3 (Auditory output correlation).
11.2.5.4 Motion actuation
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.5.4 Motion Actuation.
11.3 Understandable
11.3.1 Readable
11.3.1.1 Language of software
11.3.1.1.1 Language of software (open functionality)
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface and that supports access to assistive technologies for screen reading, it shall satisfy the success criterion in Table 11.10.
The default human language of software can be programmatically determined. |
NOTE 1: Where software platforms provide a "locale / language" setting, applications that use that setting and render their interface in that "locale / language" would comply with this success criterion. Applications that do not use the platform "locale / language" setting but instead use an accessibility-supported method for exposing the human language of the software would also comply with this success criterion. Applications implemented in technologies where assistive technologies cannot determine the human language and that do not support the platform "locale / language" setting may not be able to meet this success criterion in that locale / language. |
NOTE 2: This success criterion is identical to the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.1.1 Language of page, replacing "each web page" with "software" and with the addition of note 1 above. |
11.3.1.1.2 Language of software (closed functionality)
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface which is closed to assistive technologies for screen reading, it shall meet requirement 5.1.3.14 (Spoken languages).
11.3.1.2 Void
NOTE: To apply the related web page requirement for "Language of parts" to software would require the marking-up of all text in all locations within the software. This would be impossible so an equivalent is not included in this clause on software requirements.
11.3.2 Predictable
11.3.2.1 On focus
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.2.1 On Focus.
NOTE: Some compound documents and their user agents are designed to provide significantly different viewing and editing functionality depending upon what portion of the compound document is being interacted with (e.g. a presentation that contains an embedded spreadsheet, where the menus and toolbars of the user agent change depending upon whether the user is interacting with the presentation content, or the embedded spreadsheet content). If the user uses a mechanism other than putting focus on that portion of the compound document with which they mean to interact (e.g. by a menu choice or special keyboard gesture), any resulting change of context would not be subject to this success criterion because it was not caused by a change of focus.
11.3.2.2 On input
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.2.2 On Input.
11.3.2.3 Void
NOTE: The related web page requirement for "Consistent navigation" applies to "Sets" of web pages. While consistency within software is desirable, "sets of software" in the same sense as "sets of web pages", are extremely rare and an equivalent is not included in this clause on software requirements.
11.3.2.4 Void
NOTE: The related web page requirement for "Consistent identification" applies to "Sets" of web pages. In software, the equivalent to "sets of web pages" would be "sets of software", but these are extremely rare and an equivalent is not included in this clause on software requirements.
11.3.3 Input assistance
11.3.3.1 Error identification
11.3.3.1.1 Error identification (open functionality)
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface and that supports access to assistive technologies for screen reading, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.3.1 Error Identification.
11.3.3.1.2 Error Identification (closed functionality)
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface which is closed to assistive technologies for screen reading, it shall meet requirement 5.1.3.15 (Non-visual error identification).
11.3.3.2 Labels or instructions
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.3.2 Labels or Instructions.
11.3.3.3 Error suggestion
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface, it shall satisfy the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.3.3 Error Suggestion.
11.3.3.4 Error prevention (legal, financial, data)
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface, it shall satisfy the success criterion in Table 11.11.
For software that cause legal commitments or financial transactions for the user to occur, that modify or delete user-controllable data in data storage systems, or that submit user test responses, at least one of the following is true:
|
NOTE: This success criterion is identical to the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.3.4 Error Prevention (Legal, Financial, Data) replacing "web pages" with "software". |
11.4 Robust
11.4.1 Compatible
11.4.1.1 Parsing
11.4.1.1.1 Parsing (open functionality)
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface and that supports access to any assistive technologies, it shall satisfy the success criterion in Table 11.12.
For software that uses markup languages, in such a way that the markup is separately exposed and available to assistive technologies and accessibility features of software or to a user-selectable user agent, elements have complete start and end tags, elements are nested according to their specifications, elements do not contain duplicate attributes, and any IDs are unique, except where the specifications allow these features. |
NOTE 1: Start and end tags that are missing a critical character in their formation, such as a closing angle bracket or a mismatched attribute value quotation mark are not complete. NOTE 2: Markup is not always available to assistive technology or to user selectable user agents such as browsers. In such cases, conformance to this [requirement] would have no impact on accessibility as it can for web content where it is exposed. NOTE 3: Examples of markup that is separately exposed and available to assistive technologies and to user agents include but are not limited to: documents encoded in HTML, ODF, and OOXML. In these examples, the markup can be parsed entirely in two ways: (a) by assistive technologies which may directly open the document, (b) by assistive technologies using DOM APIs of user agents for these document formats. NOTE 4: Examples of markup used internally for persistence of the software user interface that are never exposed to assistive technology include but are not limited to: XUL, and FXML. In these examples assistive technology only interacts with the user interface of generated software. NOTE 5: This success criterion is identical to the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 4.1.1 Parsing replacing "In content implemented using markup languages" with "For software that uses markup languages, in such a way that the markup is separately exposed and available to assistive technologies and accessibility features of software or to a user-selectable user agent" with the addition of notes 2, 3 and 4 above. |
11.4.1.1.2 Parsing (closed functionality)
Not applicable.
NOTE: Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface which is closed to all assistive technology it does not have to meet the "Parsing" success criterion in Table 11.12 because the intent of this success criterion is to provide consistency so that different user agents or assistive technologies will yield the same result.
11.4.1.2 Name, role, value
11.4.1.2.1 Name, role, value (open functionality)
Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface and that supports access to any assistive technologies, it shall satisfy the success criterion in Table 11.13.
For all user interface components (including but not limited to: form elements, links and components generated by scripts), the name and role can be programmatically determined; states, properties, and values that can be set by the user can be programmatically set; and notification of changes to these items is available to user agents, including assistive technologies. |
NOTE 1: This success criterion is primarily for software developers who develop or use custom user interface components. Standard user interface components on most accessibility-supported platforms already meet this success criterion when used according to specification. NOTE 2: For conforming to this success criterion, it is usually best practice for software user interfaces to use the accessibility services provided by platform software. These accessibility services enable interoperability between software user interfaces and both assistive technologies and accessibility features of software in standardised ways. Most platform accessibility services go beyond programmatic exposure of name and role, and programmatic setting of states, properties and values (and notification of same), and specify additional information that could or should be exposed and / or set (for instance, a list of the available actions for a given user interface component, and a means to programmatically execute one of the listed actions). NOTE 3: This success criterion is identical to the WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 4.1.2 Name, Role, Value replacing the original WCAG 2.1 note with: "This success criterion is primarily for software developers who develop or use custom user interface components. Standard user interface components on most accessibility-supported platforms already meet this success criterion when used according to specification." and the addition of note 2 above. |
11.4.1.2.2 Name, role, value (closed functionality)
Not applicable.
NOTE: Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface which is closed to all assistive technology it does not have to meet the "Name, role, value" success criterion in Table 11.13 because this success criterion requires information in a programmatically determinable form.
11.4.1.3 Status messages
11.4.1.3.1 Status messages (open functionality)
Where ICT is non-web software, it shall satisfy WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 4.1.3 Status Messages.
11.4.1.3.2 Status messages (closed functionality)
Not applicable.
11.5 Interoperability with assistive technology
11.5.1 Closed functionality
Where the closed functionality of software conforms to clause 5.1 (Closed functionality) it shall not be required to conform with clause 11.5.2 to clause 11.5.2.17.
11.5.2 Accessibility services
11.5.2.1 Platform accessibility service support for software that provides a user interface
Platform software shall provide a set of documented platform services that enable software that provides a user interface running on the platform software to interoperate with assistive technology.
Where a user interface concept corresponding to one of the clauses 11.5.2.5 to 11.5.2.17 is supported within the software environment, the platform software should support that requirement. For example, selection attributes from clause 11.5.2.14 (Modification of focus and selection attributes) may not exist in environments that do not allow selection, which is most commonly associated with copy and paste.
NOTE 1: These define the minimum functionality of software providing user interfaces when using platform services.
NOTE 2: In some platforms these services may be called accessibility services, but in some other platforms these services may be provided as part of the user interface services.
NOTE 3: User interface services that provide accessibility support by default are considered to be part of the services provided to conform to this clause (e.g. the service for creating a new user interface element provides role, state, boundary, name and description).
NOTE 4: To comply with this requirement the platform software can provide its own set of services or expose the services provided by its underlying platform layers, if those services conform to this requirement.
NOTE 5: Within specific programming environments, the technical attributes associated with the user interface properties described in clauses 11.5.2.5 to 11.5.2.17 might have different names than those used within the clauses.
11.5.2.2 Platform accessibility service support for assistive technologies
Platform software shall provide a set of documented platform accessibility services that enable assistive technology to interoperate with software that provides a user interface running on the platform software.
Where a user interface concept corresponding to one of the clauses 11.5.2.5 to 11.5.2.17 is supported within the software environment, the platform software should support that requirement. For example, selection attributes from clause 11.5.2.14 (Modification of focus and selection attributes) may not exist in environments that do not allow selection, which is most commonly associated with copy and paste.
NOTE 1: These define the minimum functionality available to assistive technologies when using platform services.
NOTE 2: The definition of platform in clause 3.1 applies to software that provides services to other software, including but not limited to, operating systems, web browsers, virtual machines.
NOTE 3: In some platforms these services may be called accessibility services, but in some other platforms these services may be provided as part of the user interface services.
NOTE 4: Typically these services belong to the same set of services that are described in clause 11.5.2.1.
NOTE 5: To comply with this requirement the platform software can provide its own set of services or expose the services provided by its underlying platform layers, if those services conform to this requirement.
11.5.2.3 Use of accessibility services
Where the software provides a user interface it shall use the applicable documented platform accessibility services. If the documented platform accessibility services do not allow the software to meet the applicable requirements of clauses 11.5.2.5 to 11.5.2.17, then software that provides a user interface shall use other documented services to interoperate with assistive technology.
NOTE: The term "documented platform accessibility services" refers to the set of services provided by the platform according to clauses 11.5.2.1 and 11.5.2.2.
It is best practice to develop software using toolkits that automatically implement the underlying platform accessibility services.
11.5.2.4 Assistive technology
Where the ICT is assistive technology it shall use the documented platform accessibility services.
NOTE 1: The term "documented platform accessibility services" refers to the set of services provided by the platform according to clauses 11.5.2.1 and 11.5.2.2.
NOTE 2: Assistive technology can also use other documented accessibility services.
11.5.2.5 Object information
Where the software provides a user interface it shall, by using the services as described in clause 11.5.2.3, make the user interface elements' role, state(s), boundary, name, and description programmatically determinable by assistive technologies.
11.5.2.6 Row, column, and headers
Where the software provides a user interface it shall, by using the services as described in clause 11.5.2.3, make the row and column of each cell in a data table, including headers of the row and column if present, programmatically determinable by assistive technologies.
11.5.2.7 Values
Where the software provides a user interface, it shall, by using the services as described in clause 11.5.2.3, make the current value of a user interface element and any minimum or maximum values of the range, if the user interface element conveys information about a range of values, programmatically determinable by assistive technologies.
11.5.2.8 Label relationships
Where the software provides a user interface it shall expose the relationship that a user interface element has as a label for another element, or of being labelled by another element, using the services as described in clause 11.5.2.3, so that this information is programmatically determinable by assistive technologies.
11.5.2.9 Parent-child relationships
Where the software provides a user interface it shall, by using the services as described in clause 11.5.2.3, make the relationship between a user interface element and any parent or children elements programmatically determinable by assistive technologies.
11.5.2.10 Text
Where the software provides a user interface it shall, by using the services as described in clause 11.5.2.3, make the text contents, text attributes, and the boundary of text rendered to the screen programmatically determinable by assistive technologies.
11.5.2.11 List of available actions
Where the software provides a user interface it shall, by using the services as described in clause 11.5.2.3, make a list of available actions that can be executed on a user interface element, programmatically determinable by assistive technologies.
11.5.2.12 Execution of available actions
Where permitted by security requirements, software that provides a user interface shall, by using the services as described in clause 11.5.2.3, allow the programmatic execution of the actions exposed according to clause 11.5.2.11 by assistive technologies.
NOTE 1: In some cases the security requirements imposed on a software product may forbid external software from interfering with the ICT product. Examples of systems under strict security requirements are systems dealing with intelligence activities, cryptologic activities related to national security, command and control of military forces.
NOTE 2: Assistive technologies may be required to maintain the same level of security as the standard input mechanisms supported by the platform.
11.5.2.13 Tracking of focus and selection attributes
Where software provides a user interface it shall, by using the services as described in clause 11.5.2.3, make information and mechanisms necessary to track focus, text insertion point, and selection attributes of user interface elements programmatically determinable by assistive technologies.
11.5.2.14 Modification of focus and selection attributes
Where permitted by security requirements, software that provides a user interface shall, by using the services as described in clause 11.5.2.3, allow assistive technologies to programmatically modify focus, text insertion point, and selection attributes of user interface elements where the user can modify these items.
NOTE 1: In some cases the security requirements imposed on a software product may forbid external software from interfering with the ICT product and so this requirement would not apply. Examples of systems under strict security requirements are systems dealing with intelligence activities, cryptologic activities related to national security, command and control of military forces.
NOTE 2: Assistive technologies may be required to maintain the same level of security as the standard input mechanisms supported by the platform.
11.5.2.15 Change notification
Where software provides a user interface it shall, by using the services as described in clause 11.5.2.3, notify assistive technologies about changes in those programmatically determinable attributes of user interface elements that are referenced in requirements 11.5.2.5 to 11.5.2.11 and 11.5.2.13.
11.5.2.16 Modifications of states and properties
Where permitted by security requirements, software that provides a user interface shall, by using the services as described in clause 11.5.2.3, allow assistive technologies to programmatically modify states and properties of user interface elements, where the user can modify these items.
NOTE 1: In some cases the security requirements imposed on a software product may forbid external software from interfering with the ICT product and so this requirement would not apply. Examples of systems under strict security requirements are systems dealing with intelligence activities, cryptologic activities related to national security, command and control of military forces.
NOTE 2: Assistive technologies may be required to maintain the same level of security as the standard input mechanisms supported by the platform.
11.5.2.17 Modifications of values and text
Where permitted by security requirements, software that provides a user interface shall, by using the services as described in clause 11.5.2.3, allow assistive technologies to modify values and text of user interface elements using the input methods of the platform, where a user can modify these items without the use of assistive technology.
NOTE 1: In some cases the security requirements imposed on a software product may forbid external software from interfering with the ICT product and so this requirement would not apply. Examples of systems under strict security requirements are systems dealing with intelligence activities, cryptologic activities related to national security, command and control of military forces.
NOTE 2: Assistive technologies may be required to maintain the same level of security as the standard input mechanisms supported by the platform.
11.6 Documented accessibility usage
11.6.1 User control of accessibility features
Where software is a platform it shall provide sufficient modes of operation for user control over those platform accessibility features documented as intended for users.
11.6.2 No disruption of accessibility features
Where software provides a user interface it shall not disrupt those documented accessibility features that are defined in platform documentation except when requested to do so by the user during the operation of the software.
11.7 User preferences
Where software is not designed to be isolated from its platform, and provides a user interface, that user interface shall follow the values of the user preferences for platform settings for: units of measurement, colour, contrast, font type, font size, and focus cursor except where they are overridden by the user.
NOTE 1: Software that is isolated from its underlying platform has no access to user settings in the platform and thus cannot adhere to them.
NOTE 2: For web content, the underlying platform is the user agent.
NOTE 3: This does not preclude the software from having additional values for a setting as long as there is one mode where the application will follow the system settings even if more restricted.
11.8 Authoring tools
11.8.0 General (informative)
For those creating web content authoring tools, ATAG 2.0 [i.32] provides information that can be of interest to those who want to go beyond these requirements.
NOTE: This is applicable both to standalone and to web based authoring tools.
11.8.1 Content technology
Authoring tools shall conform to clauses 11.8.2 to 11.8.5 to the extent that information required for accessibility is supported by the format used for the output of the authoring tool.
11.8.2 Accessible content creation
Authoring tools shall enable and guide the production of content that conforms to clauses 9 (Web content) or 10 (Non-Web content) as applicable.
NOTE: Authoring tools may rely on additional tools where conformance with specific requirements is not achievable by a single tool. For example, a video editing tool may enable the creation of video files for distribution via broadcast television and the web, but authoring of caption files for multiple formats may be provided by a different tool.
11.8.3 Preservation of accessibility information in transformations
If the authoring tool provides restructuring transformations or re-coding transformations, then accessibility information shall be preserved in the output if equivalent mechanisms exist in the content technology of the output.
NOTE 1: Restructuring transformations are transformations in which the content technology stays the same, but the structural features of the content are changed (e.g. linearizing tables, splitting a document into pages).
NOTE 2: Re-coding transformations are transformations in which the technology used to encode the content is changed.
11.8.4 Repair assistance
If the accessibility checking functionality of an authoring tool can detect that content does not meet a requirement of clauses 9 (Web) or 10 (Non-web documents) as applicable, then the authoring tool shall provide repair suggestion(s).
NOTE: This does not preclude automated and semi-automated repair which is possible (and encouraged) for many types of content accessibility problems.
11.8.5 Templates
When an authoring tool provides templates, at least one template that supports the creation of content that conforms to the requirements of clauses 9 (Web) or 10 (Non-web documents) as applicable shall be available and identified as such.
12. Documentation and support services
12.1 Product documentation
12.1.1 Accessibility and compatibility features
Product documentation provided with the ICT whether provided separately or integrated within the ICT shall list and explain how to use the accessibility and compatibility features of the ICT.
NOTE 1: Accessibility and compatibility features include accessibility features that are built-in and accessibility features that provide compatibility with assistive technology.
NOTE 2: It is best practice to use WebSchemas/Accessibility 2.0 [i.38] to provide meta data on the accessibility of the ICT.
NOTE 3: The accessibility statement and help pages are both examples of the provision of product information.
12.1.2 Accessible documentation
Product documentation provided with the ICT shall be made available in at least one of the following electronic formats:
- a Web format that conforms to the requirements of clause 9; or
- a non-web format that conforms to the requirements of clause 10.
NOTE 1: This does not preclude the possibility of also providing the product documentation in other formats (electronic, printed or audio) that are not accessible.
NOTE 2: It also does not preclude the possibility of providing alternate formats that meet the needs of some specific type of users (e.g. Braille documents for blind people or easy-to-read information for persons with limited cognitive, language and learning abilities).
NOTE 3: Where documentation is incorporated into the ICT, the documentation falls under the requirements for accessibility in the present document.
NOTE 4: A user agent that supports automatic media conversion would be beneficial to enhancing accessibility.
12.2 Support services
12.2.1 General (informative)
ICT support services include, but are not limited to: help desks, call centres, technical support, relay services and training services.
12.2.2 Information on accessibility and compatibility features
ICT support services shall provide information on the accessibility and compatibility features that are mentioned in the product documentation.
NOTE: Accessibility and compatibility features include accessibility features that are built-in and accessibility features that provide compatibility with assistive technology.
12.2.3 Effective communication
ICT support services shall accommodate the communication needs of individuals with disabilities either directly or through a referral point.
12.2.4 Accessible documentation
Documentation provided by support services shall be made available in at least one of the following electronic formats:
NOTE 1: This does not preclude the possibility of also providing the documentation in other formats (electronic or printed) that are not accessible.
NOTE 2: It also does not preclude the possibility of providing alternate formats that meet the needs of some specific type of users (e.g. Braille documents for blind people or easy-to-read information for persons with limited cognitive, language and learning abilities).
NOTE 3: Where the support documentation is incorporated into the ICT, the documentation falls under the requirements for accessibility in the present document.
NOTE 4: A user agent that supports automatic media conversion would be beneficial to enhancing accessibility.
13. ICT providing relay or emergency service access
13.1 Relay services requirements
13.1.1 General (informative)
Relay services enable users of different modes of communication e.g. text, sign, speech, to interact remotely through ICT with two-way communication by providing conversion between the modes of communication, normally by a human operator.
It is best practice to meet the applicable relay service requirements of ETSI ES 202 975 [i.5].
13.1.2 Text relay services
Where ICT is intended to provide a text relay service, the text relay service shall enable text users and speech users to interact by providing conversion between the two modes of communication.
13.1.3 Sign relay services
Where ICT is intended to provide a sign relay service, the sign relay service shall enable sign language users and speech users to interact by providing conversion between the two modes of communication.
NOTE: Sign relay services are also sometimes referred to as sign language relay services or video relay services.
13.1.4 Lip-reading relay services
Where ICT is intended to provide a lip-reading relay service, the lip-reading service shall enable lip-readers and voice telephone users to interact by providing conversion between the two modes of communication.
13.1.5 Captioned telephony services
Where ICT is intended to provide a captioned telephony service, the captioned telephony service shall assist a deaf or hard of hearing user in a spoken dialogue by providing text captions translating the incoming part of the conversation.
13.1.6 Speech to speech relay services
Where ICT is intended to provide a speech to speech relay service, the speech to speech relay service shall enable telephone users who are speech impaired, have limited cognitive, language and learning abilities, as well as any other user, to communicate by providing assistance between them.
13.2 Access to relay services
Where ICT systems support two-way communication, and the system is specified for use with relay services, access to those relay services shall not be prevented for outgoing and incoming calls involving: voice, RTT, or video, either individually or in combinations supported by both the relay service and the ICT system.
NOTE 1: The purpose of this requirement is to achieve functionally equivalent communication access by persons with disabilities.
NOTE 2: The system may be specified as needing to work with relay services by, for example: procurers, regulators, or product specifications.
13.3 Access to emergency services
Where ICT systems support two-way communication, and the system is specified for use with emergency services, access to those emergency services shall not be prevented for outgoing and incoming calls involving: voice, RTT, or video, either individually or in combinations supported by both the emergency service and the ICT system.
NOTE 1: The purpose of this requirement is to achieve functionally equivalent communication access to the emergency service by persons with disabilities.
NOTE 2: The system may be specified as needing to work with emergency services by, for example: procurers, regulators, or product specifications.
14. Conformance
Conformance to the present document is achieved by meeting all the applicable requirements, these are clauses containing the word "shall". Those clauses containing the word "should" are recommendations and are not required for conformance.
All clauses except those in clause 12 are self-scoping. This means they are introduced with the phrase 'Where ICT <pre condition>'. A requirement is met when the pre-condition is true and the corresponding test (in Annex C) is passed. When one of the pre-conditions is false the requirement is not applicable. Consequently, the result of the tests in Annex C can be: not applicable, pass, fail, or (in exceptional circumstances) not testable.
ICT is often comprised of an assembly of two or more items of ICT. In some cases, two or more interoperable items of ICT may together meet more requirements of the standard when one item complements the functionality of the other and the sum together meets more of the accessibility requirements. However, combining two items of ICT, both of which fail to meet any particular requirement, will not lead to a combined ICT system that meets that requirement.
The present document does not prioritize requirements.
NOTE 1: Conformance with the accessibility requirements could be affected by subsequent implementation or maintenance.
NOTE 2: Sampling is frequently required on complex ICT when there are too many instances of the object to be tested. The present document cannot recommend specific ICT evaluation sampling techniques as these are context specific.
The inherent nature of certain situations makes it impossible to make reliable and definitive statements that accessibility requirements have been met. In those situations therefore, the requirements in the present document are not applicable:
- when the product is in a failure, repair or maintenance state where the ordinary set of input or output functions are not available;
- during those parts of start-up, shutdown, and other state transitions that can be completed without user interaction.
NOTE 3: Even in the above situations, it is best practice to apply requirements in the present document wherever it is feasible and safe to do so.
Annex A (informative): Relationship between the present document and the essential requirements of Directive 2016/2102
The present document has been prepared under the Commission's standardisation request C(2017)2585 final [i.27] to provide one voluntary means of conforming to the essential requirements of Directive 2016/2102 on the accessibility of the websites and mobile applications of public sector bodies [i.28].
Once the present document is cited in the Official Journal of the European Union under that Directive, conformance with the normative clauses of the present document given in Tables A.1 and A.2 confers, within the limits of the scope of the present document, a presumption of conformity with the corresponding essential requirements of that Directive and associated EFTA regulations.
The requirements listed in Table A.1 apply to:
- web pages (as defined in clause 3.1);
- documents that are web pages;
- documents that are embedded in web pages and that are used in the rendering or that are intended to be rendered together with the web page in which they are embedded;
- documents, including forms, that are downloadable from web pages but are neither embedded nor rendered together with the web page from which they are provided;
- software that is a web page; or
- software that is embedded in web pages and that is used in the rendering or that is intended to be rendered together with the web page in which it is embedded.
The requirements listed in Table A.2 apply to mobile applications that provide a user interface, including content (such as documents and forms) that is in the software or provided by the software.
NOTE 1: According to Directive 2016/2102 [i.28]: "Content of websites and mobile applications includes textual as well as non-textual information, downloadable documents and forms, and two-way interaction such as the processing of digital forms and the completion of authentication, identification and payment processes".
NOTE 2: Annex A is a required element in all Harmonised standards. Its purpose is to explain how the essential requirements of a Directive can be met. Tables A.1 and A.2 are therefore restricted to those elements that relate to the essential requirements of Directive 2016/2102 [i.28].
NOTE 3: Annex A describes how the standard relates to the European Web Accessibility Directive. Apart from the minimum requirements in clauses 9, 10 and 11, some of the requirements in clauses 5, 6, 7 and 12 can also be relevant to fulfill the Directive in specific situations. The tables in Annex A show which requirements are relevant.
NOTE 4: Because the Web Accessibility Directive (EU) 2016/2102 "does not apply to live time-based media", the following requirements are not listed in Tables A.1 and A.2. They are, however, necessary requirements for making live streaming media accessible:
- 9.1.2.4 Captions (live)
- 10.1.2.4 Captions (live)
- 11.1.2.4 Captions (live).
Key to Tables A.1 columns:
Requirement:
Requirement No. - A unique identifier for one row of the table which may be used to identify a requirement.
Clause with requirements in EN 301 549 V3.2.1 - Identification of clause(s) defining the requirement in the present document unless another document is referenced explicitly.
Perceivable, operable, understandable, robust- Essential requirements of Directive 2016/2012.
P, O, U, R: Correlation with the requirement in the directive
- : no correlation with the requirement in the directive
Requirement Conditionality
Conditional or unconditional -
"U" indicates that conformance with the clause is unconditionally required.
"C" indicates that conformance with the clause is required only if the specified condition is met.
Condition - For conditional requirements this column describes the condition that has to be met for conformance with the clause to be a requirement.
Assessment
Clause with assessment in EN 301 549 V3.2.1 - Indicates the clause of the present document that contains the relevant assessment method.
Presumption of conformity stays valid only as long as a reference to the present document is maintained in the list published in the Official Journal of the European Union. Users of the present document should consult frequently the latest list published in the Official Journal of the European Union.
Other Union legislation may be applicable to the product(s) falling within the scope of the present document.
Requirement | Requirement conditionality | Assessment | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Requirement No. | Clause with requirements in EN 301 549 V3.2.1 | Perceivable | Operable | Understandable | Robust | Conditional or Unconditional | Condition | Clause with assessment in EN 301 549 V3.2.1 |
1 | 5.2 Activation of accessibility features | P | O | U | R | C | Where web content has documented accessibility features | C.5.2 |
2 | 5.3 Biometrics | - | O | - | - | C | Where web content uses biological characteristics | C.5.3 |
3 | 5.4 Preservation of accessibility information during conversion | P | - | U | R | C | Where web content converts information or communication | C.5.4 |
4 | 6.1 Audio bandwidth for speech | P | - | - | - | C | Where web pages provide two-way voice communication | C.6.1 |
5 | 6.2.1.1 RTT communication | P | O | - | - | C | Where web pages provide a means for two-way voice communication | C.6.2.1.1 |
6 | 6.2.1.2 Concurrent voice and text | P | O | - | - | C | Where web pages provide a means for two-way voice communication and for users to communicate by RTT | C.6.2.1.2 |
7 | 6.2.2.1 Visually distinguishable display | P | - | - | - | C | Where web pages have RTT send and receive capabilities | C.6.2.2.1 |
8 | 6.2.2.2 Programmatically determinable send and receive direction | P | - | - | - | C | Where web pages have RTT send and receive capabilities | C.6.2.2.2 |
9 | 6.2.2.3 Speaker identification | P | - | - | - | C | Where web pages have RTT capabilities, and provide speaker identification for voice | C.6.2.2.3 |
10 | 6.2.2.4 Visual indicator of Audio with RTT | P | - | - | - | C | Where web pages provide two-way voice communication, and have RTT capabilities | C.6.2.2.4 |
11 | 6.2.3 Interoperability item a) | P | - | - | - | C | Where web pages with RTT functionality interoperate with other ICT with RTT functionality (as required by clause 6.2.1.1) | C.6.2.3.a |
12 | 6.2.3 Interoperability item b) | P | - | - | - | C | Where web pages with RTT functionality interoperate with other ICT with RTT functionality (as required by clause 6.2.1.1) | C.6.2.3.b |
13 | 6.2.3 Interoperability item c) | P | - | - | - | C | Where web pages with RTT functionality interoperate with other ICT with RTT functionality (as required by clause 6.2.1.1) | C.6.2.3.c |
14 | 6.2.3 Interoperability item d) | P | - | - | - | C | Where web pages with RTT functionality interoperate with other ICT with RTT functionality (as required by clause 6.2.1.1) | C.6.2.3.d |
15 | 6.2.4 RTT responsiveness | P | - | - | - | C | Where web pages utilise RTT input | C.6.2.4 |
16 | 6.3 Caller ID | P | O | U | R | C | Where web pages provide provides caller identification or similar telecommunications functions | C.6.3 |
17 | 6.4 Alternatives to voice-based services | P | O | U | - | C | Where web pages provide real-time voice-based communication and also provide voice mail, auto-attendant, or interactive voice response facilities | C.6.4 |
18 | 6.5.2 Resolution item a) | P | - | U | - | C | Where web pages that provide two-way voice communication includes real-time video functionality | C.6.5.2 |
19 | 6.5.3 Frame rate item a) | P | - | U | - | C | Where web pages that provide two-way voice communication includes real-time video functionality | C.6.5.3 |
20 | 6.5.4 Synchronization between audio and video | P | - | U | - | C | Where web pages provide two-way voice communication include real-time video functionality | C.6.5.4 |
21 | 6.5.5 Visual indicator of audio with video | P | - | U | - | C | Where web pages provide two-way voice communication, and include real-time video functionality | C.6.5.5 |
22 | 6.5.6 Speaker identification with video (sign language) communication | P | - | U | - | C | Where web pages provide speaker identification for voice users | C.6.5.6 |
23 | 7.1.1 Captioning playback | P | - | U | - | C | Where web content displays video with synchronized audio | C.7.1.1 |
24 | 7.1.2 Captioning synchronization | P | - | - | - | C | Where web content displays captions | C.7.1.2 |
25 | 7.1.3 Preservation of captioning | P | - | U | - | C | Where web pages transmit, convert or record video with synchronized audio | C.7.1.3 |
26 | 7.1.4 Captions characteristics | P | - | - | - | C | Where web content displays captions | C.7.1.4 |
27 | 7.1.5 Spoken subtitles | P | - | U | - | C | Where web content displays video with synchronized audio | C.7.1.5 |
28 | 7.2.1 Audio description playback | P | - | U | - | C | Where web content displays video with synchronized audio | C.7.2.1 |
29 | 7.2.2 Audio description synchronization | P | - | - | - | C | Where web content has a mechanism to play audio description | C.7.2.2 |
30 | 7.2.3 Preservation of audio description | P | - | U | - | C | Where web pages transmit, convert, or record video with synchronized audio | C.7.2.3 |
31 | 7.3 User controls for captions and audio description | P | O | - | - | C | Where web pages primarily display materials containing video with associated audio content | C.7.3 |
32 | 9.1.1.1 Non-text content | P | - | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.1.1.1 |
33 | 9.1.2.1 Audio-only and video-only (pre-recorded) | P | - | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.1.2.1 |
34 | 9.1.2.2 Captions (pre-recorded) | P | - | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.1.2.2 |
35 | 9.1.2.3 Audio description or media alternative (pre‑recorded) | P | - | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.1.2.3 |
36 | 9.1.2.5 Audio description (pre‑recorded) | P | - | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.1.2.5 |
37 | 9.1.3.1 Info and relationships | P | - | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.1.3.1 |
38 | 9.1.3.2 Meaningful sequence | P | - | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.1.3.2 |
39 | 9.1.3.3 Sensory characteristics | P | - | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.1.3.3 |
40 | 9.1.3.4 Orientation | P | O | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.1.3.4 |
41 | 9.1.3.5 Identify input purpose | P | O | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.1.3.5 |
42 | 9.1.4.1 Use of colour | P | - | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.1.4.1 |
43 | 9.1.4.2 Audio control | P | - | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.1.4.2 |
44 | 9.1.4.3 Contrast (minimum) | P | - | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.1.4.3 |
45 | 9.1.4.4 Resize text | P | - | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.1.4.4 |
46 | 9.1.4.5 Images of text | P | - | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.1.4.5 |
47 | 9.1.4.10 Reflow | P | - | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.1.4.10 |
48 | 9.1.4.11 Non-text contrast | P | - | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.1.4.11 |
49 | 9.1.4.12 Text spacing | P | O | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.1.4.12 |
50 | 9.1.4.13 Content on hover or focus | P | O | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.1.4.13 |
51 | 9.2.1.1 Keyboard | - | O | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.2.1.1 |
52 | 9.2.1.2 No keyboard trap | - | O | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.2.1.2 |
53 | 9.2.1.4 Character key shortcuts | - | O | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.2.1.4 |
54 | 9.2.2.1 Timing adjustable | - | O | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.2.2.1 |
55 | 9.2.2.2 Pause, stop, hide | - | O | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.2.2.2 |
56 | 9.2.3.1 Three flashes or below threshold | - | O | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.2.3.1 |
57 | 9.2.4.1 Bypass blocks | - | O | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.2.4.1 |
58 | 9.2.4.2 Page titled | - | O | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.2.4.2 |
59 | 9.2.4.3 Focus Order | - | O | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.2.4.3 |
60 | 9.2.4.4 Link purpose (in context) | - | O | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.2.4.4 |
61 | 9.2.4.5 Multiple ways | - | O | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.2.4.5 |
62 | 9.2.4.6 Headings and labels | - | O | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.2.4.6 |
63 | 9.2.4.7 Focus visible | - | O | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.2.4.7 |
64 | 9.2.5.1 Pointer gestures | - | O | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.2.5.1 |
65 | 9.2.5.2 Pointer cancellation | - | O | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.2.5.2 |
66 | 9.2.5.3 Label in name | - | O | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.2.5.3 |
67 | 9.2.5.4 Motion actuation | - | O | - | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.2.5.4 |
68 | 9.3.1.1 Language of page | - | - | U | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.3.1.1 |
69 | 9.3.1.2 Language of parts | - | - | U | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.3.1.2 |
70 | 9.3.2.1 On focus | - | - | U | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.3.2.1 |
71 | 9.3.2.2 On input | - | - | U | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.3.2.2 |
72 | 9.3.2.3 Consistent navigation | - | - | U | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.3.2.3 |
73 | 9.3.2.4 Consistent identification | - | - | U | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.3.2.4 |
74 | 9.3.3.1 Error identification | - | - | U | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.3.3.1 |
75 | 9.3.3.2 Labels or instructions | - | - | U | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.3.3.2 |
76 | 9.3.3.3 Error suggestion | - | - | U | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.3.3.3 |
77 | 9.3.3.4 Error prevention (legal, financial, data) | - | - |
U | - | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.3.3.4 |
78 | 9.4.1.1 Parsing | - | - | - | R | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.4.1.1 |
79 | 9.4.1.2 Name, role, value | - | - | - | R | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.4.1.2 |
80 | 9.4.1.3 Status messages | P | O | U | R | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.4.1.3 |
81 | 9.6 WCAG conformance requirements | P | O | U | R | C | Where ICT is a web page | C.9.6 |
82 | 10.1.1.1 Non-text content | P | - | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.1.1.1 |
83 | 10.1.2.1 Audio-only and video-only (pre-recorded) | P | - | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.1.2.1 |
84 | 10.1.2.2 Captions (pre-recorded) | P | - | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.1.2.2 |
85 | 10.1.2.3 Audio description or media alternative (pre-recorded) | P | - | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.1.2.3 |
86 | 10.1.2.5 Audio description (pre-recorded) | P | - | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.1.2.5 |
87 | 10.1.3.1 Info and relationships | P | - | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.1.3.1 |
88 | 10.1.3.2 Meaningful sequence | P | - | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.1.3.2 |
89 | 10.1.3.3 Sensory characteristics | P | - | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.1.3.3 |
90 | 10.1.3.4 Orientation | P | O | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.1.3.4 |
91 | 10.1.3.5 Identify input purpose | P | O | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.1.3.5 |
92 | 10.1.4.1 Use of colour | P | - | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.1.4.1 |
93 | 10.1.4.2 Audio control | P | - | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.1.4.2 |
94 | 10.1.4.3 Contrast (minimum) | P | - | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.1.4.3 |
95 | 10.1.4.4 Resize text | P | - | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.1.4.4 |
96 | 10.1.4.5 Images of text | P | - | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.1.4.5 |
97 | 10.1.4.10 Reflow | P | - | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.1.4.10 |
98 | 10.1.4.11 Non-text contrast | P | - | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.1.4.11 |
99 | 10.1.4.12 Text spacing | P | O | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.1.4.12 |
100 | 10.1.4.13 Content on hover or focus | P | O | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.1.4.13 |
101 | 10.2.1.1 Keyboard | - | O | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.2.1.1 |
102 | 10.2.1.2 No keyboard trap | - | O | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.2.1.2 |
103 | 10.2.1.4 Character key shortcuts | - | O | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.2.1.4 |
104 | 10.2.2.1 Timing adjustable | - | O | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.2.2.1 |
105 | 10.2.2.2 Pause, stop, hide | - | O | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.2.2.2 |
106 | 10.2.3.1 Three flashes or below threshold | - | O | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.2.3.1 |
107 | 10.2.4.2 Document titled | - | O | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.2.4.2 |
108 | 10.2.4.3 Focus Order | - | O | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.2.4.3 |
109 | 10.2.4.4 Link purpose (in context) | - | O | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.2.4.4 |
110 | 10.2.4.6 Headings and labels | - | O | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.2.4.6 |
111 | 10.2.4.7 Focus visible | - | O | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.2.4.7 |
112 | 10.2.5.1 Pointer gestures | - | O | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.2.5.1 |
113 | 10.2.5.2 Pointer cancellation | - | O | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.2.5.2 |
114 | 10.2.5.3 Label in name | - | O | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.2.5.3 |
115 | 10.2.5.4 Motion actuation | - | O | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.2.5.4 |
116 | 10.3.1.1 Language of document | - | - | U | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.3.1.1 |
117 | 10.3.1.2 Language of parts | - | - | U | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.3.1.2 |
118 | 10.3.2.1 On focus | - | - | U | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.3.2.1 |
119 | 10.3.2.2 On input | - | - | U | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.3.2.2 |
120 | 10.3.3.1 Error identification | - | - | U | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.3.3.1 |
121 | 10.3.3.2 Labels or instructions | - | - | U | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.3.3.2 |
122 | 10.3.3.3 Error suggestion | - | - | U | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.3.3.3 |
123 | 10.3.3.4 Error prevention (legal, financial, data) | - | - | U | - | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.3.3.4 |
124 | 10.4.1.1 Parsing | - | - | - | R | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.4.1.1 |
125 | 10.4.1.2 Name, role, value | - | - | - | R | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.4.1.2 |
126 | 10.4.1.3 Status messages | P | O | U | R | C | Where the documents and forms are downloadable from a web page | C.10.4.1.3 |
127 | 11.7 User preferences | P | O | U | R | U | - | C.11.7 |
128 | 11.8.1 Content technology | P | O | U | R | C | Where web content is an authoring tool | C.11.8.1 |
129 | 11.8.2 Accessible content creation | P | O | U | R | C | Where web content is an authoring tool | C.11.8.2 |
130 | 11.8.3 Preservation of accessibility information in transformations | P | O | U | R | C | Where web content is an authoring tool | C.11.8.3 |
131 | 11.8.4 Repair assistance | P | O | U | R | C | Where web content is an authoring tool | C.11.8.4 |
132 | 11.8.5 Templates | P | O | U | R | C | Where web content is an authoring tool | C.11.8.5 |
133 | 12.1.1 Accessibility and compatibility features | P | O | U | R | U | - | C.12.1.1 |
134 | 12.1.2 Accessible documentation | P | O | U | R | U | - | C.12.1.2 |
135 | 12.2.2 Information on accessibility and compatibility features | P | O | U | R | U | - | C.12.2.2 |
136 | 12.2.3 Effective communication | P | - | U | - | U | - | C.12.2.3 |
137 | 12.2.4 Accessible documentation | P | O | U | R | U | - | C.12.2.4 |
Key to Tables A.2 columns:
Requirement:
No A unique identifier for one row of the table which may be used to identify a requirement.
Essential requirements of Directive
Identification of article(s) defining the requirement in the Directive.
Clause(s) of the present document
Identification of clause(s) defining the requirement in the present document unless another document is referenced explicitly.
Requirement Conditionality:
"C" indicates that conformance with the clause is required only if the specified condition is met.
Requirement | Requirement conditionality | Assessment | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
No. | Clause of the present document | Essential requirements of Directive 2016/2102 | Conditional or Unconditional | Condition | Clause of the present document | |||
Perceivable | Operable | Understandable | Robust | |||||
1 | 5.2 Activation of accessibility features |
|
|
|
| C | Where ICT has documented accessibility features | C.5.2 |
2 | 5.3 Biometrics | - |
| - | - | C | Where ICT uses biological characteristics | C.5.3 |
3 | 5.4 Preservation of accessibility information during conversion |
| - |
|
| C | Where ICT converts information or communication | C.5.4 |
4 | 5.5.1 Means of operation | - |
| - | - | C | Where ICT has operable parts | C.5.5.1 |
5 | 5.5.2 Operable parts discernibility |
|
| - | - | C | Where ICT has operable parts | C.5.5.2 |
6 | 5.6.1 Tactile or auditory status |
|
| - | - | C | Where ICT has a locking or toggle control | C.5.6.1 |
7 | 5.6.2 Visual status |
|
| - | - | C | Where ICT has a locking or toggle control | C.5.6.2 |
8 | 5.7 Key repeat | - |
| - | - | C | Where ICT has a key repeat function that cannot be turned off | C.5.7 |
9 | 5.8 Double-strike key acceptance | - |
| - | - | C | Where ICT has a keyboard or keypad | C.5.8 |
10 | 5.9 Simultaneous user actions | - |
| - | - | C | Where ICT uses simultaneous user actions for its operation | C.5.9 |
11 | 6.1 Audio bandwidth for speech |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT provides two-way voice communication | C.6.1 |
12 | 6.2.1.1 RTT communication |
|
| - | - | C | Where ICT provides a means for two-way voice communication | C.6.2.1.1 |
13 | 6.2.1.2 Concurrent voice and text |
|
| - | - | C | Where ICT provides a means for two-way voice communication and for users to communicate by RTT | C.6.2.1.2 |
14 | 6.2.2.1 Visually distinguishable display |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT has RTT send and receive capabilities | C.6.2.2.1 |
15 | 6.2.2.2 Programmatically determinable send and receive direction |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT has RTT send and receive capabilities | C.6.2.2.2 |
16 | 6.2.2.3 Speaker identification |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT has RTT capabilities, and provides speaker identification for voice | C.6.2.2.3 |
17 | 6.2.2.4 Visual indicator of Audio with RTT |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT provides two-way voice communication, and has RTT capabilities | C.6.2.2.4 |
18 | 6.2.3 Interoperability item a) |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT with RTT functionality interoperates with other ICT with RTT functionality (as required by clause 6.2.1.1) | C.6.2.3.a |
19 | 6.2.3 Interoperability item b) |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT with RTT functionality interoperates with other ICT with RTT functionality (as required by clause 6.2.1.1) | C.6.2.3.b |
20 | 6.2.3 Interoperability item c) |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT with RTT functionality interoperates with other ICT with RTT functionality (as required by clause 6.2.1.1) | C.6.2.3.c |
21 | 6.2.3 Interoperability item d) |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT with RTT functionality interoperates with other ICT with RTT functionality (as required by clause 6.2.1.1) | C.6.2.3.d |
22 | 6.2.4 RTT responsiveness |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT utilises RTT input | C.6.2.4 |
23 | 6.3 Caller ID |
|
|
|
| C | Where ICT provides caller identification, or similar telecommunications functions are provided | C.6.3 |
24 | 6.4 Alternatives to voice-based services |
|
|
| - | C | Where ICT provides real-time voice-based communication and also provides voice mail, auto-attendant, or interactive voice response facilities | C.6.4 |
25 | 6.5.2 Resolution item a) |
| - |
| - | C | Where ICT that provides two-way voice communication includes real-time video functionality | C.6.5.2 |
26 | 6.5.3 Frame rate item a) |
| - |
| - | C | Where ICT that provides two-way voice communication includes real-time video functionality | C.6.5.3 |
27 | 6.5.4 Synchronization between audio and video |
| - |
| - | C | Where ICT that provides two-way voice communication includes real-time video functionality | C.6.5.4 |
28 | 6.5.5 Visual indicator of audio with video |
| - |
| - | C | Where ICT provides two-way voice communication, and includes real-time video functionality | C.6.5.5 |
29 | 6.5.6 Speaker identification with video (sign language) communication |
| - |
| - | C | Where ICT provides speaker identification for voice users | C.6.5.6 |
30 | 7.1.1 Captioning playback |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT displays video with synchronized audio | C.7.1.1 |
31 | 7.1.2 Captioning synchronization |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT displays captions | C.7.1.2 |
32 | 7.1.3 Preservation of captioning |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT transmits, converts or records video with synchronized audio | C.7.1.3 |
33 | 7.1.4 Captions characteristics |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT displays captions | C.7.1.4 |
34 | 7.1.5 Spoken subtitles |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT displays video with synchronized audio | C.7.1.5 |
35 | 7.2.1 Audio description playback |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT displays video with synchronized audio | C.7.2.1 |
36 | 7.2.2 Audio description synchronization |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT has a mechanism to play audio description | C.7.2.2 |
37 | 7.2.3 Preservation of audio description |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT transmits, converts, or records video with synchronized audio | C.7.2.3 |
38 | 7.3 User controls for captions and audio description |
|
| - | - | C | Where ICT primarily displays materials containing video with associated audio content | C.7.3 |
39 | 10.1.1.1 Non-text content |
| - | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.1.1.1 |
40 | 10.1.2.1 Audio-only and video-only (pre-recorded) |
| - | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.1.2.1 |
41 | 10.1.2.2 Captions (pre-recorded) |
| - | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.1.2.2 |
42 | 10.1.2.3 Audio description or media alternative (pre-recorded) |
| - | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.1.2.3 |
43 | 10.1.2.5 Audio description (pre-recorded) |
| - | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.1.2.5 |
44 | 10.1.3.1 Info and relationships |
| - | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.1.3.1 |
45 | 10.1.3.2 Meaningful sequence |
| - | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.1.3.2 |
46 | 10.1.3.3 Sensory characteristics |
| - | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.1.3.3 |
47 | 10.1.3.4 Orientation |
|
| - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.1.3.4 |
48 | 10.1.3.5 Identify input purpose |
|
| - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.1.3.5 |
49 | 10.1.4.1 Use of colour |
| - | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.1.4.1 |
50 | 10.1.4.2 Audio control |
| - | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.1.4.2 |
51 | 10.1.4.3 Contrast (minimum) |
| - | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.1.4.3 |
52 | 10.1.4.4 Resize text |
| - | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.1.4.4 |
53 | 10.1.4.5 Images of text |
| - | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.1.4.5 |
54 | 10.1.4.10 Reflow |
| - | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.1.4.10 |
55 | 10.1.4.11 Non-text contrast |
| - | - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.1.4.11 |
56 | 10.1.4.12 Text spacing |
|
| - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.1.4.12 |
57 | 10.1.4.13 Content on hover or focus |
|
| - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.1.4.13 |
58 | 10.2.1.1 Keyboard | - |
| - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.2.1.1 |
59 | 10.2.1.2 No keyboard trap | - |
| - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.2.1.2 |
60 | 10.2.1.4 Character key shortcuts | - |
| - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.2.1.4 |
61 | 10.2.2.1 Timing adjustable | - |
| - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.2.2.1 |
62 | 10.2.2.2 Pause, stop, hide | - |
| - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.2.2.2 |
63 | 10.2.3.1 Three flashes or below threshold | - |
| - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.2.3.1 |
64 | 10.2.4.2 Document titled | - |
| - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.2.4.2 |
65 | 10.2.4.3 Focus Order | - |
| - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.2.4.3 |
66 | 10.2.4.4 Link purpose (in context) | - |
| - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.2.4.4 |
67 | 10.2.4.6 Headings and labels | - |
| - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.2.4.6 |
68 | 10.2.4.7 Focus visible | - |
| - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.2.4.7 |
69 | 10.2.5.1 Pointer gestures | - |
| - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.2.5.1 |
70 | 10.2.5.2 Pointer cancellation | - |
| - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.2.5.2 |
71 | 10.2.5.3 Label in name | - |
| - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.2.5.3 |
72 | 10.2.5.4 Motion actuation | - |
| - | - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.2.5.4 |
73 | 10.3.1.1 Language of document | - | - |
| - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.3.1.1 |
74 | 10.3.1.2 Language of parts | - | - |
| - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.3.1.2 |
75 | 10.3.2.1 On focus | - | - |
| - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.3.2.1 |
76 | 10.3.2.2 On input | - | - |
| - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.3.2.2 |
77 | 10.3.3.1 Error identification | - | - |
| - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.3.3.1 |
78 | 10.3.3.2 Labels or instructions | - | - |
| - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.3.3.2 |
79 | 10.3.3.3 Error suggestion | - | - |
| - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.3.3.3 |
80 | 10.3.3.4 Error prevention (legal, financial, data) | - | - |
| - | C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.3.3.4 |
81 | 10.4.1.1 Parsing | - | - | - |
| C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.4.1.1 |
82 | 10.4.1.2 Name, role, value | - | - | - |
| C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.4.1.2 |
83 | 10.4.1.3 Status messages |
|
|
|
| C | Where the documents and forms are contained in or provided by the mobile applications | C.10.4.1.3 |
84 | 11.1.1.1.1 Non-text content (open functionality) |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface and that supports access to assistive technologies for screen reading | C.11.1.1.1.1 |
85 | 11.1.1.1.2 Non-text content (closed functionality) |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface which is closed to assistive technologies for screen reading | C.11.1.1.1.2 |
86 | 11.1.2.1.1 Audio-only and video-only (pre-recorded - open functionality) |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface and that supports access to assistive technologies for screen reading | C.11.1.2.1.1 |
87 | 11.1.2.1.2 Audio-only and video-only (pre-recorded - closed functionality) |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface which is closed to assistive technologies for screen reading | C.11.1.2.1.2 |
88 | 11.1.2.2 Captions (pre-recorded) |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.1.2.2 |
89 | 11.1.2.3.1 Audio description or media alternative (pre-recorded - open functionality) |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface and that supports access to assistive technologies for screen reading | C.11.1.2.3.1 |
90 | 11.1.2.3.2 Audio description or media alternative (pre-recorded - closed functionality) |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface which is closed to assistive technologies for screen reading | C.11.1.2.3.2 |
91 | 11.1.2.5 Audio description (pre-recorded) |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.1.2.5 |
92 | 11.1.3.1.1 Info and relationships (open functionality) |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface and that supports access to assistive technologies for screen reading | C.11.1.3.1.1 |
93 | 11.1.3.2.1 Meaningful sequence (open functionality) |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface and that supports access to assistive technologies for screen reading | C.11.1.3.2.1 |
94 | 11.1.3.3 Sensory characteristics |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.1.3.3 |
95 | 11.1.3.4 Orientation |
|
| - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.1.3.4 |
96 | 11.1.3.5.1 Identify input purpose (open functionality) |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface and that supports access to assistive technologies for screen reading | C.11.1.3.5.1 |
97 | 11.1.3.5.2 Identify input purpose (closed functionality) |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface which is closed to assistive technologies for screen reading | C.11.1.3.5.2 |
98 | 11.1.4.1 Use of colour |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.1.4.1 |
99 | 11.1.4.2 Audio control |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.1.4.2 |
100 | 11.1.4.3 Contrast (minimum) |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.1.4.3 |
101 | 11.1.4.4.1 Resize text (open functionality) |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface and that supports access to assistive technologies for screen reading | C.11.1.4.4.1 |
102 | 11.1.4.4.2 Resize text (closed functionality) |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface which is closed to assistive technologies for screen reading | C.11.1.4.4.2 |
103 | 11.1.4.5.1 Images of text (open functionality) |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface and that supports access to assistive technologies for screen reading | C.11.1.4.5.1 |
104 | 11.1.4.5.2 Images of text (closed functionality) |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface which is closed to assistive technologies for screen reading | C.11.1.4.5.2 |
105 | 11.1.4.10 Reflow |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.1.4.10 |
106 | 11.1.4.11 Non-text contrast |
| - | - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.1.4.11 |
107 | 11.1.4.12 Text spacing |
|
| - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.1.4.12 |
108 | 11.1.4.13 Content on hover or focus |
|
| - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.1.4.13 |
109 | 11.2.1.1.1 Keyboard (open functionality) | - |
| - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface and that supports access to assistive technologies for screen reading | C.11.2.1.1.1 |
110 | 11.2.1.1.2 Keyboard (closed functionality) | - |
| - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface which is closed to assistive technologies for screen reading | C.11.2.1.1.2 |
111 | 11.2.1.2 No keyboard trap | - |
| - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.2.1.2 |
112 | 11.2.1.4.1 Character key shortcuts (open functionality) | - |
| - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface and that supports access to assistive technologies for screen reading | C.11.2.1.4.1 |
113 | 11.2.1.4.2 Character key shortcuts (closed functionality) | - |
| - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface which is closed to assistive technologies for screen reading | C.11.2.1.4.2 |
114 | 11.2.2.1 Timing adjustable | - |
| - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.2.2.1 |
115 | 11.2.2.2 Pause, stop, hide | - |
| - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.2.2.2 |
116 | 11.2.3.1 Three flashes or below threshold | - |
| - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.2.3.1 |
117 | 11.2.4.3 Focus order | - |
| - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.2.4.3 |
118 | 11.2.4.4 Link purpose (in context) | - |
| - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.2.4.4 |
119 | 11.2.4.6 Headings and labels | - |
| - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.2.4.6 |
120 | 11.2.4.7 Focus visible | - |
| - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.2.4.7 |
121 | 11.2.5.1 Pointer gestures | - |
| - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.2.5.1 |
122 | 11.2.5.2 Pointer cancellation | - |
| - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.2.5.2 |
123 | 11.2.5.3.1 Label in name (open functionality) | - |
| - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface and that supports access to assistive technologies for screen reading | C.11.2.5.3.1 |
124 | 11.2.5.4 Motion actuation | - |
| - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.2.5.4 |
125 | 11.3.1.1.1 Language of software (open functionality) | - | - |
| - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface and that supports access to assistive technologies for screen reading | C.11.3.1.1.1 |
126 | 11.3.1.1.2 Language of software (closed functionality) | - | - |
| - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface which is closed to assistive technologies for screen reading | C.11.3.1.1.2 |
127 | 11.3.2.1 On focus | - | - |
| - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.3.2.1 |
128 | 11.3.2.2 On input | - | - |
| - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.3.2.2 |
129 | 11.3.3.1.1 Error identification (open functionality) | - | - |
| - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface and that supports access to assistive technologies for screen reading | C.11.3.3.1.1 |
130 | 11.3.3.1.2 Error Identification (closed functionality) | - | - |
| - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface which is closed to assistive technologies for screen reading | C.11.3.3.1.2 |
131 | 11.3.3.2 Labels or instructions | - | - |
| - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.3.3.2 |
132 | 11.3.3.3 Error suggestion | - | - |
| - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.3.3.3 |
133 | 11.3.3.4 Error prevention (legal, financial, data) | - | - |
| - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.3.3.4 |
134 | 11.4.1.1.1 Parsing (open functionality) | - | - | - |
| C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface and that supports access to assistive technologies for screen reading | C.11.4.1.1.1 |
135 | 11.4.1.2.1 Name, role, value (open functionality) | - | - | - |
| C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface and that supports access to assistive technologies for screen reading | C.11.4.1.2.1 |
136 | 11.4.1.3.1 Status messages (open functionality) | - | - | - |
| C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface and that supports access to assistive technologies for screen reading | C.11.4.1.3.1 |
137 | 11.5.2.3 Use of accessibility services |
|
|
|
| C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.5.2.3 |
138 | 11.5.2.5 Object information |
| - |
| - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.5.2.5 |
139 | 11.5.2.6 Row, column, and headers |
| - |
| - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.5.2.6 |
140 | 11.5.2.7 Values |
| - |
| - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.5.2.7 |
141 | 11.5.2.8 Label relationships |
| - |
| - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.5.2.8 |
142 | 11.5.2.9 Parent-child relationships |
| - |
| - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.5.2.9 |
143 | 11.5.2.10 Text |
| - |
| - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.5.2.10 |
144 | 11.5.2.11 List of available actions | - |
| - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.5.2.11 |
145 | 11.5.2.12 Execution of available actions | - |
| - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.5.2.12 |
146 | 11.5.2.13 Tracking of focus and selection attributes | - |
| - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.5.2.13 |
147 | 11.5.2.14 Modification of focus and selection attributes | - |
| - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.5.2.14 |
148 | 11.5.2.15 Change notification | - |
|
| - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.5.2.15 |
149 | 11.5.2.16 Modifications of states and properties | - |
| - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.5.2.16 |
150 | 11.5.2.17 Modifications of values and text | - |
| - | - | C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.5.2.17 |
151 | 11.6.2 No disruption of accessibility features |
|
|
|
| C | Where ICT is non-web software that provides a user interface | C.11.6.2 |
152 | 11.7 User preferences |
|
|
|
| C | Where ICT is non-web software that is not designed to be isolated from its platform, and that provides a user interface | C.11.7 |
153 | 11.8.1 Content technology |
|
|
|
| C | Where ICT is an authoring tool | C.11.8.1 |
154 | 11.8.2 Accessible content creation |
|
|
|
| C | Where ICT is an authoring tool | C.11.8.2 |
155 | 11.8.3 Preservation of accessibility information in transformations |
|
|
|
| C | Where ICT is an authoring tool that provides restructuring transformations or re-coding transformations | C.11.8.3 |
156 | 11.8.4 Repair assistance |
|
|
|
| C | Where ICT is an authoring tool | C.11.8.4 |
157 | 11.8.5 Templates |
|
|
|
| C | Where ICT is an authoring tool that provides templates | C.11.8.5 |
158 | 12.1.1 Accessibility and compatibility features |
|
|
|
| U | - | C.12.1.1 |
159 | 12.1.2 Accessible documentation |
|
|
|
| U | - | C.12.1.2 |
160 | 12.2.2 Information on accessibility and compatibility features |
|
|
|
| U | - | C.12.2.2 |
161 | 12.2.3 Effective communication |
| - |
| - | U | - | C.12.2.3 |
162 | 12.2.4 Accessible documentation |
|
|
|
| U | - | C.12.2.4 |
Annex B (informative): Relationship between requirements and functional performance statements
B.1 Relationships between clauses 5 to 13 and the functional performance statements
Table B.2 shows which of the requirements set out in clauses 5 to 13 support each of the functional performance statements set out in clause 4.2.
To allow Table B.2 to fit the page, the abbreviations shown in Table B.1 have been used in the column headers of Table B.2.
Clause number | Column header abbreviation | Functional performance statement |
|---|---|---|
4.2.1 | WV | Usage without vision |
4.2.2 | LV | Usage with limited vision |
4.2.3 | WPC | Usage without perception of colour |
4.2.4 | WH | Usage without hearing |
4.2.5 | LH | Usage with limited hearing |
4.2.6 | WVC | Usage without vocal capability |
4.2.7 | LMS | Usage with limited manipulation or strength |
4.2.8 | LR | Usage with limited reach |
4.2.9 | PST | Minimize photosensitive seizure triggers |
4.2.10 | LC | Usage with limited cognition |
4.2.11 | P | Privacy |
The following abbreviations have been used to represent the relationship between the requirements in clauses 5 to 13 and the functional performance statements:
- P = Primary relationship. The requirement supports the functional performance statement.
- S = Secondary relationship. The requirement provides partial support for the functional performance statement because some users may use the feature in specific situations.
Requirements | 4.2.1 WV | 4.2.2 | 4.2.3 | 4.2.4 | 4.2.5 | 4.2.6 | 4.2.7 | 4.2.8 | 4.2.9 | 4.2.10 | 4.2.11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
5.1.2.1 Closed functionality | P | P | P | P | P | P | P | P | P | P | P |
5.1.2.2 Assistive technology | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | S |
5.1.3.1 General (belongs to 5.1.3 Non-visual access) | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
5.1.3.2 Auditory output delivery including speech | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
5.1.3.3 Auditory output correlation | - | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
5.1.3.4 Speech output user control | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
5.1.3.5 Speech output automatic interruption | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
5.1.3.6 Speech output for non-text content | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
5.1.3.7 Speech output for video information | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
5.1.3.8 Masked entry | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | P |
5.1.3.9 Private access to personal data | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | P |
5.1.3.10 Non-interfering audio output | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
5.1.3.11 Private listening volume | P | S | - | - | S | - | - | - | - | S | S |
5.1.3.12 Speaker volume | P | S | - | - | S | - | - | - | - | S | - |
5.1.3.13 Volume reset | P | S | - | - | S | - | - | - | - | S | - |
5.1.3.14 Spoken languages | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
5.1.3.15 Non-visual error identification | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
5.1.3.16 Receipts, tickets, and transactional outputs | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
5.1.4 Functionality closed to text enlargement | - | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
5.1.5 Visual output for auditory information | - | - | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | S | - |
5.1.6.1 Operation without keyboard interface (closed functionality) | P | P | - | - | - | S | P | - | - | - | - |
5.1.6.2 Operation without keyboard interface (Input focus) | P | P | - | - | - | S | P | - | - | - | - |
5.1.7 Access without speech | - | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | - | - | - |
5.2 Activation of accessibility features | P | P | P | P | P | - | P | - | - | - | - |
5.3 Biometrics | P | P | - | P | - | P | P | P | - | - | P |
5.4 Preservation of accessibility information during conversion | P | P | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | S | - |
5.5.1 Means of operation | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | - | - |
5.5.2 Operable part discernibility | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
5.6.1 Tactile or auditory status | P | P | - | P | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
5.6.2 Visual status | - | - | - | P | P | - | P | P | - | S | - |
5.7 Key repeat | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | S | - |
5.8 Double-strike key acceptance | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | P | - | S | - |
5.9 Simultaneous user actions | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | P | - | S | - |
6.1 Audio bandwidth for speech (informative recommendation) | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | - | - | - | - |
6.2.1.1 RTT communication | - | - | - | P | S | S | - | - | - | - | - |
6.2.1.2 Concurrent voice and text | - | - | - | P | P | S | - | - | - | - | - |
6.2.2.1 Visually distinguishable display | - | - | - | P | S | S | - | - | - | - | - |
6.2.2.2 Programmatically determinable send and receive direction | - | - | - | P | S | S | - | - | - | - | - |
6.2.2.3 Speaker identification | - | - | - | P | P | S | - | - | - | - | - |
6.2.2.4 Visual indicator of Audio with RTT | - | - | - | P | P | S | - | - | - | - | - |
6.2.3 Interoperability | - | - | - | P | S | S | - | - | - | - | - |
6.2.4 RTT responsiveness | - | - | - | P | S | S | - | - | - | - | - |
6.3 Caller ID | P | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
6.4 Alternatives to voice-based services | - | - | - | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | - |
6.5.2 Resolution | - | - | - | P | P | S | - | - | - | - | - |
6.5.3 Frame rate | - | - | - | P | P | S | - | - | - | - | - |
6.5.4 Synchronization between audio and video | - | - | - | P | P | S | - | - | - | - | - |
6.5.5 Visual indicator of audio with video | - | - | - | P | P | S | - | - | - | - | - |
6.5.6 Speaker identification with video (sign language) communication | - | - | - | P | P | S | - | - | - | - | - |
6.6 Alternatives to video-based services | P | S | - | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | - |
7.1.1 Captioning playback | - | - | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | S | - |
7.1.2 Captioning synchronization | - | - | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | S | - |
7.1.3 Preservation of captioning | - | - | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | S | - |
7.1.4 Captions characteristics | - | S | S | P | P | - | - | - | - | S | - |
7.1.5 Spoken subtitles | P | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
7.2.1 Audio description playback | P | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
7.2.2 Audio description synchronization | P | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
7.2.3 Preservation of audio description | P | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
7.3 User controls for captions and audio description | P | P | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | S | - |
8.1.2 Standard connections | P | P | - | - | P | - | P | P | - | P | - |
8.1.3 Colour | - | S | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
8.2.1.1 Speech volume range | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | - | - | - | - |
8.2.1.2 Incremental volume control | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | - | - | - | - |
8.2.2.1 Fixed-line devices | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | - | - | - | - |
8.2.2.2 Wireless communication devices | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | - | - | - | - |
8.3.0 Stationary ICT, General (informative recommendation) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | - |
8.3.1 Forward or side reach | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | - |
8.3.2.1 Unobstructed high forward reach | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | - |
8.3.2.2 Unobstructed low forward reach | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | - |
8.3.2.3.1 Obstructed forward reach - Clear space | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | - |
8.3.2.3.2 Obstructed | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | - |
8.3.2.3.3 Obstructed | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | - |
8.3.2.4 Knee and toe clearance width | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | - |
8.3.2.5 Toe clearance | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | - |
8.3.2.6 Knee clearance | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | - |
8.3.3.1 Unobstructed high side reach | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | - |
8.3.3.2 Unobstructed low side reach | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | - |
8.3.3.3.1 Obstructed | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | - |
8.3.3.3.2 Obstructed | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | - |
8.3.4.1 Change in level | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | - |
8.3.4.2 Clear floor or ground space | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | - |
8.3.4.3.1 Approach - General | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | - |
8.3.4.3.2 Forward approach | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | - |
8.3.4.3.3 Parallel approach | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | - |
8.3.5 Visibility | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | - |
8.3.6 Installation instructions | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | - |
8.4.1 Numeric keys | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
8.4.2.1 Means of operation of mechanical parts | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | - | - |
8.4.2.2 Force of operation of mechanical parts | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | - | - |
8.4.3 Keys, tickets and fare cards | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
8.5 Tactile indication of speech mode | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
9.1.1.1 Non-text content | P | P | - | P | S | - | - | - | - | S | S |
9.1.2.1 Audio-only and video-only (pre-recorded) | P | P | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | S | - |
9.1.2.2 Captions (pre‑recorded) | - | - | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | S | - |
9.1.2.3 Audio description or media alternative (pre‑recorded) | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
9.1.2.4 Captions (live) | - | - | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | S | - |
9.1.2.5 Audio description | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
9.1.3.1 Info and relationships | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
9.1.3.2 Meaningful sequence | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
9.1.3.3 Sensory characteristics | P | P | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | S | - |
9.1.3.4 Orientation | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | P | - | S | - |
9.1.3.5 Identify input purpose | - | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
9.1.4.1 Use of colour | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
9.1.4.2 Audio control | P | - | - | - | P | - | - | - | - | S | - |
9.1.4.3 Contrast (minimum) | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
9.1.4.4 Resize text | - | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
9.1.4.5 Images of text | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
9.1.4.10 Reflow | - | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
9.1.4.11 Non-text contrast | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | - | S | - | |
9.1.4.12 Text spacing | - | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - |
9.1.4.13 Content on hover or focus | - | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - |
9.2.1.1 Keyboard | P | P | - | - | - | S | P | - | - | - | - |
9.2.1.2 No keyboard trap | P | P | - | - | - | S | P | - | - | - | - |
9.2.1.4 Character key shortcuts | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | P | - | S | - |
9.2.2.1 Timing adjustable | P | P | - | P | P | - | P | - | - | P | - |
9.2.2.2 Pause, stop, hide | P | P | - | P | P | - | P | - | - | P | - |
9.2.3.1 Three flashes or below threshold | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - | - |
9.2.4.1 Bypass blocks | P | P | - | - | - | S | P | - | - | P | - |
9.2.4.2 Page titled | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | P | - |
9.2.4.3 Focus order | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | P | - |
9.2.4.4 Link purpose | P | P | - | - | - | S | P | - | - | P | - |
9.2.4.5 Multiple ways | P | P | - | - | - | S | P | - | - | P | - |
9.2.4.6 Headings and labels | P | P | - | S | - | S | P | - | - | P | - |
9.2.4.7 Focus visible | P | P | - | - | - | S | P | - | - | P | - |
9.2.5.1 Pointer gestures | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | P | - | P | - |
9.2.5.2 Pointer cancellation | - | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | - | P | - |
9.2.5.3 Label in name | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | P | - | S | - |
9.2.5.4 Motion actuation | S | S | - | - | - | - | P | P | - | S | - |
9.3.1.1 Language of page | P | S | - | S | S | - | - | - | - | S | - |
9.3.1.2 Language of parts | P | S | - | S | S | - | - | - | - | S | - |
9.3.2.1 On focus | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | P | - |
9.3.2.2 On Input | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | P | - |
9.3.2.3 Consistent navigation | P | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - |
9.3.2.4 Consistent identification | S | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - |
9.3.3.1 Error identification | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - |
9.3.3.2 Labels or instructions | P | P | - | - | - | S | S | - | - | P | - |
9.3.3.3 Error suggestion | P | P | - | - | - | S | S | - | - | P | - |
9.3.3.4 Error prevention (legal, financial, data) | P | P | - | - | - | - | S | - | - | P | - |
9.4.1.1 Parsing | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
9.4.1.2 Name, role, value | P | P | - | - | - | - | S | - | - | - | - |
9.4.1.3 Status messages | P | P | P | P | P | S | P | P | P | P | - |
9.6 WCAG Conformance requirements | P | P | P | P | P | S | P | P | P | P | S |
10.1.1.1 Non-text content | P | P | - | P | S | - | - | - | - | S | S |
10.1.2.1 Audio-only and video-only (pre-recorded) | P | P | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | S | - |
10.1.2.2 Captions | - | - | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | S | - |
10.1.2.3 Audio description or media alternative | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
10.1.2.4 Captions (live) | - | - | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | S | - |
10.1.2.5 Audio description (pre-recorded) | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
10.1.3.1 Info and relationships | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
10.1.3.2 Meaningful sequence | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
10.1.3.3 Sensory characteristics | P | P | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | S | - |
10.1.3.4 Orientation | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | P | - | S | - |
10.1.3.5 Identify input purpose | - | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
10.1.4.1 Use of colour | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
10.1.4.2 Audio control | P | - | - | - | P | - | - | - | - | S | - |
10.1.4.3 Contrast (minimum) | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
10.1.4.4 Resize text | - | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
10.1.4.5 Images of text | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
10.1.4.10 Reflow | - | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
10.1.4.11 Non-text contrast | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | - | S | - | |
10.1.4.12 Text spacing | - | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - |
10.1.4.13 Content on hover or focus | - | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - |
10.2.1.1 Keyboard | P | P | - | - | - | S | P | - | - | - | - |
10.2.1.2 No keyboard trap | P | P | - | - | - | S | P | - | - | - | - |
10.2.1.4 Character key shortcuts | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | P | - | S | - |
10.2.2.1 Timing adjustable | P | P | - | P | P | - | P | - | - | P | - |
10.2.2.2 Pause, stop, hide | P | P | - | P | P | - | P | - | - | P | - |
10.2.3.1 Three flashes or below threshold | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - | - |
10.2.4.2 Document titled | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | P | - |
10.2.4.3 Focus order | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | P | - |
10.2.4.4 Link purpose | P | P | - | - | - | S | P | - | - | P | - |
10.2.4.6 Headings and labels | P | P | - | S | - | S | P | - | - | P | - |
10.2.4.7 Focus visible | P | P | - | - | - | S | P | - | - | P | - |
10.2.5.1 Pointer gestures | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | P | - | P | - |
10.2.5.2 Pointer cancellation | - | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | - | P | - |
10.2.5.3 Label in name | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | P | - | S | - |
10.2.5.4 Motion actuation | S | S | - | - | - | - | P | P | - | S | - |
10.3.1.1 Language of page | P | S | - | S | S | - | - | - | - | S | - |
10.3.1.2 Language of parts | P | S | - | S | S | - | - | - | - | S | - |
10.3.2.1 On focus | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | P | - |
10.3.2.2 On input | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | P | - |
10.3.3.1 Error identification | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - |
10.3.3.2 Labels or instructions | P | P | - | - | - | S | S | - | - | P | - |
10.3.3.3 Error suggestion | P | P | - | - | - | S | S | - | - | P | - |
10.3.3.4 Error prevention (legal, financial, data) | P | P | - | - | - | - | S | - | - | P | - |
10.4.1.1 Parsing | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
10.4.1.2 Name, role, value | P | P | - | - | - | - | S | - | - | - | - |
10.4.1.3 Status messages | P | P | P | P | P | P | P | P | P | P | - |
10.5 Caption positioning | - | - | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | S | - |
10.6 Audio description timing | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
11.1.1.1.1 Non-text content (open functionality) | P | P | - | P | S | - | - | - | - | S | S |
11.1.1.1.2 Non-text content (closed functionality | P | P | - | P | S | - | - | - | - | S | S |
11.1.2.1.1 Audio-only and video-only (pre-recorded - open functionality) | P | P | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | S | - |
11.1.2.1.2.1 Pre-recorded audio-only (closed functionality) | - | - | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | S | - |
11.1.2.1.2.2 Pre-recorded video-only (closed functionality) | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
11.1.2.2 Captions | - | - | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | S | - |
11.1.2.3.1 Audio description or media alternative | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
11.1.2.3.2 Audio description or media alternative | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
11.1.2.4 Captions (live) | - | - | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | S | - |
11.1.2.5 Audio description | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
11.1.3.1.1 Info and relationships (open functionality) | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
11.1.3.1.2 Info and relationships (closed functionality) | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
11.1.3.2.1 Meaningful sequence (open functionality) | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
11.1.3.2.2 Meaningful sequence (closed functionality) | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
11.1.3.3 Sensory characteristics | P | P | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | S | - |
11.1.3.4 Orientation | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | P | - | S | - |
11.1.3.5.1 Identify input purpose (open functionality) | - | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
11.1.3.5.2 Identify input purpose (closed functionality) | - | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
11.1.4.1 Use of colour | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
11.1.4.2 Audio control | P | - | - | - | P | - | - | - | - | S | - |
11.1.4.3 Contrast (minimum) | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
11.1.4.4.1 Resize text (open functionality) | - | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
11.1.4.4.2 Resize text (closed functionality) | - | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
11.1.4.5.1 Images of text (open functionality) | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
11.1.4.5.2 Images of text (closed functionality) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
11.1.4.10 Reflow | - | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
11.1.4.11 Non-text contrast | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | - | S | - | |
11.1.4.12 Text spacing | - | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - |
11.1.4.13 Content on hover or focus | - | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - |
11.2.1.1.1 Keyboard (open functionality) | P | P | - | - | - | S | P | - | - | - | - |
11.2.1.1.2 Keyboard (closed functionality) | P | P | - | - | - | S | P | - | - | - | - |
11.2.1.2 No keyboard trap | P | P | - | - | - | S | P | - | - | - | - |
11.2.1.4.1 Character key shortcuts (open functionality) | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | P | - | S | - |
11.2.1.4.2 Character key shortcuts (closed functionality) | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | P | - | S | - |
11.2.2.1 Timing adjustable | P | P | - | P | P | - | P | - | - | P | - |
11.2.2.2 Pause, stop, hide | P | P | - | P | P | - | P | - | - | P | - |
11.2.3.1 Three flashes or below threshold | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - | - |
11.2.4.3 Focus order | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | P | - |
11.2.4.4 Link purpose | P | P | - | - | - | S | P | - | - | P | - |
11.2.4.6 Headings and labels | P | P | - | S | - | S | P | - | - | P | - |
11.2.4.7 Focus visible | P | P | - | - | - | S | P | - | - | P | - |
11.2.5.1 Pointer gestures | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | P | - | P | - |
11.2.5.2 Pointer cancellation | - | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | - | P | - |
11.2.5.3.1 Label in name (open functionality) | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | P | - | S | - |
11.2.5.3.2 Label in name (closed functionality) | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | P | - | S | - |
11.2.5.4 Motion actuation | S | S | - | - | - | - | P | P | - | S | - |
11.3.1.1.1 Language of software (open functionality) | P | S | - | S | S | - | - | - | - | S | - |
11.3.1.1.2 Language of software (closed functionality) | P | S | - | S | S | - | - | - | - | S | - |
11.3.2.1 On focus | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | P | - |
11.3.2.2 On input | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | P | - |
11.3.3.1.1 Error identification (open functionality) | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - |
11.3.3.1.2 Error Identification (closed functionality) | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - |
11.3.3.2 Labels or instructions | P | P | - | - | - | S | S | - | - | P | - |
11.3.3.3 Error suggestion | P | P | - | - | - | S | S | - | - | P | - |
11.3.3.4 Error prevention (legal, financial, data) | P | P | - | - | - | - | S | - | - | P | - |
11.4.1.1.1 Parsing (open functionality) | P | S | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
11.4.1.1.2 Parsing (closed functionality) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
11.4.1.2.1 Name, role, value (open functionality) | P | P | - | - | - | - | S | - | - | - | - |
11.4.1.2.2 Name, role, value (closed functionality) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
11.4.1.3.1 Status messages (open functionality) | P | P | P | P | P | P | P | P | P | P | - |
11.5.1 Closed functionality | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
11.5.2.1 Platform accessibility service support for software that provides a user interface | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | S | - |
11.5.2.2 Platform accessibility service support for assistive technologies | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | S | - |
11.5.2.3 Use of accessibility services | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | S | - |
11.5.2.4 Assistive technology | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | S | - |
11.5.2.5 Object information | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | S | - |
11.5.2.6 Row, column, and headers | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | S | - |
11.5.2.7 Values | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | S | - |
11.5.2.8 Label relationships | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | S | - |
11.5.2.9 Parent-child relationships | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | S | - |
11.5.2.10 Text | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | S | - |
11.5.2.11 List of available actions | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | S | - |
11.5.2.12 Execution of available actions | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | S | - |
11.5.2.13 Tracking of focus and selection attributes | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | S | - |
11.5.2.14 Modification of focus and selection attributes | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | S | - |
11.5.2.15 Change notification | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | S | - |
11.5.2.16 Modifications of states and properties | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | S | - |
11.5.2.17 Modifications of values and text | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | - | - | S | - |
11.6.1 User control of accessibility features | P | P | P | P | P | - | P | - | - | - | - |
11.6.2 No disruption of accessibility features | P | P | P | P | P | - | P | - | - | - | - |
11.7 User preferences | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | S | - |
11.8.1 Content technology | P | P | P | P | P | S | P | P | P | P | S |
11.8.2 Accessible content creation | P | P | P | P | P | S | P | P | P | P | S |
11.8.3 Preservation of accessibility information in transformations | P | P | P | P | P | S | P | P | P | P | S |
11.8.4 Repair assistance | P | P | P | P | P | S | P | P | P | P | S |
11.8.5 Templates | P | P | P | P | P | S | P | P | P | P | S |
12.1.1 Accessibility and compatibility features | P | P | P | P | P | - | P | - | - | S | - |
12.1.2 Accessible documentation | P | P | P | P | P | S | P | P | P | P | S |
12.2.2 Information on accessibility and compatibility features | P | P | P | P | P | - | P | - | - | S | - |
12.2.3 Effective communication | - | - | - | P | P | P | - | - | - | S | - |
12.2.4 Accessible documentation | P | P | P | P | P | S | P | P | P | P | S |
13.1.2 Text relay services | - | - | - | P | P | P | - | - | - | S | - |
13.1.3 Sign relay services | - | - | - | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | - |
13.1.4 Lip-reading relay services | - | - | - | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | - |
13.1.5 Captioned telephony services | - | - | - | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | - |
13.1.6 Speech to speech relay services | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | P | - |
13.2 Access to relay services | - | - | - | P | P | P | - | - | - | S | - |
13.3 Access to emergency services | - | - | - | P | P | P | - | - | - | S | - |
B.2 Interpretation of Table B.2
B.2.0 General
Table B.2 illustrates the impact a specific accessibility issue might have on different users. It does this by mapping the requirements in the standard with the functional performance statements in clause 4. A requirement can be Primary (P) or Secondary (S).
The technical requirements are listed in a vertical column and the functional performance statements horizontally.
The table indicates which functional performance statements, and corresponding user needs, are covered by each requirement.
B.2.1 Example
B.2.1.1 Step 1
For requirement 5.1.3.11, which relates to the possibility of changing the volume when the user is listening in a private headset, the table can be read like this:
The requirement for private listening volume has a "P" for primary support in the column "WV", which stands for "without vision".
This means that private listening volume supports the functional performance statements for users who cannot see. In other words, the possibility for the user to control the volume when listening via a private headset is necessary for blind users.
B.2.1.2 Step 2
The third column shows that, for users with low vision, the possibility to control the volume when listening via a private headset is not as necessary as for blind users, it has an S for Secondary, where the first column had a P for Primary.
Secondary support means that some users in this group may use the accessibility feature in specific situations.
B.2.1.3 Step 3
In this way it is possible to assess the impact on functional performance statements if a particular requirement is not met.
The fourth column considers users who are color blind; the requirement on private listening volume is not marked at all. Of course, the possibility of changing the volume when listening in private headset is nice to have for all users, no matter their ability to distinguish between colors, but the listening volume does not compensate for the color blindness.
B.2.1.4 Step 4
The table can also be read the other way around:
Since blind users cannot see the screen, they need an alternative way to use the interface. If this alternative is audio via private headset, blind users need the possibility to change the volume.
Some users who can see, but not well, need or prefer to use audio as an alternative way to use the interface. If this alternative is audio via private headset, some low vision users will benefit from the possibility to change the volume.
Annex C (normative): Determination of conformance
C.1 Introduction
This normative annex sets out the means necessary to determine conformance with the individual requirements set out in the body of the present document.
To assist the reader, empty clauses are inserted in order to make the numbering of the annex reflect the clause numbers in the requirements.
C.2 Empty clause
This clause is intentionally left empty.
C.3 Empty clause
This clause is intentionally left empty.
C.4 Functional performance
Clause 4 is informative and does not contain requirements that require testing.
C.5 Generic requirements
C.5.1 Closed functionality
C.5.1.1 Introduction
Clause 5.1.1 is informative and does not contain requirements that require testing.
C.5.1.2 General
C.5.1.2.1 Closed functionality
See clauses C.5.2 to C.13, as applicable.
C.5.1.2.2 Assistive technology
Type of assessment | Testing |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 2 is true Fail: Check 2 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.5.1.3 Non-visual access
C.5.1.3.1 Audio output of visual information
Type of assessment | Testing |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 2 is true Fail: Check 2 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.5.1.3.2 Auditory output delivery including speech
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 or 2 is true Fail: Checks 1 and 2 are false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.5.1.3.3 Auditory output correlation
Clause 5.1.3.3 is informative only and contains no requirements requiring test.
C.5.1.3.4 Speech output user control
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: All checks are true Fail: Any check is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.5.1.3.5 Speech output automatic interruption
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 2 and 3 are true Fail: Check 2 or 3 are false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.5.1.3.6 Speech output for non-text content
Type of assessment | Testing |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Checks 1 and 2 and 3 and 4 are true; or 1 and 2 are false; or 1 and 3 are false Fail: Checks 1 is true and 2 false; or 1 is true and 3 false; or 1 and 2 and 3 are true and 4 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.5.1.3.7 Speech output for video information
Type of assessment | Testing |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-conditions 1 or 2 are not met |
C.5.1.3.8 Masked entry
Type of assessment | Testing |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Any check is true Fail: All checks are false Not applicable: Pre-conditions 1 or 2 are not met |
C.5.1.3.9 Private access to personal data
Type of assessment | Testing |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Checks 1 and 2 or 3 are true Fail: Checks 1 or 2 and 3 are false Not applicable: Pre-conditions 1 or 3 are not met |
C.5.1.3.10 Non-interfering audio output
Type of assessment | Testing |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-conditions 1 or 2 are not met |
C.5.1.3.11 Private listening volume
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-conditions 1 or 2 are not met |
C.5.1.3.12 Speaker volume
Type of assessment | Inspection and measurement |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Checks 1 and 2 are true Fail: Check 1 or 2 is false Not applicable: Pre-conditions 1 or 2 are not met |
C.5.1.3.13 Volume reset
Type of assessment | Inspection and measurement |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-conditions 1 or 2 are not met |
C.5.1.3.14 Spoken languages
Type of assessment | Testing |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-conditions 1 or 3 are not met |
C.5.1.3.15 Non-visual error identification
Type of assessment | Testing |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Checks 1 and 2 are true Fail: Check 1 or check 2 false Not applicable: Pre-conditions 1 or 2 are not met |
C.5.1.3.16 Receipts, tickets and transactional outputs
Type of assessment | Testing |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-conditions 1, 2 or 3 are not met |
C.5.1.4 Functionality closed to text enlargement
Type of assessment | Inspection and measurement |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 2 is true Fail: Check 2 is false Not applicable: Pre-conditions 1 or 2 are not met |
C.5.1.5 Visual output for auditory information
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.5.1.6 Operation without keyboard interface
C.5.1.6.1 Closed functionality
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.5.1.6.2 Input focus
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met |
C.5.1.7 Access without speech
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.5.2 Activation of accessibility features
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.5.3 Biometrics
Type of assessment | Test 1 |
Pre-conditions | 1. The ICT uses biological characteristic for user identification. |
Procedure | 1. Check that more than one means can be used for user identification. |
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
Type of assessment | Test 2 |
Pre-conditions | 1. The ICT uses biological characteristic for control of ICT. |
Procedure | 1. Check that more than one means can be used for control of ICT. |
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.5.4 Preservation of accessibility information during conversion
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1, 2, 3 or 4 is not met |
C.5.5 Operable parts
C.5.5.1 Means of operation
Type of assessment | Testing |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.5.5.2 Operable part discernibility
Type of assessment | Testing |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Checks 1 and 2 are true Fail: Checks 1 or 2 are false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.5.6 Locking or toggle controls
C.5.6.1 Tactile or auditory status
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 or 2 is true Fail: Checks 1 and 2 are false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met |
C.5.6.2 Visual status
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met |
C.5.7 Key repeat
Type of assessment | Testing |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Checks 1 and 2 are true Fail: Check 1 or 2 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met |
C.5.8 Double-strike key acceptance
Type of assessment | Testing |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true and check 5 is false Fail: Check 1 is false or check 5 is true Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.5.9 Simultaneous user actions
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 3 is true Fail: Check 3 is false for all modes of operation Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.6 ICT with two-way voice communication
C.6.1 Audio bandwidth for speech
Type of assessment | Measurement |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.6.2 Real-Time Text (RTT) functionality
C.6.2.1 RTT provision
C.6.2.1.1 RTT communication
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met Not testable: Pre-condition 3 is not met |
NOTE: An "RTT reference terminal" is a terminal specifically designed for testing RTT capable devices in a manner that would confirm their functionality and interoperability. These are generally created by a national or international standards entity so that all testing is done with a consistent "RTT reference terminal". | |
C.6.2.1.2 Concurrent voice and text
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Checks 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met |
C.6.2.2 Display of RTT
C.6.2.2.1 Visually distinguishable display
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 5 is true Fail: Check 5 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met Not testable: Pre-condition 3 is not met |
NOTE: An "RTT reference terminal" is a terminal specifically designed for testing RTT capable devices in a manner that would confirm their functionality and interoperability. These are generally created by a national or international standards entity so that all testing is done with a consistent "RTT reference terminal". | |
C.6.2.2.2 Programmatically determinable send and receive direction
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 5 is true Fail: Check 5 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met Not testable: Pre-condition 3 is not met |
NOTE: An "RTT reference terminal" is a terminal specifically designed for testing RTT capable devices in a manner that would confirm their functionality and interoperability. These are generally created by a national or international standards entity so that all testing is done with a consistent "RTT reference terminal". | |
C.6.2.2.3 Speaker Identification
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 2 is true Fail: Check 2 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met Not testable: Pre-condition 3 is not met |
NOTE: An "RTT reference terminal" is a terminal specifically designed for testing RTT capable devices in a manner that would confirm their functionality and interoperability. These are generally created by a national or international standards entity so that all testing is done with a consistent "RTT reference terminal". | |
C.6.2.2.4 Visual indicator of audio with RTT
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 3 is true Fail: Check 3 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met |
NOTE: The indicator should flicker in real time in a way that reflects the audio activity. | |
C.6.2.3.a Interoperability (a)
Type of assessment | Test |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met Not testable: Pre-condition 3 is not met |
NOTE: A "V.18 reference terminal" is a terminal specifically designed for testing V.18 capable devices in a manner that would confirm their functionality and interoperability. These are generally created by a national or international standards entity so that all testing is done with a consistent reference terminal. | |
C.6.2.3.b Interoperability (b)
Type of assessment | Test |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true and, if the ICT interoperates with other ICT using the IP Multimedia Sub-System (IMS) to implement VOIP, check 2 is true. Fail: Check 1 is false or, if the ICT interoperates with other ICT using the IP Multimedia Sub-System (IMS) to implement VOIP, check 2 is false. Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met Not testable: Pre-condition 3 is not met |
NOTE: An "RTT reference terminal" is a terminal specifically designed for testing RTT capable devices in a manner that would confirm their functionality and interoperability. These are generally created by a national or international standards entity so that all testing is done with a consistent "RTT reference terminal". | |
C.6.2.3.c Interoperability (c)
Type of assessment | Test |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 and 2 are true Fail: Checks 1 or 2 are false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met Not testable: Pre-condition 3 is not met |
NOTE: An "RTT reference terminal" is a terminal specifically designed for testing RTT capable devices in a manner that would confirm their functionality and interoperability. These are generally created by a national or international standards entity so that all testing is done with a consistent "RTT reference terminal". | |
C.6.2.3.d Interoperability (d)
Type of assessment | Test |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 and Check 2 are true Fail: Checks 1 or 2 are false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met Not testable: Pre-condition 3 is not met |
C.6.2.4 RTT responsiveness
Type of assessment | Inspection of Measurement data or Test |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 3 is less than or equal to 500 ms. Fail: Check 3 is greater than 500 ms. Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met Not testable: Pre-condition 2 is not met |
NOTE: As described in the notes to clause 6.2.4, the identification of when input entry has occurred may vary according to the type of RTT system under test. | |
C.6.3 Caller ID
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true and either check 2 is true or the functionality is closed Fail: Check 1 is false or check 2 is false when the functionality is not closed Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.6.4 Alternatives to voice-based services
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Checks 1 and 2 are true Fail: Check 1 or 2 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met |
C.6.5 Video communication
C.6.5.1 General
Clause 6.5.1 is informative only and contains no requirements requiring test.
C.6.5.2 Resolution
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met |
C.6.5.3 Frame rate
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met |
C.6.5.4 Synchronization between audio and video
Type of assessment | Measurement |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met |
C.6.5.5 Visual indicator of audio with video
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 3 is true Fail: Check 3 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met |
NOTE: The indicator should flicker in real time in a way that reflects the audio activity. | |
C.6.5.6 Speaker identification with video (sign language) communication
Type of assessment | Measurement |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 2 is true Fail: Check 2 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met |
C.6.6 Alternatives to video-based services
Clause 6.6 is advisory only and contains no testable requirements.
C.7 ICT with video capabilities
C.7.1 Caption processing technology
C.7.1.1 Captioning playback
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false |
Type of assessment | Test 2 |
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met |
C.7.1.2 Captioning synchronization
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.7.1.3 Preservation of captioning
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure | |
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.7.1.4 Captions characteristics
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met |
C.7.1.5 Spoken subtitles
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met |
C.7.2 Audio description technology
C.7.2.1 Audio description playback
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 and 2 are true or 1 is false and 3 is true Fail: Check 1 is true and 2 is false or 1 is false and 3 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.7.2.2 Audio description synchronization
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.7.2.3 Preservation of audio description
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure | |
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.7.3 User controls for captions and audio description
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.8 Hardware
C.8.1 General
C.8.1.1 Generic requirements
Clause 8.1.1 is advisory only and contains no testable requirements.
C.8.1.2 Standard connections
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 or 2 is true Fail: Checks 1 and 2 are false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
NOTE: The connections may be physical or wireless connections. | |
C.8.1.3 Colour
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.8.2 Hardware products with speech output
C.8.2.1 Speech volume gain
C.8.2.1.1 Speech volume range
Type of assessment | Inspection based on measurement data |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 or 4 is true Fail: Check 1 and 4 are false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.8.2.1.2 Incremental volume control
Type of assessment | Inspection based on measurement data |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 2 is true Fail: Check 2 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met |
C.8.2.2 Magnetic coupling
C.8.2.2.1 Fixed-line devices
Type of assessment | Inspection based on measurement data |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure | |
Result | Pass: Check 1 or 2 is true and check 3 is true Fail: Checks 1 and 2 are false or check 3 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.8.2.2.2 Wireless communication devices
Type of assessment | Inspection based on measurement data |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure | |
Result | Pass: Check 1 or 2 is true Fail: Checks 1 and 2 are false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.8.3 Stationary ICT
C.8.3.0 General
Clause 8.3.0 is advisory only and contains no testable requirements.
C.8.3.1 Forward or side reach
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure | |
Result | Pass: Check 1 or 2 is true Fail: Checks 1 and 2 are false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.8.3.2 Forward reach
C.8.3.2.1 Unobstructed high forward reach
Type of assessment | Inspection and measurement |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met |
C.8.3.2.2 Unobstructed low forward reach
Type of assessment | Inspection and measurement |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met |
C.8.3.2.3 Obstructed forward reach
C.8.3.2.3.1 Clear space
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met |
C.8.3.2.3.2 Obstructed (< 510 mm) forward reach
Type of assessment | Inspection and measurement |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met |
C.8.3.2.3.3 Obstructed (< 635 mm) forward reach
Type of assessment | Inspection and measurement |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met |
C.8.3.2.4 Knee and toe clearance width
Type of assessment | Inspection and measurement |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Checks 1 and 2 are true Fail: Checks 1 or 2 are false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met |
C.8.3.2.5 Toe clearance
a)
Type of assessment | Inspection and measurement |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1, 2 or 3 is not met |
b)
Type of assessment | Inspection and measurement |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1, 2 or 3 is not met |
c)
Type of assessment | Inspection and measurement |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1, 2 or 3 is not met |
C.8.3.2.6 Knee clearance
a)
Type of assessment | Inspection and measurement |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1, 2 or 3 is not met |
b)
Type of assessment | Inspection and measurement |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1, 2 or 3 is not met |
c)
Type of assessment | Inspection and measurement |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1, 2 or 3 is not met |
d)
Type of assessment | Inspection and measurement |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1, 2 or 3 is not met |
C.8.3.3 Side reach
C.8.3.3.1 Unobstructed high side reach
Type of assessment | Inspection and measurement |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met |
C.8.3.3.2 Unobstructed low side reach
Type of assessment | Inspection and measurement |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met |
C.8.3.3.3 Obstructed side reach
C.8.3.3.3.1 Obstructed (< 255 mm) side reach
Type of assessment | Inspection and measurement |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met |
C.8.3.3.3.2 Obstructed (< 610 mm) side reach
Type of assessment | Inspection and measurement |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met |
C.8.3.4 Clear floor or ground space
C.8.3.4.1 Change in level
Type of assessment | Inspection and measurement |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 or 2 or 3 is true Fail: Checks 1 and 2 and 3 are false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 or 3 is not met |
C.8.3.4.2 Clear floor or ground space
Type of assessment | Inspection and measurement |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met |
C.8.3.4.3 Approach
C.8.3.4.3.1 General
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met |
C.8.3.4.3.2 Forward Approach
Type of assessment | Inspection and measurement |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1, 2, 3 or 4 is not met |
C.8.3.4.3.3 Parallel Approach
Type of assessment | Inspection and measurement |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1, 2, 3 or 4 is not met |
C.8.3.5 Visibility
Type of assessment | Inspection and measurement |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met |
C.8.3.6 Installation instructions
Type of assessment | Inspection and measurement |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Checks 1, 2 and 3 are true Fail: Checks 1 or 2 or 3 are false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.8.4 Mechanically operable parts
C.8.4.1 Numeric keys
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.8.4.2 Operation of mechanical parts
C.8.4.2.1 Means of operation of mechanical parts
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.8.4.2.2 Force of operation of mechanical parts
Type of assessment | Inspection and measurement |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.8.4.3 Keys, tickets and fare cards
Type of assessment | Inspection and measurement |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.8.5 Tactile indication of speech mode
Type of assessment | Inspection and measurement |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met. |
C.9 Web
C.9.0 General (informative)
Clause 9.0 is informative only and contains no requirements requiring test.
C.9.1 Perceivable
C.9.1.1 Text alternatives
C.9.1.1.1 Non-text content
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.1.1 Non-text content. |
C.9.1.2 Time-based media
C.9.1.2.1 Audio-only and video-only (pre-recorded)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.2.1 Audio-only and Video-only (Prerecorded). |
C.9.1.2.2 Captions (pre-recorded)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.2.2 Captions (Prerecorded). |
C.9.1.2.3 Audio description or media alternative (pre-recorded)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.2.3 Audio Description or Media Alternative (Prerecorded). |
C.9.1.2.4 Captions (live)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.2.4 Captions (Live). |
C.9.1.2.5 Audio description (pre-recorded)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.2.5 Audio Description (Prerecorded). |
C.9.1.3 Adaptable
C.9.1.3.1 Info and relationships
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.3.1 Info and Relationships. |
C.9.1.3.2 Meaningful sequence
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.3.2 Meaningful Sequence. |
C.9.1.3.3 Sensory characteristics
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.3.3 Sensory Characteristics. |
C.9.1.3.4 Orientation
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.3.4 Orientation. |
C.9.1.3.5 Identify input purpose
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.3.5 Identify Input Purpose. |
C.9.1.4 Distinguishable
C.9.1.4.1 Use of colour
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.1 Use of Color. |
C.9.1.4.2 Audio control
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.2 Audio Control. |
C.9.1.4.3 Contrast (minimum)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.3 Contrast (Minimum). |
C.9.1.4.4 Resize text
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.4 Resize text. |
C.9.1.4.5 Images of text
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.5 Images of Text. |
C.9.1.4.6 Void
C.9.1.4.7 Void
C.9.1.4.8 Void
C.9.1.4.9 Void
C.9.1.4.10 Reflow
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.10 Reflow. |
C.9.1.4.11 Non-text contrast
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.11 Non-text Contrast. |
C.9.1.4.12 Text spacing
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.12 Text spacing. |
C.9.1.4.13 Content on hover or focus
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.13 Content on Hover or Focus. |
C.9.2 Operable
C.9.2.1 Keyboard accessible
C.9.2.1.1 Keyboard
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.1.1 Keyboard. |
C.9.2.1.2 No keyboard trap
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.1.2 No Keyboard Trap. |
C.9.2.1.3 Void
C.9.2.1.4 Character key shortcuts
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.1.4 Character Key Shortcuts. |
C.9.2.2 Enough time
C.9.2.2.1 Timing adjustable
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.2.1 Timing Adjustable. |
C.9.2.2.2 Pause, stop, hide
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.2.2 Pause, Stop, Hide. |
C.9.2.3 Seizures and physical reactions
C.9.2.3.1 Three flashes or below threshold
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.3.1 Three Flashes or Below Threshold. |
C.9.2.4 Navigable
C.9.2.4.1 Bypass blocks
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.4.1 Bypass Blocks. |
C.9.2.4.2 Page titled
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.4.2 Page Titled. |
C.9.2.4.3 Focus Order
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.4.3 Focus Order. |
C.9.2.4.4 Link purpose (in context)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.4.4 Link Purpose (In Context). |
C.9.2.4.5 Multiple ways
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.4.5 Multiple Ways. |
C.9.2.4.6 Headings and labels
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.4.6 Headings and Labels. |
C.9.2.4.7 Focus visible
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.4.7 Focus Visible. |
C.9.2.5 Input modalities
C.9.2.5.1 Pointer gestures
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.5.1 Pointer Gestures. |
C.9.2.5.2 Pointer cancellation
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.5.2 Pointer Cancellation. |
C.9.2.5.3 Label in name
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.5.3 Label in Name. |
C.9.2.5.4 Motion actuation
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.5.4 Motion Actuation. |
C.9.3 Understandable
C.9.3.1 Readable
C.9.3.1.1 Language of page
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.1.1 Language of Page. |
C.9.3.1.2 Language of parts
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.1.2 Language of Parts. |
C.9.3.2 Predictable
C.9.3.2.1 On focus
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.2.1 On Focus. |
C.9.3.2.2 On input
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.2.2 On Input. |
C.9.3.2.3 Consistent navigation
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.2.3 Consistent Navigation. |
C.9.3.2.4 Consistent identification
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.2.4 Consistent Identification. |
C.9.3.3 Input assistance
C.9.3.3.1 Error identification
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.3.1 Error Identification. |
C.9.3.3.2 Labels or instructions
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.3.2 Labels or Instructions. |
C.9.3.3.3 Error suggestion
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.3.3 Error Suggestion. |
C.9.3.3.4 Error prevention (legal, financial, data)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.3.4 Error Prevention (Legal, Financial, Data). |
C.9.4 Robust
C.9.4.1 Compatible
C.9.4.1.1 Parsing
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 4.1.1 Parsing. |
C.9.4.1.2 Name, role, value
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 4.1.2 Name, Role, Value. |
C.9.4.1.3 Status messages
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the web page does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 4.1.3 Status Messages. |
C.9.5 WCAG 2.1 AAA Success Criteria (informative)
Clause 9.5 is informative only and contains no requirements requiring test.
C.9.6 WCAG 2.1 conformance requirements
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: All checks are true Fail: Any check is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.10 Non-web documents
C.10.0 General (informative)
Clause 10.0 is advisory only and contains no requirements requiring test.
C.10.1 Perceivable
C.10.1.1 Text alternatives
C.10.1.1.1 Non-text content
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the non-web document does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.1.1 Non-text content. |
C.10.1.2 Time-based media
C.10.1.2.1 Audio-only and video-only (pre-recorded)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the non-web document does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.2.1 Audio-only and Video-only (Prerecorded). |
C.10.1.2.2 Captions (pre-recorded)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the non-web document does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.2.2 Captions (Prerecorded). |
C.10.1.2.3 Audio description or media alternative (pre-recorded)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the non-web document does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.2.3 Audio Description or Media Alternative (Prerecorded). |
C.10.1.2.4 Captions (live)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the non-web document does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.2.4 Captions (Live). |
C.10.1.2.5 Audio description (pre-recorded)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the non-web document does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.2.5 Audio Description (Prerecorded). |
C.10.1.3 Adaptable
C.10.1.3.1 Info and relationships
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the non-web document does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.3.1 Info and Relationships. |
C.10.1.3.2 Meaningful sequence
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the non-web document does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.3.2 Meaningful Sequence. |
C.10.1.3.3 Sensory characteristics
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the non-web document does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.3.3 Sensory Characteristics. |
C.10.1.3.4 Orientation
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the non-web document does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.3.4 Orientation. |
C.10.1.3.5 Identify input purpose
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the non-web document does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.3.5 Identify Input Purpose. |
C.10.1.4 Distinguishable
C.10.1.4.1 Use of colour
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the non-web document does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.1 Use of Color. |
C.10.1.4.2 Audio control
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met |
C.10.1.4.3 Contrast (minimum)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the non-web document does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.3 Contrast (Minimum). |
C.10.1.4.4 Resize text
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the non-web document does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.4 Resize text. |
C.10.1.4.5 Images of text
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the non-web document does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.5 Images of Text. |
C.10.1.4.6 Void
C.10.1.4.7 Void
C.10.1.4.8 Void
C.10.1.4.9 Void
C.10.1.4.10 Reflow
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.10.1.4.11 Non-text contrast
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the non-web document does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.11 Non-text Contrast. |
C.10.1.4.12 Text spacing
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the non-web document does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.12 Text spacing. |
C.10.1.4.13 Content on hover or focus
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the non-web document does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.13 Content on Hover or Focus. |
C.10.2 Operable
C.10.2.1 Keyboard accessible
C.10.2.1.1 Keyboard
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the non-web document does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.1.1 Keyboard. |
C.10.2.1.2 No keyboard trap
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.10.2.1.3 Void
C.10.2.1.4 Character key shortcuts
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the non-web document does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.1.4 Character Key Shortcuts. |
C.10.2.2 Enough time
C.10.2.2.1 Timing adjustable
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.10.2.2.2 Pause, stop, hide
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the non-web document does not contain content relevant to WCAG |
C.10.2.3 Seizures and physical reactions
C.10.2.3.1 Three flashes or below threshold
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.10.2.4 Navigable
C.10.2.4.1 Void
C.10.2.4.2 Document titled
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.10.2.4.3 Focus order
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.10.2.4.4 Link purpose (in context)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the non-web document does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.4.4 Link Purpose (In Context). |
C.10.2.4.5 Void
C.10.2.4.6 Headings and labels
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the non-web document does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.4.6 Headings and Labels. |
C.10.2.4.7 Focus visible
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the non-web document does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.4.7 Focus Visible. |
C.10.2.5 Input modalities
C.10.2.5.1 Pointer gestures
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.10.2.5.2 Pointer cancellation
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.10.2.5.3 Label in name
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the non-web document does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.5.3 Label in Name. |
C.10.2.5.4 Motion actuation
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the non-web document does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.5.4 Motion Actuation. |
C.10.3 Understandable
C.10.3.1 Readable
C.10.3.1.1 Language of document
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.10.3.1.2 Language of parts
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.10.3.2 Predictable
C.10.3.2.1 On focus
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the non-web document does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.2.1 On Focus. |
C.10.3.2.2 On input
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the non-web document does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.2.2 On Input. |
C.10.3.2.3 Void
C.10.3.2.4 Void
C.10.3.3 Input assistance
C.10.3.3.1 Error identification
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the non-web document does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.3.1 Error Identification. |
C.10.3.3.2 Labels or instructions
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the non-web document does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.3.2 Labels or Instructions. |
C.10.3.3.3 Error suggestion
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the non-web document does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.3.3 Error Suggestion |
C.10.3.3.4 Error prevention (legal, financial, data)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.10.4 Robust
C.10.4.1 Compatible
C.10.4.1.1 Parsing
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.10.4.1.2 Name, role, value
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.10.4.1.3 Status messages
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the non-web document does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 4.1.3 Status Messages. |
C.10.5 Caption positioning
Clause 10.5 is advisory only and contains no testable requirements.
C.10.6 Audio description timing
Clause 10.6 is advisory only and contains no testable requirements.
C.11 Software
C.11.0 General
Clause 11.0 is advisory only and contains no requirements requiring test.
C.11.1 Perceivable
C.11.1.1 Text alternatives
C.11.1.1.1 Non-text content
C.11.1.1.1.1 Non-text content (screen reading supported open functionality)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met. |
C.11.1.1.1.2 Non-text content (closed functionality)
Type of assessment | Testing |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check (1 and 2 and 3 and 4 are true) or (1 and 2 are false) or (1 and 3 are false) Fail: Checks (1 true and 2 false) or (1 true and 3 false) or (1 and 2 and 3 are true and 4 is false) Not applicable: Pre-condition 1, 2 or 3 is not met. |
C.11.1.2 Time-based media
C.11.1.2.1 Audio-only and video-only (pre-recorded)
C.11.1.2.1.1 Audio-only and video-only (pre-recorded - open functionality)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1, 2 or 3 is not met. |
C.11.1.2.1.2 Audio-only and video-only (pre-recorded - closed functionality)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1, 2 or 3 is not met. |
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1, 2, 3 or 4 is not met. |
C.11.1.2.2 Captions (pre-recorded)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met or the non-web software does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.2.2 Captions (Prerecorded). |
C.11.1.2.3 Audio description or media alternative (pre-recorded)
C.11.1.2.3.1 Audio description or media alternative (pre-recorded - open functionality)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met, or the non-web software does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.2.3 Audio Description or Media Alternative (Prerecorded). |
C.11.1.2.3.2 Audio description or media alternative (pre-recorded - closed functionality)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1, 2, or 3 is not met. |
C.11.1.2.4 Captions (live)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met, or the non-web software does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.2.4 Captions (Live). |
C.11.1.2.5 Audio description (pre-recorded)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met, or the non-web software does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.2.5 Audio Description (Prerecorded). |
C.11.1.3 Adaptable
C.11.1.3.1 Info and relationships
C.11.1.3.1.1 Info and relationships (open functionality)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met. |
C.11.1.3.1.2 Info and relationships (closed functionality)
Clause 11.1.3.1.2 is advisory only and contains no testable requirements.
C.11.1.3.2 Meaningful sequence
C.11.1.3.2.1 Meaningful sequence (open functionality)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met. |
C.11.1.3.2.2 Meaningful sequence (closed functionality)
Clause 11.1.3.2.2 is advisory only and contains no testable requirements.
C.11.1.3.3 Sensory characteristics
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met, or the non-web software does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.3.3 Sensory Characteristics. |
C.11.1.3.4 Orientation
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met, or the non-web software does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.3.4 Orientation. |
C.11.1.3.5 Identify input purpose
C.11.1.3.5.1 Identify input purpose (open functionality)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met, or the non-web software does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.3.5 Identify Input Purpose. |
C.11.1.3.5.2 Identify input purpose (closed functionality)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Checks (1 or 2) is true and 3 is true Fail: Checks (1 and 2) are false or 3 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1, 2 or 3 is not met. |
C.11.1.4 Distinguishable
C.11.1.4.1 Use of colour
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met, or the non-web software does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.1 Use of Color. |
C.11.1.4.2 Audio control
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.11.1.4.3 Contrast (minimum)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met, or the non-web software does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.3 Contrast (Minimum). |
C.11.1.4.4 Resize text
C.11.1.4.4.1 Resize text (open functionality)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met, or the non-web software does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.4 Resize text. |
C.11.1.4.4.2 Resize text (closed functionality)
Type of assessment | Inspection and measurement |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 2 is true Fail: Check 2 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1, 2 or 3 is not met. |
C.11.1.4.5 Images of text
C.11.1.4.5.1 Images of text (open functionality)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met, or the non-web software does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.5 Images of Text. |
C.11.1.4.5.2 Images of text (closed functionality)
Type of assessment | Testing |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check (1 and 2 and 3 and 4 are true) or (1 and 2 are false) or (1 and 3 are false) Fail: Checks (1 true and 2 false) or (1 true and 3 false) or (1 and 2 and 3 are true and 4 is false) Not applicable: Pre-condition 1, 2 or 3 is not met. |
C.11.1.4.6 Void
C.11.1.4.7 Void
C.11.1.4.8 Void
C.11.1.4.9 Void
C.11.1.4.10 Reflow
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.11.1.4.11 Non-text contrast
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met, or the non-web software does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.11 Non-text Contrast. |
C.11.1.4.12 Text spacing
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met, or the non-web software does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.12 Text spacing. |
C.11.1.4.13 Content on hover or focus
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met, or the non-web software does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 1.4.13 Content on hover or focus. |
C.11.2 Operable
C.11.2.1 Keyboard accessible
C.11.2.1.1 Keyboard
C.11.2.1.1.1 Keyboard (open functionality)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met, or the non-web software does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.1.1 Keyboard. |
C.11.2.1.1.2 Keyboard (closed functionality)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met. |
C.11.2.1.2 No keyboard trap
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met. |
C.11.2.1.3 Void
C.11.2.1.4 Character key shortcuts
C.11.2.1.4.1 Character key shortcuts (open functionality)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met, or the non-web software does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.1.4 Character Key Shortcuts. |
C.11.2.1.4.2 Character key shortcuts (closed functionality)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met. |
C.11.2.2 Enough time
C.11.2.2.1 Timing adjustable
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.11.2.2.2 Pause, stop, hide
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.11.2.3 Seizures and physical reactions
C.11.2.3.1 Three flashes or below threshold
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.11.2.4 Navigable
C.11.2.4.1 Void
C.11.2.4.2 Void
C.11.2.4.3 Focus order
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.11.2.4.4 Link purpose (in context)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met, or the non-web software does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.4.4 Link Purpose (In Context). |
C.11.2.4.5 Void
C.11.2.4.6 Headings and labels
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met, or the non-web software does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.4.6 Headings and Labels. |
C.11.2.4.7 Focus visible
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met, or the non-web software does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.4.7 Focus Visible. |
C.11.2.5 Input modalities
C.11.2.5.1 Pointer gestures
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met. |
C.11.2.5.2 Pointer cancellation
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met. |
C.11.2.5.3 Label in name
C.11.2.5.3.1 Label in name (open functionality)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met, or the non-web software does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.5.3 Label in Name. |
C.11.2.5.3.2 Label in name (closed functionality)
Clause 11.2.5.3.2 is informative only and contains no requirements requiring test.
C.11.2.5.4 Motion actuation
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met, or the non-web software does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 2.5.4 Motion Actuation. |
C.11.3 Understandable
C.11.3.1 Readable
C.11.3.1.1 Language of software
C.11.3.1.1.1 Language of software (open functionality)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met. |
C.11.3.1.1.2 Language of software (closed functionality)
Type of assessment | Testing |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 or 7 is not met. |
C.11.3.1.2 Void
C.11.3.2 Predictable
C.11.3.2.1 On focus
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met, or the non-web software does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.2.1 On Focus. |
C.11.3.2.2 On input
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met, or the non-web software does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.2.2 On Input. |
C.11.3.2.3 Void
C.11.3.2.4 Void
C.11.3.3 Input assistance
C.11.3.3.1 Error identification
C.11.3.3.1.1 Error identification (open functionality)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met, or the non-web software does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.3.1 Error Identification. |
C.11.3.3.1.2 Error Identification (closed functionality)
Type of assessment | Testing |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Checks 1 and 2 are true Fail: Check 1 or check 2 false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1, 2,3 or 4 is not met. |
C.11.3.3.2 Labels or instructions
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met, or the non-web software does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.3.2 Labels or Instructions. |
C.11.3.3.3 Error suggestion
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met, or the non-web software does not contain content relevant to WCAG 2.1 Success Criterion 3.3.3 Error Suggestion. |
C.11.3.3.4 Error prevention (legal, financial, data)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.11.4 Robust
C.11.4.1 Compatible
C.11.4.1.1 Parsing
C.11.4.1.1.1 Parsing (open functionality)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met. |
C.11.4.1.1.2 Parsing (closed functionality)
Clause 11.4.1.1.2 contains no requirements requiring test.
C.11.4.1.2 Name, role, value
C.11.4.1.2.1 Name, role, value (open functionality)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met. |
C.11.4.1.2.2 Name, role, value (closed functionality)
Clause 11.4.1.2.2 contains no testable requirements.
C.11.4.1.3 Status messages
C.11.4.1.3.1 Status messages (open functionality)
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met, or the non-web software does not contain content relevant to G 2.1 Success Criterion 4.1.3 Status messages |
C.11.4.1.3.2 Status messages (closed functionality)
Clause 11.4.1.3.2 contains no testable requirements.
C.11.5 Interoperability with assistive technology
C.11.5.1 Closed functionality
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | If check 1 is true, the software is not required to conform to clause 11.5.2 If check 1 is false the software is required to conform to clause 11.5.2 Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.11.5.2 Accessibility services
C.11.5.2.1 Platform accessibility service support for software that provides a user interface
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.11.5.2.2 Platform accessibility service support for assistive technologies
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.11.5.2.3 Use of accessibility services
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true and check 2 or check 3 is true Fail: Check 1 or check 3 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.11.5.2.4 Assistive technology
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.11.5.2.5 Object information
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Checks 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 are true Fail: Check 1 or 2 or 3 or 4 or 5 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.11.5.2.6 Row, column, and headers
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Checks 2, 3, 4 and 5 are true Fail: Check 2 or 3 or 4 or 5 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met. |
C.11.5.2.7 Values
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Checks 2, 3 and 4 are true Fail: Check 2 or 3 or 4 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met. |
C.11.5.2.8 Label relationships
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Checks 2 or 3 are true Fail: Check 2 and 3 are false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met. |
C.11.5.2.9 Parent-child relationships
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Checks 1 or 2 is true and check 3 or 4 is true Fail: Checks 1 and 2 are false or check 3 and 4 are false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met. |
NOTE: For this requirement it is enough that one of the two directions of a parent-child relationship is programmatically determinable. This is the reason why the requirement checks are in pairs and why the requirement is met if one member of each pair is true. | |
C.11.5.2.10 Text
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Checks 1, 2 and 3 are true Fail: Check 1 or 2 or 3 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met. |
C.11.5.2.11 List of available actions
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Checks 1 and 2 are true Fail: Check 1 or 2 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met. |
C.11.5.2.12 Execution of available actions
Type of assessment | Inspection and testing |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Checks 1 and 2 are true Fail: Check 1 or 2 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1, 2 or 3 is not met. |
C.11.5.2.13 Tracking of focus and selection attributes
Type of assessment | Inspection and testing |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Checks 2 and 5 are true Fail: Check 1 or 5 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met. |
C.11.5.2.14 Modification of focus and selection attributes
Type of assessment | Testing |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: All checks are true Fail: Any check is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1, 2 or 3 is not met. |
C.11.5.2.15 Change notification
Type of assessment | Inspection and testing |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Checks 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 and 9 are true Fail: Check 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 or 9 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.11.5.2.16 Modifications of states and properties
Type of assessment | Testing |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: All checks are true Fail: Any check is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1, 2 or 3 is not met. |
C.11.5.2.17 Modifications of values and text
Type of assessment | Testing |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: all checks are true Fail: any check is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1, 2 or 3 is not met. |
C.11.6 Documented accessibility usage
C.11.6.1 User control of accessibility features
Type of assessment | Testing |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.11.6.2 No disruption of accessibility features
Type of assessment | Testing |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is false or both checks are true Fail: Check 1 is true and check 2 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.11.7 User preferences
Type of assessment | Inspection and Testing |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1, 2 or 3 is not met. |
C.11.8 Authoring tools
C.11.8.1 Content technology
Type of assessment | Inspection and Testing |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure | |
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met |
NOTE: Where the output format of the authoring tool does not support certain types of information required for accessibility, conformance with requirements that relate to that type of information is not required. | |
C.11.8.2 Accessible content creation
Type of assessment | Inspection and Testing |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.11.8.3 Preservation of accessibility information in transformations
Type of assessment | Inspection and Testing |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true or checks 1 and 2 are false or check 3 is true or checks 3 and 4 are false Fail: Check 1 is false and check 2 is true Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met. |
C.11.8.4 Repair assistance
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions | |
Procedure | |
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met. |
C.11.8.5 Templates
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Checks 1 and 2 are true Fail: Check 1 or 2 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met. |
NOTE: The identification as conforming to the requirements of clauses 9 or 10 (as applicable) described in check 2 may be described in terms such as "Conformant to WCAG 2.1". Where the identification does not explicitly state that all of the requirements identified in clauses 9 or 10 (as appropriate) are covered, it may be necessary to use the template to create a web site or document and then test that web site or document according to the requirements of clauses 9 or 10 to provide full assurance that the template behaves as required. | |
C.12 Documentation and support services
C.12.1 Product documentation
C.12.1.1 Accessibility and compatibility features
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.12.1.2 Accessible documentation
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.12.2 Support services
C.12.2.1 General
Clause 12.2.1 is informative only and contains no requirements requiring test.
C.12.2.2 Information on accessibility and compatibility features
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.12.2.3 Effective communication
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
NOTE: The provision of any level of support for the communication needs of individuals with disabilities constitutes a pass of this requirement. Suppliers may wish to provide further information about the level of support that is provided to enable the adequacy and quality of the support to be judged. | |
C.12.2.4 Accessible documentation
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure | |
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.13 ICT providing relay or emergency service access
C.13.1 Relay service requirements
C.13.1.1 General
Clause 13.1.1 is informative only and contains no requirements requiring test.
C.13.1.2 Text relay services
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.13.1.3 Sign relay services
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.13.1.4 Lip-reading relay services
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.13.1.5 Captioned telephony services
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.13.1.6 Speech to speech relay services
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 is not met. |
C.13.2 Access to relay services
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met. |
C.13.3 Access to emergency services
Type of assessment | Inspection |
|---|---|
Pre-conditions |
|
Procedure |
|
Result | Pass: Check 1 is true Fail: Check 1 is false Not applicable: Pre-condition 1 or 2 is not met. |
Annex D (informative): Further resources for cognitive accessibility
It is evident that people with limited cognitive, language and learning abilities have diverse accessibility needs and preferences and that there is a need for further guidelines and standards. Research in this area is ongoing.
Relevant standardisation work is currently being undertaken by the W3C Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI). WAI are working to improve the requirements and technical guidance for developers, to better address Web accessibility for people with limited cognitive, language and learning abilities. Current W3C activity in this area can be found at https://www.w3.org/WAI/cognitive/.
Annex E (informative): Guidance for users of the present document
E.1 Introduction
This explanatory annex is designed to enable users of the present document to make best use of it.
The standard was originally intended for procurement purposes. The scope is now changed and the current version also contains the minimum requirements of the European Web Accessibility Directive (Directive 2016/2102 [i.28]).
EN 301 549 contains a wide range of requirements to cover a variety of ICT solutions. There are for example requirements on function, physical characteristics and software. No matter if you are responsible for procuring, testing, planning, manufacturing, maintaining or reporting on accessibility, it is necessary to understand which requirements are relevant for a specific product or service in a specific situation or context.
Testing for accessibility requirements does not always result in a yes or no. Sometimes, you end up in a grey zone where it is equally important to understand the prerequisites and potential alternatives for different end user groups. Remember that accessibility has to do with humans.
The examples mentioned in this annex are only inspirational and the standard can of course be used in many different ways and settings.
E.2 Overview
The present document consists of fourteen clauses (equivalent to chapters in a book) and six annexes.
Clauses 0 to 3 contain background information, the scope of the standard, links to references, definitions of terminology and explanations of abbreviations. These clauses have a lot of valuable information, but it can be hard to read the standard from A to Z.
Clause 4 covers functional performance statements, which are directly related to end-user needs. The clause explains what functionality is needed to enable end users to locate, identify and operate functions in technology, no matter of their abilities. This is an important clause where you can learn about what challenges accessibility requirements aim to solve.
Clauses 5 to 13 are the actual technical requirements. Most readers start here, but clause 4 can possibly be a better place to begin, to really understand how to use the detailed technical parts.
The technical requirements cover many different kinds of ICT divided into separate clauses, but it is always a good idea to have a look at clause 5, since this is where the general requirements are.
Clauses 9, 10 and 11 are the ones that are most relevant to the European Web Accessibility Directive [i.28]. They cover websites, documents and apps. However, requirements from other clauses apply, as listed in the tables in Annex A.
Clause 14 deals with conformance to EN 301 549 as a whole and to the individual requirements.
Annex A describes how the standard relates to the European Web Accessibility Directive [i.28]. Apart from the minimum requirements in clauses 9, 10 and 11, some of the requirements in clauses 5, 6, 7 and 12 can also be relevant to fulfill the Directive, in specific situations. The tables in Annex A show which of the requirements are important to look at.
Annex B describes how the functional performance statements of clause 4 relate to the technical requirements in clauses 5 to 13. This is a useful tool that will, for example, help you to use the standard in procurement to identify the impact that specific requirements have on end users when comparing proposals.
Annex C describes how you can test that each requirement of the standard is met. The annex does not provide a testing methodology and you still have to know quite a lot about functional performance statements and testing procedures to make use of it.
Annex D provides a link to further resources for cognitive accessibility.
Annex E is what you are reading right now.
Annex F provides a change history table.
E.3 Clause 4
Clause 4 is in a sense the heart of the standard. The end users, with their different needs, are the reason accessibility matters. The user needs behind each functional performance statement are also the reason for each of the requirements in the present document.
Clause 4 does not include any requirements in itself, just descriptions. This may make it seem less important but, in reality, it is the other way around. The aim of the whole standard is to ensure that end users with the varying abilities described in this clause can use products and services.
In this clause, ten functional performance statements based on variations of impairments are described, plus privacy. The impairments can be permanent, temporary or situational. End users with multiple impairments might need specific combinations of accessibility solutions. Therefore, it is necessary to consider all different functional performance statements as well as a combination of them.
The concept behind the standard is to let technology help compensate the challenges that end users can have. You can also look at accessibility as alternative ways to use technology. For example: if the end user cannot see, technology can provide sound. If the end user cannot hear, the technology can provide text. This is what clause 4 is describing for each user group, in detail.
After reading clause 4, you will understand the logic of the requirements in the standard much better.
E.4 How to use the standard
E.4.1 Self scoping requirements
The requirements in the present document are called self-scoping. This means that they consist of two parts; the first part is a precondition for the second part, which holds the actual requirement. If the first part is true, you need to meet the second part of the requirement. If the first part is not true, this means that the requirement is not applicable.
For example, a requirement saying "Where ICT hardware has speech output, it shall provide […]" can be met in two ways:
- If your product or service provides speech, you need to fulfill the second part of the requirement.
- If your product or service does not provide speech, you do not need to think about the second part of the requirement. The requirement is not applicable.
To meet the standard means that all applicable requirements in the standard are met.
To get an overview of the requirements in scope of your product or service, you can focus on the requirements with the same scoping statements. There are online tools that can help you filter out requirements that are automatically met.
E.4.2 Connection between requirements and functional performance statements
The table in Annex B helps you understand the connection between the requirements and the functional performance statements. There is an instruction on how to use the table under clause B.2.
Before making a decision about the most suitable solution, you also need to think about the context. Here are some examples:
- In what situation is the solution going to be used?
- Which failed requirements are possible to compensate with other alternatives, like for example a service desk?
- What would it cost to solve an issue with an alternative like that?
- Will the failed requirements be possible to fix in the next version of the solution?
Suppliers may show how their product or service addresses the functional performance statements in clause 4 in addition to meeting the requirements in clauses 5 to 13. This can help you choose which product or service is most suitable.
E.5 The European Web Accessibility Directive [i.28]
The European Web Accessibility Directive (Directive 2016/2102 [i.28]) is a minimum harmonisation Directive. This means that all EU member states and EFTA countries are required to at least comply with the minimum requirements referred to in the Directive. Each country can choose to go beyond these requirements in their national legislation when it comes to both requirements and scope.
The Directive covers, as a minimum, public sector bodies and some government owned, funded or led organizations.
NOTE: The definition of public sector body is referring to the Procurement Directive (Directive 2014/24/EU [i.40]) article 2(1) point 4, which defines "bodies governed by public law" as bodies that have all of the following characteristics:
- they are established for the specific purpose of meeting needs in the general interest, not having an industrial or commercial character;
- they have legal personality; and
- they are financed, for the most part, by the State, regional or local authorities, or by other bodies governed by public law; or are subject to management supervision by those authorities or bodies; or have an administrative, managerial or supervisory board, more than half of whose members are appointed by the State, regional or local authorities, or by other bodies governed by public law.
Most of the requirements that relate to the European Web Accessibility Directive are found in clauses 9, 10 and 11, which cover websites, documents and software. The complete list of requirements are listed in the tables in Annex A. The Directive also covers intranets and extranets, which are to meet the requirements of clause 9 for web content and clause 10 for documents.
There are different grace periods for different kinds of content and there are also exceptions to what content is covered by the Directive. For example, live video is not covered by the Directive. This means that requirements 9.1.2.4 for websites, 10.1.2.4 for documents and 11.1.2.4 for apps are not relevant to meeting the requirements of the Directive.
Please note that there are also other requirements in the Directive, for example on monitoring and accessibility statements. These are not covered in EN 301 549.
E.6 Annex D: Further resources for cognitive accessibility
Annex D provides a link to W3C resources that can be used as guidance to improve the inclusion of accessibility for people with limited cognitive, language and learning abilities when using ICT products and services.
Annex F (informative): Change history
Version | Information about changes |
|---|---|
2.1.2 | First publication as a harmonised standard |
3.1.1 | The requirements related to Real-Time Text (RTT) in clause 6.2 have been revised and extended |
3.1.1 | The WCAG 2.1 AAA Success Criteria that were previously in an Annex D are now included in clause 9.5 |
3.1.1 | A new Annex D, "Further resources for cognitive accessibility", has been added |
3.1.1 | A new Annex E "Guidance for users of the present document" has been added |
3.2.1 | A new Annex F "Change history" (this Annex) has been added |
History
V1.1.1 | February 2014 | Publication |
V1.1.2 | April 2015 | Publication |
V2.1.2 | August 2018 | Publication |
V3.1.1 | November 2019 | Publication |
V3.2.1 | December 2020 | EN Approval Procedure AP 20210310: 2020-12-10 to 2021-03-10 |
V3.2.1 | March 2021 | Publication |